Saponins as cytotoxic agents: a review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Saponins as cytotoxic agents: a review
Irma Podolak et al. Phytochem Rev. 2010 Sep.
Abstract
Saponins are natural glycosides which possess a wide range of pharmacological properties including cytotoxic activity. In this review, the recent studies (2005-2009) concerning the cytotoxic activity of saponins have been summarized. The correlations between the structure and the cytotoxicity of both steroid and triterpenoid saponins have been described as well as the most common mechanisms of action.
Figures
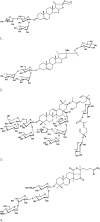
Fig. 1
Chemical structures of polyphyllin D (1), methyl protodioscin (2), albizoside C (3) and saponin PE (4)
Similar articles
- Research Progress on Natural Triterpenoid Saponins in the Chemoprevention and Chemotherapy of Cancer.
Du JR, Long FY, Chen C. Du JR, et al. Enzymes. 2014;36:95-130. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-802215-3.00006-9. Enzymes. 2014. PMID: 27102701 - Saponins from Chinese Medicines as Anticancer Agents.
Xu XH, Li T, Fong CM, Chen X, Chen XJ, Wang YT, Huang MQ, Lu JJ. Xu XH, et al. Molecules. 2016 Oct 5;21(10):1326. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101326. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27782048 Free PMC article. Review. - Immunomodulatory, hemolytic and cytotoxic activity potentials of triterpenoid saponins from eight Cephalaria species.
Sarikahya NB, Nalbantsoy A, Top H, Gokturk RS, Sumbul H, Kirmizigul S. Sarikahya NB, et al. Phytomedicine. 2018 Jan 1;38:135-144. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2017.11.009. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29425646 - Chemical Synthesis of Saponins.
Yang Y, Laval S, Yu B. Yang Y, et al. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 2021;79:63-150. doi: 10.1016/bs.accb.2021.10.001. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34865729 - Triterpene and Steroid Glycosides from Marine Sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae): Structures, Taxonomical Distribution, Biological Activities.
Ivanchina NV, Kalinin VI. Ivanchina NV, et al. Molecules. 2023 Mar 9;28(6):2503. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062503. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985476 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Factors Affecting Extracellular Vesicles Based Drug Delivery Systems.
Gaurav I, Thakur A, Iyaswamy A, Wang X, Chen X, Yang Z. Gaurav I, et al. Molecules. 2021 Mar 11;26(6):1544. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061544. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33799765 Free PMC article. Review. - Dried-leaf Artemisia annua: A practical malaria therapeutic for developing countries?
Weathers PJ, Towler M, Hassanali A, Lutgen P, Engeu PO. Weathers PJ, et al. World J Pharmacol. 2014 Dec 9;3(4):39-55. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v3.i4.39. World J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25678989 Free PMC article. - Screening of saponins and sapogenins from Medicago species as potential PPARγ agonists and X-ray structure of the complex PPARγ/caulophyllogenin.
Montanari R, Capelli D, Tava A, Galli A, Laghezza A, Tortorella P, Loiodice F, Pochetti G. Montanari R, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 10;6:27658. doi: 10.1038/srep27658. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27283034 Free PMC article. - Extracellular Vesicles in Modifying the Effects of Ionizing Radiation.
Szatmári T, Hargitai R, Sáfrány G, Lumniczky K. Szatmári T, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 6;20(22):5527. doi: 10.3390/ijms20225527. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31698689 Free PMC article. Review. - Horse Chestnut Saponins-Escins, Isoescins, Transescins, and Desacylescins.
Savarino P, Colson E, André J, Gerbaux P. Savarino P, et al. Molecules. 2023 Feb 23;28(5):2087. doi: 10.3390/molecules28052087. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36903330 Free PMC article.
References
- Abe H, Konishi H, Komiya H, et al. Effects of saikosaponins on biological membranes. Planta Med. 1981;42:356–363. - PubMed
- Acharya D, Mitaine-Offer A-C, Kaushik N, et al. Cytotoxic spirostane-type saponins from the roots of Chlorophytum borivilianum. J Nat Prod. 2009;72:177–181. - PubMed
- Avilov SA, Silchenko AS, Antonov AS, et al. Synaptosides A and A1, triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Synapta maculata containing 3-O-methylglucuronic acid and their cytotoxic activity against tumor cells. J Nat Prod. 2008;71:525–531. - PubMed
- Bachran C, Sutherland M, Heisler I, et al. The saponin-mediated enhanced uptake of targeted saporin-based drugs is strongly dependent on the saponin structure. Exp Biol Med. 2006;231:412–420. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources