Topiramate-antagonism of L-glutamate-induced paroxysms in planarians - PubMed (original) (raw)
Topiramate-antagonism of L-glutamate-induced paroxysms in planarians
Robert B Raffa et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010.
Abstract
We recently reported that NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) and AMPA (α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid) induce concentration-dependent paroxysms in planarians (Dugesia dorotocephala). Since the postulated mechanisms of action of the sulfamate-substituted monosaccharide antiepileptic drug topiramate include inhibition of glutamate-activated ion channels, we tested the hypothesis that topiramate would inhibit glutamate-induced paroxysms in our model. We demonstrate that: (1) L-glutamate (1-10 mM), but not D-glutamate, induced dose-related paroxysms, and that (2) topiramate dose-relatedly (0.3-3 mM) inhibited L-glutamate-induced paroxysms. These results provide further evidence of a topiramate-sensitive glutamate receptor-mediated activity in this model.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Fig 1
Representative photographs of the spontaneous locomotor activity displayed by planarians tested in water. When quantified as rate of gridlines crossed, locomotor activity is nearly linear for at least 10 minutes (see refs in Raffa and Rawls, 2008).
Fig 2
Representative photographs of paroxysms displayed when planarians were tested in L-glutamate. The behavior consisted of spasmodic twisting and contracture in-place, with loss of forward movement.
Fig 3
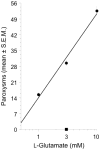
L-glutamate (filled circles), but not D-glutamate (filled square), induced concentration-related paroxysms, expressed as the mean (± S.E.M.) over a 5-min observation period. N = 8 planarians per group.
Fig 4
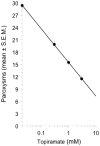
Topiramate (0.3, 1, 3 mM) attenuated the paroxysms induced by a fixed concentration of L-glutamate (3 mM). N = 8 planarians per group.
Similar articles
- Topiramate antagonizes NMDA- and AMPA-induced seizure-like activity in planarians.
Rawls SM, Thomas T, Adeola M, Patil T, Raymondi N, Poles A, Loo M, Raffa RB. Rawls SM, et al. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009 Oct;93(4):363-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2009.05.005. Epub 2009 May 15. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009. PMID: 19447129 - Topiramate in the treatment of migraine: a kainate (glutamate) receptor antagonist within the trigeminothalamic pathway.
Andreou AP, Goadsby PJ. Andreou AP, et al. Cephalalgia. 2011 Oct;31(13):1343-58. doi: 10.1177/0333102411418259. Epub 2011 Sep 5. Cephalalgia. 2011. PMID: 21893557 - Topiramate blocks kainate-evoked cobalt influx into cultured neurons.
Skradski S, White HS. Skradski S, et al. Epilepsia. 2000;41(S1):45-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.2000.tb02171.x. Epilepsia. 2000. PMID: 10768300 - [Target pharmacology of topiramate, a new antiepileptic drug].
Nakamura J, Kuwana Y, Yukitoshi N. Nakamura J, et al. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2000 Jan;115(1):53-7. doi: 10.1254/fpj.115.53. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2000. PMID: 10876816 Review. Japanese. - Topiramate: a review of preclinical, pharmacokinetic, and clinical data.
Rosenfeld WE. Rosenfeld WE. Clin Ther. 1997 Nov-Dec;19(6):1294-308. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(97)80006-9. Clin Ther. 1997. PMID: 9444441 Review.
Cited by
- Nicotine-induced C-shape movements in planarians are reduced by antinociceptive drugs: Implications for pain in planarian paroxysm etiology?
Kim A, Rawls SM. Kim A, et al. Brain Res. 2022 Mar 1;1778:147770. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147770. Epub 2021 Dec 31. Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 34979130 Free PMC article. - Levamisole and cocaine synergism: a prevalent adulterant enhances cocaine's action in vivo.
Tallarida CS, Egan E, Alejo GD, Raffa R, Tallarida RJ, Rawls SM. Tallarida CS, et al. Neuropharmacology. 2014 Apr;79:590-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.01.002. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24440755 Free PMC article. - Topiramate via NMDA, AMPA/kainate, GABAA and Alpha2 receptors and by modulation of CREB/BDNF and Akt/GSK3 signaling pathway exerts neuroprotective effects against methylphenidate-induced neurotoxicity in rats.
Motaghinejad M, Motevalian M, Fatima S, Beiranvand T, Mozaffari S. Motaghinejad M, et al. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2017 Nov;124(11):1369-1387. doi: 10.1007/s00702-017-1771-2. Epub 2017 Aug 9. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2017. PMID: 28795276 - Transcriptome profiling and pathway analysis of genes expressed differentially in participants with or without a positive response to topiramate treatment for methamphetamine addiction.
Li MD, Wang J, Niu T, Ma JZ, Seneviratne C, Ait-Daoud N, Saadvandi J, Morris R, Weiss D, Campbell J, Haning W, Mawhinney DJ, Weis D, McCann M, Stock C, Kahn R, Iturriaga E, Yu E, Elkashef A, Johnson BA. Li MD, et al. BMC Med Genomics. 2014 Dec 12;7:65. doi: 10.1186/s12920-014-0065-x. BMC Med Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25495887 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Ethanol and cocaine: environmental place conditioning, stereotypy, and synergism in planarians.
Tallarida CS, Bires K, Avershal J, Tallarida RJ, Seo S, Rawls SM. Tallarida CS, et al. Alcohol. 2014 Sep;48(6):579-86. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2014.07.006. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Alcohol. 2014. PMID: 25212751 Free PMC article.
References
- Angehagen M, Ben-Menachem E, Shank R, Ronnback L, Hansson E. Topiramate modulation of kainate-induced calcium currents is inversely related to channel phosphorylation level. J Neurochem. 2004;88:320–325. - PubMed
- Bazan NG, Tu B, Rodriguez de Turco EB. What synaptic lipid signaling tells us about seizure-induced damage and epileptogenesis. Prog Brain Res. 2002;135:175–185. - PubMed
- Cebrià F, Kudome T, Nakazawa M, Mineta K, Ikeo K, Gojobori T, Agata K. The expression of neural-specific genes reveals the structural and molecular complexity of the planarian central nervous system. Mech Dev. 2002;116:199–204. - PubMed
- Dalby NO, Mody I. The process of epileptogenesis: a pathophysiological approach. Curr Opin Neurol. 2001;14:187–192. - PubMed
- Dodgson SJ, Shank RP, Maryanoff BE. Topiramate as aninhibitor of carbonic anhydrase isozymes. Epilepsia. 2000;41(Suppl 1):S35–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DA15378/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R15 DA022694/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA022694/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA015378/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R15 DA022694-01A1/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA015378-03/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources