CXCL12 / CXCR4 / CXCR7 chemokine axis and cancer progression - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
CXCL12 / CXCR4 / CXCR7 chemokine axis and cancer progression
Xueqing Sun et al. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010 Dec.
Erratum in
- Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011 Jun;30(2):269-70
Abstract
Chemokines, small pro-inflammatory chemoattractant cytokines that bind to specific G-protein-coupled seven-span transmembrane receptors, are major regulators of cell trafficking and adhesion. The chemokine CXCL12 (also called stromal-derived factor-1) is an important α-chemokine that binds primarily to its cognate receptor CXCR4 and thus regulates the trafficking of normal and malignant cells. For many years, it was believed that CXCR4 was the only receptor for CXCL12. Yet, recent work has demonstrated that CXCL12 also binds to another seven-transmembrane span receptor called CXCR7. Our group and others have established critical roles for CXCR4 and CXCR7 on mediating tumor metastasis in several types of cancers, in addition to their contributions as biomarkers of tumor behavior as well as potential therapeutic targets. Here, we review the current concepts regarding the role of CXCL12 / CXCR4 / CXCR7 axis activation, which regulates the pattern of tumor growth and metastatic spread to organs expressing high levels of CXCL12 to develop secondary tumors. We also summarize recent therapeutic approaches to target these receptors and/or their ligands.
Figures
Figure 1. Chemokine family and their cognate receptors
Most chemokines can bind multiple receptors, and a single receptor can bind multiple chemokines. As shown in this case for most CC (green) and CXC (blue) chemokines. Decoy receptors (black) can also interact with multiple chemokines. By contrast, a minority of receptors (red) have only one ligand.
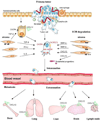
Figure 2. Schematic representation showing the role of microenvironment in tumor cell CXCR4 receptor activation in both the primary and metastatic sites
Molecular cross-talks between stroma and tumor cells in microenviroment may upregulate CXCR4 expression, which involve in tumorigenesis, and tumor cell intravasation. By CXCL12 gradients chemoattrcting of organ secretion, CXCR4-positive tumor cells in circulation may be responsible for the process of extravasation, and organ-specific metastasis. Abbreviation: CXL12 (SDF-1), stroma-derived factor; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; ECM, extracellular matric; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; MMP-2,9, matrix metalloproteinase-2,9.
Similar articles
- Biological/pathological functions of the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axes in the pathogenesis of bladder cancer.
Nazari A, Khorramdelazad H, Hassanshahi G. Nazari A, et al. Int J Clin Oncol. 2017 Dec;22(6):991-1000. doi: 10.1007/s10147-017-1187-x. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Int J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29022185 Review. - CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 Axis in Colorectal Cancer: Therapeutic Target in Preclinical and Clinical Studies.
Khare T, Bissonnette M, Khare S. Khare T, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 9;22(14):7371. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147371. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34298991 Free PMC article. Review. - The role of the CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in the progression and metastasis of bone sarcomas (Review).
Liao YX, Zhou CH, Zeng H, Zuo DQ, Wang ZY, Yin F, Hua YQ, Cai ZD. Liao YX, et al. Int J Mol Med. 2013 Dec;32(6):1239-46. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1521. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Int J Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 24127013 Review. - The chemokine receptors CXCR4/CXCR7 and their primary heterodimeric ligands CXCL12 and CXCL12/high mobility group box 1 in pancreatic cancer growth and development: finding flow.
Shakir M, Tang D, Zeh HJ, Tang SW, Anderson CJ, Bahary N, Lotze MT. Shakir M, et al. Pancreas. 2015 May;44(4):528-34. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000298. Pancreas. 2015. PMID: 25872129 Review. - The role of stromal-derived factor-1--CXCR7 axis in development and cancer.
Maksym RB, Tarnowski M, Grymula K, Tarnowska J, Wysoczynski M, Liu R, Czerny B, Ratajczak J, Kucia M, Ratajczak MZ. Maksym RB, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 25;625(1-3):31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.04.071. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19835865 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The Effect of C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 12 in Colorectal Cancer Associated with Chemoresistance and Radioresistance as Well as Stemness.
Dong W, Lin W, Li C. Dong W, et al. Iran J Public Health. 2024 Sep;53(9):2079-2089. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v53i9.16461. Iran J Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39429654 Free PMC article. - A Bioinformatics Investigation of Hub Genes Involved in Treg Migration and Its Synergistic Effects, Using Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Immunotherapies.
Kim N, Na S, Pyo J, Jang J, Lee SM, Kim K. Kim N, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 28;25(17):9341. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179341. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273290 Free PMC article. - Network analysis to identify driver genes and combination drugs in brain cancer.
Roshani F, Ahvar M, Ebrahimi A. Roshani F, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 12;14(1):18666. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69705-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39134610 Free PMC article. - Vascular restoration through local delivery of angiogenic factors stimulates bone regeneration in critical size defects.
Fang L, Liu Z, Wang C, Shi M, He Y, Lu A, Li X, Li T, Zhu D, Zhang B, Guan J, Shen J. Fang L, et al. Bioact Mater. 2024 Jul 10;36:580-594. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.07.003. eCollection 2024 Jun. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 39100886 Free PMC article.
References
- Vindrieux D, Escobar P, Lazennec G. Emerging roles of chemokines in prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2009;16(3):663–673. - PubMed
- Bieche I, Chavey C, Andrieu C, Busson M, Vacher S, Le Corre L, et al. Cxc chemokines located in the 4q21 region are up-regulated in breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007;14(4):1039–1052. - PubMed
- New DC, Wong YH. Cc chemokine receptor-coupled signalling pathways. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao (Shanghai) 2003;35(9):779–788. - PubMed
- Rot A, von Andrian UH. Chemokines in innate and adaptive host defense: Basic chemokinese grammar for immune cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:891–928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources