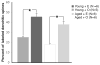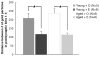Estrogen and aging affect the synaptic distribution of estrogen receptor β-immunoreactivity in the CA1 region of female rat hippocampus - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Estrogen and aging affect the synaptic distribution of estrogen receptor β-immunoreactivity in the CA1 region of female rat hippocampus
Elizabeth M Waters et al. Brain Res. 2011.
Abstract
Estradiol (E) mediates increased synaptogenesis in the hippocampal CA1 stratum radiatum (sr) and enhances memory in young and some aged female rats, depending on dose and age. Young female rats express more estrogen receptor α (ERα) immunolabeling in CA1sr spine synapse complexes than aged rats and ERα regulation is E sensitive in young but not aged rats. The current study examined whether estrogen receptor β (ERβ) expression in spine synapse complexes may be altered by age or E treatment. Young (3-4 months) and aged (22-23 months) female rats were ovariectomized 7 days prior to implantation of silastic capsules containing either vehicle (cholesterol) or E (10% in cholesterol) for 2 days. ERβ immunoreactivity (ir) in CA1sr was quantitatively analyzed using post-embedding electron microscopy. ERβ-ir was more prominent post-synaptically than pre-synaptically and both age and E treatment affected its synaptic distribution. While age decreased the spine synaptic complex localization of ERβ-ir (i.e., within 60 nm of the pre- and post-synaptic membranes), E treatment increased synaptic ERβ in both young and aged rats. In addition, the E treatment, but not age, increased dendritic shaft labeling. This data demonstrates that like ERα the levels of ERβ-ir decrease in CA1 axospinous synapses with age, however, unlike ERα the levels of ERβ-ir increase in these synapses in both young and aged rats in response to E. This suggests that synaptic ERβ may be a more responsive target to E, particularly in aged females.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
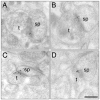
Fig. 1
Representative electron micrographs show the distribution of ERβ immunogold particles (black puncta) in the CA1 stratum radiatum of young OVX + Veh (A), young OVX + E (B), aged OVX + Veh (C) and aged OVX + E (D) rats. t, terminal; sp, dendritic spine. Bar, 100 nm
Fig. 2
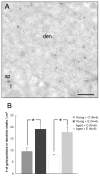
The overall percentage of ERβ immunoreactive axospinous synapses labeled dendritic spines is not affected by age but is significantly increased following E-replacement in both young and aged OVX rats. N = number of animals. * p < 0.02
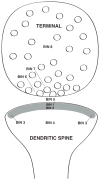
Fig. 3
Schematic drawing showing a pre- and postsynaptic profile with the eight Bin divisions used in the EM analysis.
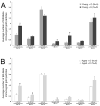
Fig. 4
Both age and estrogen altered the subcellular distribution of ERβ immunogold particles in pre- and postsynaptic profiles in the CA1sr region. A. In young OVX rats, E administration significantly increased ERβ-ir presynaptically (Bin 6) and postsynaptically (Bin 1) and in the synaptic cleft (Bin 5). B. In aged OVX rats, E administration significantly increased ERβ-ir only in Bins 1 and 8. Moreover, E administration to aged OVX significantly decreased ERβ-ir in Bin 4. * p < 0.05
Fig. 5
The overall numbers of ERβ immunogold particles in dendrites are not significantly different in aged rats compared to young rats. A. Clusters of ERβ immunogold particles are visible in dendrites in the CA1sr. B. ERβ immunogold particles are significantly increased following E-replacement in both young and aged rats. * p < 0.02
Fig. 6
The average distance between ERβ immunogold particles in postsynaptic profiles (dendritic spines, Bins 1 – 4) significantly increased following E administration in both young and aged rats. * p < 0.02
Fig. 7
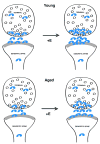
Schematic diagram depicting the effects of E administration on the levels and subcellular distribution of ERβ immunogold particles in spine synapse complexes in young and aged rats. ERβ-ir was detected in pre- and postsynaptic compartments of asymmetric synapses in the CA1sr in young and aged females. Although synapses contained fewer ERβ immunogold particles in aged females compared to young females, in both groups E treatment increased synaptic ERβ-ir.
Similar articles
- Effects of estrogen and aging on the synaptic distribution of phosphorylated Akt-immunoreactivity in the CA1 region of the female rat hippocampus.
Yildirim M, Janssen WG, Lou WY, Akama KT, McEwen BS, Milner TA, Morrison JH. Yildirim M, et al. Brain Res. 2011 Mar 16;1379:98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.07.053. Epub 2010 Aug 13. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 20709039 Free PMC article. - Estrogen and aging affect synaptic distribution of phosphorylated LIM kinase (pLIMK) in CA1 region of female rat hippocampus.
Yildirim M, Janssen WG, Tabori NE, Adams MM, Yuen GS, Akama KT, McEwen BS, Milner TA, Morrison JH. Yildirim M, et al. Neuroscience. 2008 Mar 18;152(2):360-70. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.004. Epub 2008 Jan 12. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18294775 Free PMC article. - Estrogen and aging affect the subcellular distribution of estrogen receptor-alpha in the hippocampus of female rats.
Adams MM, Fink SE, Shah RA, Janssen WG, Hayashi S, Milner TA, McEwen BS, Morrison JH. Adams MM, et al. J Neurosci. 2002 May 1;22(9):3608-14. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-09-03608.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11978836 Free PMC article. - Tracking the estrogen receptor in neurons: implications for estrogen-induced synapse formation.
McEwen B, Akama K, Alves S, Brake WG, Bulloch K, Lee S, Li C, Yuen G, Milner TA. McEwen B, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jun 19;98(13):7093-100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.121146898. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11416193 Free PMC article. Review. - Interactive effects of age and estrogen on cortical neurons: implications for cognitive aging.
Bailey ME, Wang AC, Hao J, Janssen WG, Hara Y, Dumitriu D, Hof PR, Morrison JH. Bailey ME, et al. Neuroscience. 2011 Sep 15;191:148-58. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.05.045. Epub 2011 Jun 2. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21664255 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Rapid estrogen signaling in the brain: implications for the fine-tuning of neuronal circuitry.
Srivastava DP, Waters EM, Mermelstein PG, Kramár EA, Shors TJ, Liu F. Srivastava DP, et al. J Neurosci. 2011 Nov 9;31(45):16056-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4097-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22072656 Free PMC article. Review. - Periodic Estrogen Receptor-Beta Activation: A Novel Approach to Prevent Ischemic Brain Damage.
Cue L, Diaz F, Briegel KJ, Patel HH, Raval AP. Cue L, et al. Neurochem Res. 2015 Oct;40(10):2009-17. doi: 10.1007/s11064-014-1346-7. Epub 2014 Jun 7. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 24906488 Review. - The impact of estradiol on serotonin, glutamate, and dopamine systems.
Bendis PC, Zimmerman S, Onisiforou A, Zanos P, Georgiou P. Bendis PC, et al. Front Neurosci. 2024 Mar 22;18:1348551. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1348551. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38586193 Free PMC article. Review. - Isoflavone-Enriched Soybean Leaves (Glycine Max) Alleviate Cognitive Impairment Induced by Ovariectomy and Modulate PI3K/Akt Signaling in the Hippocampus of C57BL6 Mice.
Yoo DY, Jung S, Kang JS, Baek JH, Park KH, Lee DH, Kang SS, Kim HJ. Yoo DY, et al. Nutrients. 2022 Nov 10;14(22):4753. doi: 10.3390/nu14224753. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36432439 Free PMC article. - Effects of selective estrogen receptor alpha and beta modulators on prepulse inhibition in male mice.
Labouesse MA, Langhans W, Meyer U. Labouesse MA, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Aug;232(16):2981-94. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-3935-9. Epub 2015 Apr 18. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25893642
References
- Adams MM, Morrison JH, Gore AC. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor mRNA levels change during reproductive senescence in the hippocampus of female rats. Exp Neurol. 2001a;170:171–179. - PubMed
- Adams MM, Oung T, Morrison JH, Gore AC. Length of postovariectomy interval and age, but not estrogen replacement, regulate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor mRNA levels in the hippocampus of female rats. Exp Neurol. 2001b;170:345–356. - PubMed
- Adams MM, Fink SE, Janssen WG, Shah RA, Morrison JH. Estrogen modulates synaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit distribution in the aged hippocampus. J Comp Neurol. 2004a;474:419–426. - PubMed
- Adams MM, Fink SE, Janssen WG, Shah RA, Morrison JH. Estrogen modulates synaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit distribution in the aged hippocampus. J Comp Neurol. 2004b;474:419–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS07080/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DA08259/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS007080/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA008259/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS007080-43/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01-AG16765/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG016765/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous