Sources of variability in children's language growth - PubMed (original) (raw)
Sources of variability in children's language growth
Janellen Huttenlocher et al. Cogn Psychol. 2010 Dec.
Abstract
The present longitudinal study examines the role of caregiver speech in language development, especially syntactic development, using 47 parent-child pairs of diverse SES background from 14 to 46 months. We assess the diversity (variety) of words and syntactic structures produced by caregivers and children. We use lagged correlations to examine language growth and its relation to caregiver speech. Results show substantial individual differences among children, and indicate that diversity of earlier caregiver speech significantly predicts corresponding diversity in later child speech. For vocabulary, earlier child speech also predicts later caregiver speech, suggesting mutual influence. However, for syntax, earlier child speech does not significantly predict later caregiver speech, suggesting a causal flow from caregiver to child. Finally, demographic factors, notably SES, are related to language growth, and are, at least partially, mediated by differences in caregiver speech, showing the pervasive influence of caregiver speech on language growth.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
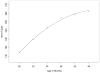
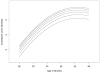
Figure 1
Children’s average growth trajectory for lexical diversity
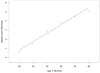
Figure 2
Children’s average growth trajectory for constituent diversity
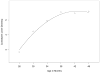
Figure 3
Children’s average growth trajectory for clausal diversity
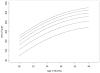
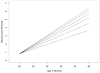
Figure 4
Modeled growth curves for children’s lexical diversity as a function of SES
Figure 5
Modeled growth curves for children’s constituent diversity as a function of SES
Figure 6
Modeled growth curves for children’s clausal diversity as a function of SES
Similar articles
- Spanish-English bilingual toddlers' vocabulary skills: The role of caregiver language input and warmth.
Gámez PB, Palermo F, Perry JS, Galindo M. Gámez PB, et al. Dev Sci. 2023 Mar;26(2):e13308. doi: 10.1111/desc.13308. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Dev Sci. 2023. PMID: 35913423 Free PMC article. - Functions of Turkish evidentials in early child-caregiver interactions: a growth curve analysis of longitudinal data.
Uzundağ BA, Taşçi SS, Küntay AC, Aksu-Koç A. Uzundağ BA, et al. J Child Lang. 2018 Jul;45(4):878-899. doi: 10.1017/S0305000917000526. Epub 2018 Feb 21. J Child Lang. 2018. PMID: 29463324 - Language input and language growth.
Huttenlocher J. Huttenlocher J. Prev Med. 1998 Mar-Apr;27(2):195-9. doi: 10.1006/pmed.1998.0301. Prev Med. 1998. PMID: 9578994 Review. - The role of caregiver speech in supporting language development in infants and toddlers with autism spectrum disorder.
Swanson MR. Swanson MR. Dev Psychopathol. 2020 Oct;32(4):1230-1239. doi: 10.1017/S0954579420000838. Dev Psychopathol. 2020. PMID: 32893764 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- eLIPS: Development and Validation of an Observational Tool for Examining Early Language in Play Settings.
Duncan LG, Gollek C, Potter DD. Duncan LG, et al. Front Psychol. 2020 Jul 31;11:1813. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01813. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32849070 Free PMC article. - Language learning, socioeconomic status, and child-directed speech.
Schwab JF, Lew-Williams C. Schwab JF, et al. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2016 Jul;7(4):264-75. doi: 10.1002/wcs.1393. Epub 2016 May 19. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2016. PMID: 27196418 Free PMC article. Review. - Caregiver linguistic alignment to autistic and typically developing children: A natural language processing approach illuminates the interactive components of language development.
Fusaroli R, Weed E, Rocca R, Fein D, Naigles L. Fusaroli R, et al. Cognition. 2023 Jul;236:105422. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2023.105422. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Cognition. 2023. PMID: 36871399 Free PMC article. - Child-oriented word associations improve models of early word learning.
Cox CR, Haebig E. Cox CR, et al. Behav Res Methods. 2023 Jan;55(1):16-37. doi: 10.3758/s13428-022-01790-y. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Behav Res Methods. 2023. PMID: 35254630 Free PMC article. - Háblame Bebé: A phone application intervention to support Hispanic children's early language environments and bilingualism.
Baralt M, Mahoney AD, Brito N. Baralt M, et al. Child Lang Teach Ther. 2020 Feb;36(1):33-57. doi: 10.1177/0265659020903779. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Child Lang Teach Ther. 2020. PMID: 35875512 Free PMC article.
References
- Aslin N, Saffran J, Newport E. Statistical learning in linguistic and nonlinguistic domains. In: MacWhinney B, editor. The emergence of language. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Publishers; 1999. pp. 359–380.
- Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic and statistical consideration. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1986;51:1173–1182. - PubMed
- Brown R. A First Language: the Early Stages. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1973.
- Braine MD. Children’s first word combinations. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development. 1976;41:1–97. - PubMed
- Brooks P, Tomasello M, Dodson K, Lewis L. Young children’s overgeneralizations with fixed transitivity verbs. Child Development. 1999;70:1325–1337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical