Common genetic variation in Neuregulin 3 (NRG3) influences risk for schizophrenia and impacts NRG3 expression in human brain - PubMed (original) (raw)
Common genetic variation in Neuregulin 3 (NRG3) influences risk for schizophrenia and impacts NRG3 expression in human brain
Wee-Tin Kao et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010.
Abstract
Structural and polymorphic variations in Neuregulin 3 (NRG3), 10q22-23 are associated with a broad spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders including developmental delay, cognitive impairment, autism, and schizophrenia. NRG3 is a member of the neuregulin family of EGF proteins and a ligand for the ErbB4 receptor tyrosine kinase that plays pleotropic roles in neurodevelopment. Several genes in the NRG-ErbB signaling pathway including NRG1 and ErbB4 have been implicated in genetic predisposition to schizophrenia. Previous fine mapping of the 10q22-23 locus in schizophrenia identified genome-wide significant association between delusion severity and polymorphisms in intron 1 of NRG3 (rs10883866, rs10748842, and rs6584400). The biological mechanisms remain unknown. We identified significant association of these SNPs with increased risk for schizophrenia in 350 families with an affected offspring and confirmed association to patient delusion and positive symptom severity. Molecular cloning and cDNA sequencing in human brain revealed that NRG3 undergoes complex splicing, giving rise to multiple structurally distinct isoforms. RNA expression profiling of these isoforms in the prefrontal cortex of 400 individuals revealed that NRG3 expression is developmentally regulated and pathologically increased in schizophrenia. Moreover, we show that rs10748842 lies within a DNA ultraconserved element and homedomain and strongly predicts brain expression of NRG3 isoforms that contain a unique developmentally regulated 5' exon (P = 1.097E(-12) to 1.445E(-15)). Our observations strengthen the evidence that NRG3 is a schizophrenia susceptibility gene, provide quantitative insight into NRG3 transcription traits in the human brain, and reveal a probable mechanistic basis for disease association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
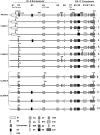
Fig. 1.
Schematic overview of SNPs associated with schizophrenia in 356 families (P < 0.05). Heat map shows LD _r_2 values.
Fig. 2.
Organization of NRG3 transcripts cloned from adult human brain (whole brain and hippocampus). Exons are shown in the order in which they occur in the transcript. The length of each exon is not proportional to the number of amino acids encoded. The nomenclature describing each exon is listed in the box (Bottom). The top row is a compendium of all exon nomenclatures (reference). The numbering is consistent with RefSeq gene annotations for NRG3 [University of California, Santa Cruz, Genome Browser or NCBI36/hg18 and GRCh37 Assembly (hg19)]. Isoforms are numbered and subdivided into classes based on common exon inclusion. Class categories were used to design primer probe sets for QPCR. Numerical annotation refers to “transcript.” Sequence annotation features for functional domains are derived from the Protein Knowledgebase (
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P56975
). Nucleotide sequences for NRG3 variants have been deposited in GenBank database under accession numbers HM068873–HM068885.
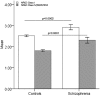
Fig. 3.
Quantitative expression of full-length NRG3 transcripts comprising leader exons E1 (class I) and E3 contiguous with E4 (class IV and DQ857894) is significantly increased in the DLPFC of patients with schizophrenia (n = 245 normal individuals and n = 113 with schizophrenia). Values are mean ± SEM.
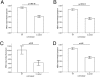
Fig. 4.
Allele-associated differences in expression of NRG3 class II and III in the adult DLPFC (A and B) and fetal DLPFC (C and D) associated with rs10748842. A_–_D show increased expression of NRG3 transcripts in T/T individuals compared with C-carrier individuals. In A and B, n = 315; 223 T/T and 92 C-carriers. In C and D, n = 34 fetal DLPFC; 24 T/T individuals and 10 C-carriers. No diagnosis by genotype interactions were observed. Values are mean ± SEM.
Similar articles
- Temporal, Diagnostic, and Tissue-Specific Regulation of NRG3 Isoform Expression in Human Brain Development and Affective Disorders.
Paterson C, Wang Y, Hyde TM, Weinberger DR, Kleinman JE, Law AJ. Paterson C, et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2017 Mar 1;174(3):256-265. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2016.16060721. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Am J Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27771971 Free PMC article. - Neuregulin 3 (NRG3) as a susceptibility gene in a schizophrenia subtype with florid delusions and relatively spared cognition.
Morar B, Dragović M, Waters FA, Chandler D, Kalaydjieva L, Jablensky A. Morar B, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2011 Aug;16(8):860-6. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.70. Epub 2010 Jun 15. Mol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 20548296 - Fine mapping on chromosome 10q22-q23 implicates Neuregulin 3 in schizophrenia.
Chen PL, Avramopoulos D, Lasseter VK, McGrath JA, Fallin MD, Liang KY, Nestadt G, Feng N, Steel G, Cutting AS, Wolyniec P, Pulver AE, Valle D. Chen PL, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2009 Jan;84(1):21-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.12.005. Am J Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19118813 Free PMC article. - Neuregulin 3 and its roles in schizophrenia risk and presentation.
Avramopoulos D. Avramopoulos D. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2018 Mar;177(2):257-266. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32552. Epub 2017 May 29. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28556469 Free PMC article. Review. - Exploring Neuregulin3: From physiology to pathology, a novel target for rational drug design.
Nadeem A, Sharma P, Gupta P, Sandeep P, Sharma B, Sharma N, Yadav M, Dhiman N. Nadeem A, et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;238:116964. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2025.116964. Epub 2025 May 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40320052 Review.
Cited by
- Genome-wide copy number analysis uncovers a new HSCR gene: NRG3.
Tang CS, Cheng G, So MT, Yip BH, Miao XP, Wong EH, Ngan ES, Lui VC, Song YQ, Chan D, Cheung K, Yuan ZW, Lei L, Chung PH, Liu XL, Wong KK, Marshall CR, Scherer SW, Cherny SS, Sham PC, Tam PK, Garcia-Barceló MM. Tang CS, et al. PLoS Genet. 2012;8(5):e1002687. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002687. Epub 2012 May 10. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22589734 Free PMC article. - Genetic dissection of acute ethanol responsive gene networks in prefrontal cortex: functional and mechanistic implications.
Wolen AR, Phillips CA, Langston MA, Putman AH, Vorster PJ, Bruce NA, York TP, Williams RW, Miles MF. Wolen AR, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e33575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033575. Epub 2012 Apr 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22511924 Free PMC article. - Transcriptomic analysis of postmortem brain identifies dysregulated splicing events in novel candidate genes for schizophrenia.
Cohen OS, Mccoy SY, Middleton FA, Bialosuknia S, Zhang-James Y, Liu L, Tsuang MT, Faraone SV, Glatt SJ. Cohen OS, et al. Schizophr Res. 2012 Dec;142(1-3):188-99. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2012.09.015. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Schizophr Res. 2012. PMID: 23062752 Free PMC article. - ErbB4 Null Mice Display Altered Mesocorticolimbic and Nigrostriatal Dopamine Levels as well as Deficits in Cognitive and Motivational Behaviors.
Skirzewski M, Cronin ME, Murphy R, Fobbs W, Kravitz AV, Buonanno A. Skirzewski M, et al. eNeuro. 2020 May 21;7(3):ENEURO.0395-19.2020. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0395-19.2020. Print 2020 May/Jun. eNeuro. 2020. PMID: 32354758 Free PMC article. - Expression of the Longest RGS4 Splice Variant in the Prefrontal Cortex Is Associated with Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Schizophrenia Patients.
Ding L, Styblo M, Drobná Z, Hegde AN. Ding L, et al. Front Psychiatry. 2016 Feb 29;7:26. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2016.00026. eCollection 2016. Front Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26973546 Free PMC article.
References
- Faraone SV, et al. Genome scan of Han Chinese schizophrenia families from Taiwan: Confirmation of linkage to 10q22.3. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163:1760–1766. - PubMed
- Morar B, et al. Neuregulin 3 (NRG3) as a susceptibility gene in a schizophrenia subtype with florid delusions and relatively spared cognition. Mol Psychiatry. 2010;(Jun):15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous