Anti-GD2 antibody with GM-CSF, interleukin-2, and isotretinoin for neuroblastoma - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2010 Sep 30;363(14):1324-34.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0911123.
Andrew L Gilman, M Fevzi Ozkaynak, Wendy B London, Susan G Kreissman, Helen X Chen, Malcolm Smith, Barry Anderson, Judith G Villablanca, Katherine K Matthay, Hiro Shimada, Stephan A Grupp, Robert Seeger, C Patrick Reynolds, Allen Buxton, Ralph A Reisfeld, Steven D Gillies, Susan L Cohn, John M Maris, Paul M Sondel; Children's Oncology Group
Affiliations
- PMID: 20879881
- PMCID: PMC3086629
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0911123
Randomized Controlled Trial
Anti-GD2 antibody with GM-CSF, interleukin-2, and isotretinoin for neuroblastoma
Alice L Yu et al. N Engl J Med. 2010.
Abstract
Background: Preclinical and preliminary clinical data indicate that ch14.18, a monoclonal antibody against the tumor-associated disialoganglioside GD2, has activity against neuroblastoma and that such activity is enhanced when ch14.18 is combined with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) or interleukin-2. We conducted a study to determine whether adding ch14.18, GM-CSF, and interleukin-2 to standard isotretinoin therapy after intensive multimodal therapy would improve outcomes in high-risk neuroblastoma.
Methods: Patients with high-risk neuroblastoma who had a response to induction therapy and stem-cell transplantation were randomly assigned, in a 1:1 ratio, to receive standard therapy (six cycles of isotretinoin) or immunotherapy (six cycles of isotretinoin and five concomitant cycles of ch14.18 in combination with alternating GM-CSF and interleukin-2). Event-free survival and overall survival were compared between the immunotherapy group and the standard-therapy group, on an intention-to-treat basis.
Results: A total of 226 eligible patients were randomly assigned to a treatment group. In the immunotherapy group, a total of 52% of patients had pain of grade 3, 4, or 5, and 23% and 25% of patients had capillary leak syndrome and hypersensitivity reactions, respectively. With 61% of the number of expected events observed, the study met the criteria for early stopping owing to efficacy. The median duration of follow-up was 2.1 years. Immunotherapy was superior to standard therapy with regard to rates of event-free survival (66±5% vs. 46±5% at 2 years, P=0.01) and overall survival (86±4% vs. 75±5% at 2 years, P=0.02 without adjustment for interim analyses).
Conclusions: Immunotherapy with ch14.18, GM-CSF, and interleukin-2 was associated with a significantly improved outcome as compared with standard therapy in patients with high-risk neuroblastoma. (Funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Food and Drug Administration; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00026312.)
Figures
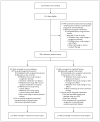
Figure 1. Enrollment, Randomization, and Follow-up of the Study Patients
Patients receiving protocol therapy were still being treated with isotretinoin, with or without immunotherapy, at the time the data were analyzed.
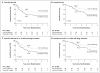
Figure 2. Kaplan–Meier Estimates of Survival among the 226 Study Patients Who Had Been Randomly Assigned, According to Treatment Group
Data are shown for event-free survival (Panel A) and overall survival (Panel B) for all 226 patients and for event-free survival (Panel C) and overall survival (Panel D) for the 179 patients 1 year of age or older at enrollment. The estimated survival (±SE) at 2 years is indicated in each plot.
Comment in
- Antibody therapy and neuroblastoma.
Tao X. Tao X. N Engl J Med. 2011 Jan 20;364(3):289; author reply 289-90. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1012160. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 21247330 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Interleukin 2 with anti-GD2 antibody ch14.18/CHO (dinutuximab beta) in patients with high-risk neuroblastoma (HR-NBL1/SIOPEN): a multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial.
Ladenstein R, Pötschger U, Valteau-Couanet D, Luksch R, Castel V, Yaniv I, Laureys G, Brock P, Michon JM, Owens C, Trahair T, Chan GCF, Ruud E, Schroeder H, Beck Popovic M, Schreier G, Loibner H, Ambros P, Holmes K, Castellani MR, Gaze MN, Garaventa A, Pearson ADJ, Lode HN. Ladenstein R, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2018 Dec;19(12):1617-1629. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30578-3. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30442501 Clinical Trial. - Lack of survival advantage with autologous stem-cell transplantation in high-risk neuroblastoma consolidated by anti-GD2 immunotherapy and isotretinoin.
Kushner BH, Ostrovnaya I, Cheung IY, Kuk D, Modak S, Kramer K, Roberts SS, Basu EM, Yataghene K, Cheung NK. Kushner BH, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 26;7(4):4155-66. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6393. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26623730 Free PMC article. - Anti-GD2 antibody-containing immunotherapy postconsolidation therapy for people with high-risk neuroblastoma treated with autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Peinemann F, van Dalen EC, Enk H, Tytgat GA. Peinemann F, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 24;4(4):CD012442. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012442.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31016728 Free PMC article. - Targeted immunotherapy for high-risk neuroblastoma--the role of monoclonal antibodies.
Parsons K, Bernhardt B, Strickland B. Parsons K, et al. Ann Pharmacother. 2013 Feb;47(2):210-8. doi: 10.1345/aph.1R353. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Ann Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 23386066 Review.
Cited by
- Using a combination of gangliosides and cell surface vimentin as surface biomarkers for isolating osteosarcoma cells in microfluidic devices.
Fasanya HO, Dopico PJ, Yeager Z, Fan ZH, Siemann DW. Fasanya HO, et al. J Bone Oncol. 2021 Mar 24;28:100357. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2021.100357. eCollection 2021 Jun. J Bone Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33912384 Free PMC article. - Venetoclax-based Rational Combinations are Effective in Models of _MYCN_-amplified Neuroblastoma.
Dalton KM, Krytska K, Lochmann TL, Sano R, Casey C, D'Aulerio A, Khan QA, Crowther GS, Coon C, Cai J, Jacob S, Kurupi R, Hu B, Dozmorov M, Greninger P, Souers AJ, Benes CH, Mossé YP, Faber AC. Dalton KM, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021 Aug;20(8):1400-1411. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0710. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021. PMID: 34088831 Free PMC article. - Cardiovascular disease and chimeric antigen receptor cellular therapy.
Rao A, Stewart A, Eljalby M, Ramakrishnan P, Anderson LD Jr, Awan FT, Chandra A, Vallabhaneni S, Zhang K, Zaha VG. Rao A, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Sep 23;9:932347. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.932347. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36211558 Free PMC article. Review. - Heightened metabolic responses in NK cells from patients with neuroblastoma suggests increased potential for immunotherapy.
Slattery K, Breheny M, Woods E, Keating S, Brennan K, Rooney C, Augustine S, Ryan A, Owens C, Gardiner CM. Slattery K, et al. Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 7;12:1004871. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1004871. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36276144 Free PMC article. - Approaches to improve tumor accumulation and interactions between monoclonal antibodies and immune cells.
Marcucci F, Bellone M, Rumio C, Corti A. Marcucci F, et al. MAbs. 2013 Jan-Feb;5(1):34-46. doi: 10.4161/mabs.22775. Epub 2012 Dec 4. MAbs. 2013. PMID: 23211740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program. SEER★Stat mortality database: total US. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 1969–2006.
- Maris JM, Hogarty MD, Bagatell R, Cohn SL. Neuroblastoma. Lancet. 2007;369:2106–20. - PubMed
- Matthay KK, Villablanca JG, Seeger RC, et al. Treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma with intensive chemotherapy, radiotherapy, autologous bone marrow transplantation, and 13-cis-retinoic acid. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1165–73. - PubMed
- Schulz G, Cheresh DA, Varki NM, Yu A, Staffileno LK, Reisfeld RA. Detection of ganglioside GD2 in tumor tissues and sera of neuroblastoma patients. Cancer Res. 1984;44:5914–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- FD-R-002319/FD/FDA HHS/United States
- U10-CA98543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA032685/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA098413/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA029139/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA098543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10-CA98413/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10-CA29139/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous