Psychedelic 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine: metabolism, pharmacokinetics, drug interactions, and pharmacological actions - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Psychedelic 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine: metabolism, pharmacokinetics, drug interactions, and pharmacological actions
Hong-Wu Shen et al. Curr Drug Metab. 2010 Oct.
Abstract
5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-MeO-DMT) belongs to a group of naturally-occurring psychoactive indolealkylamine drugs. It acts as a nonselective serotonin (5-HT) agonist and causes many physiological and behavioral changes. 5-MeO-DMT is O-demethylated by polymorphic cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) to an active metabolite, bufotenine, while it is mainly inactivated through the deamination pathway mediated by monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A). 5-MeO-DMT is often used with MAO-A inhibitors such as harmaline. Concurrent use of harmaline reduces 5-MeO-DMT deamination metabolism and leads to a prolonged and increased exposure to the parent drug 5-MeO-DMT, as well as the active metabolite bufotenine. Harmaline, 5-MeO-DMT and bufotenine act agonistically on serotonergic systems and may result in hyperserotonergic effects or serotonin toxicity. Interestingly, CYP2D6 also has important contribution to harmaline metabolism, and CYP2D6 genetic polymorphism may cause considerable variability in the metabolism, pharmacokinetics and dynamics of harmaline and its interaction with 5-MeO-DMT. Therefore, this review summarizes recent findings on biotransformation, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacological actions of 5-MeO-DMT. In addition, the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic drug-drug interactions between harmaline and 5-MeO-DMT, potential involvement of CYP2D6 pharmacogenetics, and risks of 5-MeO-DMT intoxication are discussed.
Figures
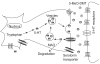
Figure 1
5-MeO-DMT biotransformation and the metabolic interactions with harmaline. _O_-demethylation of 5-MeO-DMT by CYP2D6 produces an active metabolite bufotenine. Both 5-MeO-DMT and bufotenine are readily deaminated by MAO-A to indoleacetic acid derivatives. The MAOI harmaline, which is inactivated by CYP2D6, blocks the deamination metabolism of 5-MeO-DMT and bufotenine.
Figure 2
Hyperserotonergic effects may be induced when harmaline blocks 5-HT degradation, and the concurrent 5-MeO-DMT activates 5-HT receptors within the synaptic cleft, beside their pharmacokinetic interactions.
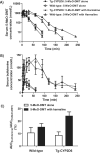
Figure 3
Harmaline (5 mg/kg, i.p.) co-administered with 5-MeO-DMT (2 mg/kg, i.p.) markedly alters blood concentrations of the parent drug 5-MeO-DMT (A), the active metabolite bufotenine (B), and the ratio of their systemic exposures (C) in wild-type and/or Tg-CYP2D6 mouse models [37].
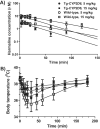
Figure 4
Studies using wild-type and Tg-CYP2D6 mouse model demonstrate that CYP2D6 status has significant impact on harmaline pharmacokinetics (A) and harmaline-induced hypothermia (B) [113].
Similar articles
- Effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitor and cytochrome P450 2D6 status on 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine metabolism and pharmacokinetics.
Shen HW, Wu C, Jiang XL, Yu AM. Shen HW, et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Jul 1;80(1):122-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.02.020. Epub 2010 Mar 3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20206139 Free PMC article. - Pharmacokinetic interactions between monoamine oxidase A inhibitor harmaline and 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine, and the impact of CYP2D6 status.
Jiang XL, Shen HW, Mager DE, Yu AM. Jiang XL, et al. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013 May;41(5):975-86. doi: 10.1124/dmd.112.050724. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013. PMID: 23393220 Free PMC article. - Potentiation of 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine-induced hyperthermia by harmaline and the involvement of activation of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors.
Jiang XL, Shen HW, Yu AM. Jiang XL, et al. Neuropharmacology. 2015 Feb;89:342-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.10.013. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25446678 Free PMC article. - A narrative synthesis of research with 5-MeO-DMT.
Ermakova AO, Dunbar F, Rucker J, Johnson MW. Ermakova AO, et al. J Psychopharmacol. 2022 Mar;36(3):273-294. doi: 10.1177/02698811211050543. Epub 2021 Oct 19. J Psychopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34666554 Free PMC article. Review. - The clinical pharmacology and potential therapeutic applications of 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-MeO-DMT).
Reckweg JT, Uthaug MV, Szabo A, Davis AK, Lancelotta R, Mason NL, Ramaekers JG. Reckweg JT, et al. J Neurochem. 2022 Jul;162(1):128-146. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15587. Epub 2022 Mar 8. J Neurochem. 2022. PMID: 35149998 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Short-term safety and tolerability profile of 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine in human subjects: a systematic review of clinical trials.
Kwaśny A, Wilkowska A, Cubała WJ. Kwaśny A, et al. Front Psychiatry. 2024 Sep 19;15:1477996. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1477996. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39364380 Free PMC article. - Novel Thermosensitive and Mucoadhesive Nasal Hydrogel Containing 5-MeO-DMT Optimized Using Box-Behnken Experimental Design.
Miranda P, Castro A, Díaz P, Minini L, Ferraro F, Paulsen E, Faccio R, Pardo H. Miranda P, et al. Polymers (Basel). 2024 Jul 29;16(15):2148. doi: 10.3390/polym16152148. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39125174 Free PMC article. - Serotonergic psychedelic 5-MeO-DMT alters plasticity-related gene expression and generates anxiolytic effects in stressed mice.
Nogueira M, Ferreira Golbert DC, Menezes R, Nóbrega de Almeida R, Galvão-Coelho NL, Siroky AN, Lima TZ, Maia H, Leão KE, Leão RN. Nogueira M, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Jan;30(1):50-60. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02655-w. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 38969716 - Effects of hallucinogenic drugs on the human heart.
Neumann J, Dhein S, Kirchhefer U, Hofmann B, Gergs U. Neumann J, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 2;15:1334218. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1334218. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38370480 Free PMC article. Review. - Making Sense of Psychedelics in the CNS.
Fordyce BA, Roth BL. Fordyce BA, et al. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2024 Feb 1;27(2):pyae007. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyae007. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38289825 Free PMC article.
References
- Pachter IJ, Zacharias DE, Ribeiro O. Indole alkaloids of acer saccharinum (the Silver Maple), Dictyoloma incanescens, Piptadenia colubrina, and Mimosa hostilis. J Org Chem. 1959;24:1285–1287.
- Ott J. Pharmepena-Psychonautics: Human intranasal, sublingual and oral pharmacology of 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyl-tryptamine. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2001;33:403–407. - PubMed
- McKenna DJ. Clinical investigations of the therapeutic potential of ayahuasca: rationale and regulatory challenges. Pharmacol Ther. 2004;102:111–129. - PubMed
- Gambelunghe C, Aroni K, Rossi R, Moretti L, Bacci M. Identification of N,N-dimethyltryptamine and beta-carbolines in psychotropic ayahuasca beverage. Biomed Chromatogr. 2008;22:1056–1059. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources