Development, validation and use of an insulin sensitivity score in youths with diabetes: the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Development, validation and use of an insulin sensitivity score in youths with diabetes: the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study
D Dabelea et al. Diabetologia. 2011 Jan.
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: The ability to measure insulin sensitivity across the phenotypic spectrum of diabetes may contribute to a more accurate characterisation of diabetes type. Our goal was to develop and validate an insulin sensitivity (IS) score using the euglycaemic-hyperinsulinaemic clamp in a subset (n = 85) of 12- to 19-year-old youths with diabetes participating in the SEARCH study in Colorado, USA.
Methods: Youths with a diagnosis of type 1 (n = 60) or type 2 diabetes (n = 25) underwent a 3 h clamp to measure glucose disposal rate (GDR, mg kg⁻¹ min⁻¹). Demographic (age, sex, race), clinical (BMI, waist, Tanner stage) and metabolic characteristics (HbA₁(c), lipids, blood pressure, urine albumin:creatinine) were used to estimate log(e)IS score via stepwise linear regression on a model-development set (n = 53). Estimated IS score was evaluated for reproducibility on two validation sets: youths with diabetes (n = 33) and healthy control youths (n = 22).
Results: The best model included waist, triacylglycerol (TG) and HbA₁(c) levels (R² = 0.74). Diabetes type did not enter the model and there were no significant interactions between diabetes type and other predictors. Estimated IS score correlated well (r = 0.65, p < 0.0001; r = 0.62, p = 0.002) with GDR on the two validation sets. Based on this analysis, we propose the following formula to estimate insulin sensitivity in youths with diabetes: [Formula: see text].
Conclusions/interpretation: Insulin sensitivity can be estimated in adolescents with diabetes using routinely collected measures. This score can be applied to epidemiological studies of youths with diabetes to characterise relationships between dimensions of diabetes type.
Conflict of interest statement
Duality of interest The authors declare that there is no duality of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures
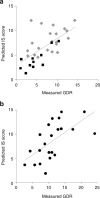
Fig. 1
Relationship between measured GDR and estimated IS score in (a) youths with diabetes (_n_=32), _r_=0.65, p<0.0001 (grey diamonds, type 1 diabetes; black squares, type 2 diabetes); (b) youths without diabetes (_n_=22), _r_=0.62, _p_=0.002 (black circles)
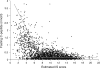
Fig. 2
Relationship between fasting C-peptide (FCP, nmol/l) and estimated IS score among all SEARCH participants (_n_=2,417): two-piece orthogonal regression splines. y_1=−0.541_x+4.309, y_2=−0.00132_x+0.151 with a knot at _x_=7.7 (IS score), _y_=0.14 (FCP in nmol/l)
Fig. 3
Relationship between fasting C-peptide and insulin sensitivity by DA status among SEARCH participants: smooth spline averages. DA-positive: black (n = 1,780). DA-negative: grey (_n_=610)
Similar articles
- A new model to estimate insulin resistance via clinical parameters in adults with type 1 diabetes.
Zheng X, Huang B, Luo S, Yang D, Bao W, Li J, Yao B, Weng J, Yan J. Zheng X, et al. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017 May;33(4). doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2880. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 28029212 - Can clinical factors estimate insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes?
Williams KV, Erbey JR, Becker D, Arslanian S, Orchard TJ. Williams KV, et al. Diabetes. 2000 Apr;49(4):626-32. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.49.4.626. Diabetes. 2000. PMID: 10871201 - Association of insulin sensitivity to lipids across the lifespan in people with Type 1 diabetes.
Maahs DM, Nadeau K, Snell-Bergeon JK, Schauer I, Bergman B, West NA, Rewers M, Daniels SR, Ogden LG, Hamman RF, Dabelea D. Maahs DM, et al. Diabet Med. 2011 Feb;28(2):148-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.03143.x. Diabet Med. 2011. PMID: 21219421 Free PMC article. - Hyperinsulinaemic-hypoglycaemic glucose clamps in human research: a systematic review of the literature.
Fabricius TW, Verhulst CEM, Kristensen PL, Tack CJ, McCrimmon RJ, Heller S, Evans ML, Amiel SA, Pieber TR, de Galan BE, Pedersen-Bjergaard U; Hypo-RESOLVE consortium. Fabricius TW, et al. Diabetologia. 2021 Apr;64(4):727-736. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05361-8. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Diabetologia. 2021. PMID: 33566134 Free PMC article. - Pathophysiology of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 90-year perspective.
Zaccardi F, Webb DR, Yates T, Davies MJ. Zaccardi F, et al. Postgrad Med J. 2016 Feb;92(1084):63-9. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2015-133281. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Postgrad Med J. 2016. PMID: 26621825 Review.
Cited by
- Advanced lipoprotein profile disturbances in type 1 diabetes mellitus: a focus on LDL particles.
Amor AJ, Castelblanco E, Hernández M, Gimenez M, Granado-Casas M, Blanco J, Soldevila B, Esmatjes E, Conget I, Alonso N, Ortega E, Mauricio D. Amor AJ, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Aug 9;19(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01099-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32772924 Free PMC article. - Clinical evolution of beta cell function in youth with diabetes: the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study.
Dabelea D, Mayer-Davis EJ, Andrews JS, Dolan LM, Pihoker C, Hamman RF, Greenbaum C, Marcovina S, Fujimoto W, Linder B, Imperatore G, D'Agostino R Jr. Dabelea D, et al. Diabetologia. 2012 Dec;55(12):3359-68. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2719-6. Epub 2012 Sep 20. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22990715 Free PMC article. - Clinical and Metabolic Characteristics among Mexican Children with Different Types of Diabetes Mellitus.
Evia-Viscarra ML, Guardado-Mendoza R, Rodea-Montero ER. Evia-Viscarra ML, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Dec 16;11(12):e0168377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168377. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27992493 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Association of Type 1 Diabetes vs Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed During Childhood and Adolescence With Complications During Teenage Years and Young Adulthood.
Dabelea D, Stafford JM, Mayer-Davis EJ, D'Agostino R Jr, Dolan L, Imperatore G, Linder B, Lawrence JM, Marcovina SM, Mottl AK, Black MH, Pop-Busui R, Saydah S, Hamman RF, Pihoker C; SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Research Group. Dabelea D, et al. JAMA. 2017 Feb 28;317(8):825-835. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.0686. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 28245334 Free PMC article. - Twenty years of pediatric diabetes surveillance: what do we know and why it matters.
Dabelea D, Sauder KA, Jensen ET, Mottl AK, Huang A, Pihoker C, Hamman RF, Lawrence J, Dolan LM, Agostino R Jr, Wagenknecht L, Mayer-Davis EJ, Marcovina SM. Dabelea D, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2021 Jul;1495(1):99-120. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14573. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2021. PMID: 33543783 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Gale EA. Declassifying diabetes. Diabetologia. 2006;49:1989–1995. - PubMed
- Greenbaum CJ. Insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes. Diab Metab Res Rev. 2002;18:192–200. - PubMed
- Wilkin TJ. The accelerator hypothesis: a review of the evidence for insulin resistance as the basis for type I as well as type II diabetes. Int J Obes Lond. 2009;33:716–726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 DK057516/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DP000247/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- R01 DK059184/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DP000248/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U01 DP000244/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DP000245/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- DP-05-069/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- K23 RR020038/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DP000250/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U01 DP000246/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U01 DP000254/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous