SolexaQA: At-a-glance quality assessment of Illumina second-generation sequencing data - PubMed (original) (raw)
SolexaQA: At-a-glance quality assessment of Illumina second-generation sequencing data
Murray P Cox et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010.
Abstract
Background: Illumina's second-generation sequencing platform is playing an increasingly prominent role in modern DNA and RNA sequencing efforts. However, rapid, simple, standardized and independent measures of run quality are currently lacking, as are tools to process sequences for use in downstream applications based on read-level quality data.
Results: We present SolexaQA, a user-friendly software package designed to generate detailed statistics and at-a-glance graphics of sequence data quality both quickly and in an automated fashion. This package contains associated software to trim sequences dynamically using the quality scores of bases within individual reads.
Conclusion: The SolexaQA package produces standardized outputs within minutes, thus facilitating ready comparison between flow cell lanes and machine runs, as well as providing immediate diagnostic information to guide the manipulation of sequence data for downstream analyses.
Figures
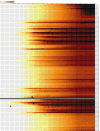
Figure 1
Example heat map showing several commonly observed quality defects. Nucleotide positions 1-75 are plotted from left-to-right along the _x_-axis; tiles 1-100 are ranked from top-to-bottom along the _y_-axis. (These numbers may vary for other datasets). The scale depicts the mean probability of observing a base call error for each tile at each nucleotide position. The defects evident in this dataset (see text for details) are atypical of Illumina sequencing; this dataset was chosen specifically to illustrate the capabilities of SolexaQA.
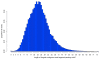
Figure 2
Distribution of mean quality (probability of error, _y_-axis) at each nucleotide position (_x_-axis) for each tile individually (dotted black lines) and the entire dataset combined (red circles). Note the considerable variance in data quality between tiles. The defects evident in this dataset (see text for details) are atypical of Illumina sequencing; this dataset was chosen specifically to illustrate the capabilities of SolexaQA.
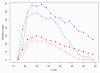
Figure 3
Distribution of longest read segments passing a user-defined quality threshold (here, P = 0.05, or equivalently, Phred quality score Q ≈ 13, or a base call error rate of 1-in-20). Note that reads in this dataset would be trimmed on average to ~25 nucleotides (i.e., only approximately one-third of the initial 75 nucleotide read length). The defects evident in this dataset (see text for details) are atypical of Illumina sequencing; this dataset was chosen specifically to illustrate the capabilities of SolexaQA.
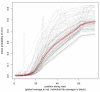
Figure 4
Effect of dynamically trimmed versus untrimmed reads on de novo assembly with the Velvet assembler. Dynamically trimmed reads (solid symbols) relative to untrimmed reads (open symbols) yield improved N50 values (red squares) and maximum contig sizes (blue triangles). Summary statistics were averaged across de novo assemblies for 20 isolates of Campylobacter coli and C. jejuni, and normalized by the total number of reads employed in each assembly.
Similar articles
- BIGpre: a quality assessment package for next-generation sequencing data.
Zhang T, Luo Y, Liu K, Pan L, Zhang B, Yu J, Hu S. Zhang T, et al. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2011 Dec;9(6):238-44. doi: 10.1016/S1672-0229(11)60027-2. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 22289480 Free PMC article. - ConDeTri--a content dependent read trimmer for Illumina data.
Smeds L, Künstner A. Smeds L, et al. PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26314. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026314. Epub 2011 Oct 19. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22039460 Free PMC article. - TagDust--a program to eliminate artifacts from next generation sequencing data.
Lassmann T, Hayashizaki Y, Daub CO. Lassmann T, et al. Bioinformatics. 2009 Nov 1;25(21):2839-40. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp527. Epub 2009 Sep 7. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19737799 Free PMC article. - MiSeq: A Next Generation Sequencing Platform for Genomic Analysis.
Ravi RK, Walton K, Khosroheidari M. Ravi RK, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1706:223-232. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7471-9_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29423801 Review. - De novo assembly of short sequence reads.
Paszkiewicz K, Studholme DJ. Paszkiewicz K, et al. Brief Bioinform. 2010 Sep;11(5):457-72. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbq020. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Brief Bioinform. 2010. PMID: 20724458 Review.
Cited by
- Inter-Individual Differences in the Oral Bacteriome Are Greater than Intra-Day Fluctuations in Individuals.
Sato Y, Yamagishi J, Yamashita R, Shinozaki N, Ye B, Yamada T, Yamamoto M, Nagasaki M, Tsuboi A. Sato Y, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Jun 29;10(6):e0131607. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131607. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26121551 Free PMC article. - Metabolic potential of lithifying cyanobacteria-dominated thrombolitic mats.
Mobberley JM, Khodadad CL, Foster JS. Mobberley JM, et al. Photosynth Res. 2013 Nov;118(1-2):125-40. doi: 10.1007/s11120-013-9890-6. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Photosynth Res. 2013. PMID: 23868401 Free PMC article. - Genome evolution in an ancient bacteria-ant symbiosis: parallel gene loss among Blochmannia spanning the origin of the ant tribe Camponotini.
Williams LE, Wernegreen JJ. Williams LE, et al. PeerJ. 2015 Apr 2;3:e881. doi: 10.7717/peerj.881. eCollection 2015. PeerJ. 2015. PMID: 25861561 Free PMC article. - Australian black field crickets show changes in neural gene expression associated with socially-induced morphological, life-history, and behavioral plasticity.
Kasumovic MM, Chen Z, Wilkins MR. Kasumovic MM, et al. BMC Genomics. 2016 Oct 24;17(1):827. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3119-y. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27776492 Free PMC article. - BIGpre: a quality assessment package for next-generation sequencing data.
Zhang T, Luo Y, Liu K, Pan L, Zhang B, Yu J, Hu S. Zhang T, et al. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2011 Dec;9(6):238-44. doi: 10.1016/S1672-0229(11)60027-2. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 22289480 Free PMC article.
References
- Hannon GJ. FASTX-Toolkit. 2010. http://hannonlab.cshl.edu/fastx_toolkit/
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources