Steady-state pharmacokinetics of oral testosterone undecanoate with concomitant inhibition of 5α-reductase by finasteride - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
Steady-state pharmacokinetics of oral testosterone undecanoate with concomitant inhibition of 5α-reductase by finasteride
M Y Roth et al. Int J Androl. 2011 Dec.
Abstract
Oral testosterone undecanoate (TU) is used to treat testosterone deficiency; however, oral TU treatment elevates dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which may be associated with an increased risk of acne, male pattern baldness and prostate hyperplasia. Co-administration of 5α-reductase inhibitors with other formulations of oral testosterone suppresses DHT production and increases serum testosterone. We hypothesized that finasteride would increase serum testosterone and lower DHT during treatment with oral TU. Therefore, we studied the steady-state pharmacokinetics of oral TU, 200 mg equivalents of testosterone twice daily for 7 days, alone and with finasteride 0.5 and 1.0 mg po twice daily in an open-label, three-way crossover study in 11 young men with experimentally induced hypogonadism. On the seventh day of each dosing period, serum testosterone, DHT and oestradiol were measured at baseline and 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 13, 14, 16, 20 and 24 h after the morning dose. Serum testosterone and DHT were significantly increased into and above their normal ranges similarly by all three treatments. Co-administration of finasteride at 0.5 and 1.0 mg po twice daily had no significant effect on either serum testosterone or DHT. Oral TU differs from other formulations of oral testosterone in its response to concomitant inhibition of 5α-reductase, perhaps because of its unique lymphatic route of absorption.
© 2010 The Authors. International Journal of Andrology © 2011 European Academy of Andrology.
Figures
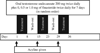
Figure 1
Study design. Treatment with oral testosterone undecanoate 200 mg twice daily for three separate 1-week periods, with 1-week wash-out periods in between dosing, co-administered with 0, 0.5 or 1.0 mg finasteride twice daily. Acyline (300 mcg/kg) was administered on days 1, 15 and 29 to induce hypogonadism. The sequence of finasteride doses was randomized to minimize carryover effect.
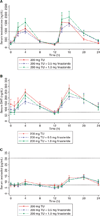
Figure 2
Serum testosterone (A), dihydrotestosterone (DHT) (B) and oestradiol (C) after 7 days of dosing with oral testosterone undecanoate (200 mg) by mouth twice a day alone or with 0.5 or 1.0 mg of finasteride twice a day in 11 normal men with experimentally induced hypogonadism. Each subject underwent all three treatments in random order. The short dashed lines represent the upper and lower limits of the normal range. All values are geometric means ± SE. TU, testosterone undecanoate.
Similar articles
- [Effect of selective 5alpha-reductase inhibitor or/and testosterone undecanoate on the reproductive function of male rats].
Jia Y, Cue YG, Wang XD, Wang XH, Tong JS, Ma DZ, Cai RF, Di FS. Jia Y, et al. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2005 Jan;11(1):38-41. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2005. PMID: 15704680 Chinese. - Pharmacokinetics of 2 novel formulations of modified-release oral testosterone alone and with finasteride in normal men with experimental hypogonadism.
Snyder CN, Clark RV, Caricofe RB, Bush MA, Roth MY, Page ST, Bremner WJ, Amory JK. Snyder CN, et al. J Androl. 2010 Nov-Dec;31(6):527-35. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.109.009746. Epub 2010 Apr 8. J Androl. 2010. PMID: 20378927 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - MK-386, an inhibitor of 5alpha-reductase type 1, reduces dihydrotestosterone concentrations in serum and sebum without affecting dihydrotestosterone concentrations in semen.
Schwartz JI, Tanaka WK, Wang DZ, Ebel DL, Geissler LA, Dallob A, Hafkin B, Gertz BJ. Schwartz JI, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997 May;82(5):1373-7. doi: 10.1210/jcem.82.5.3912. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997. PMID: 9141518 Clinical Trial. - Dihydrotestosterone and the concept of 5alpha-reductase inhibition in human benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Bartsch G, Rittmaster RS, Klocker H. Bartsch G, et al. Eur Urol. 2000 Apr;37(4):367-80. doi: 10.1159/000020181. Eur Urol. 2000. PMID: 10765065 Review. - Dihydrotestosterone and the concept of 5alpha-reductase inhibition in human benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Bartsch G, Rittmaster RS, Klocker H. Bartsch G, et al. World J Urol. 2002 Apr;19(6):413-25. doi: 10.1007/s00345-002-0248-5. World J Urol. 2002. PMID: 12022710 Review.
Cited by
- Pharmacokinetics of modified slow-release oral testosterone over 9 days in normal men with experimental hypogonadism.
Lee A, Rubinow K, Clark RV, Caricofe RB, Bush MA, Zhi H, Roth MY, Page ST, Bremner WJ, Amory JK. Lee A, et al. J Androl. 2012 May-Jun;33(3):420-6. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.111.014514. Epub 2011 Aug 25. J Androl. 2012. PMID: 21868746 Free PMC article. - Meta-Analysis on the Efficacy and Safety of Traditional Chinese Medicine as Adjuvant Therapy for Refractory Androgenetic Alopecia.
You Q, Li L, Ma X, Gao T, Xiong S, Yan Y, Fang H, Li F, Chen H, Liu Y. You Q, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Oct 31;2019:9274148. doi: 10.1155/2019/9274148. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31781285 Free PMC article. Review. - Cardiovascular risks and elevation of serum DHT vary by route of testosterone administration: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Borst SE, Shuster JJ, Zou B, Ye F, Jia H, Wokhlu A, Yarrow JF. Borst SE, et al. BMC Med. 2014 Nov 27;12:211. doi: 10.1186/s12916-014-0211-5. BMC Med. 2014. PMID: 25428524 Free PMC article. Review. - Dietary fat modulates the testosterone pharmacokinetics of a new self-emulsifying formulation of oral testosterone undecanoate in hypogonadal men.
Yin A, Alfadhli E, Htun M, Dudley R, Faulkner S, Hull L, Leung A, Bross R, Longstreth J, Swerdloff R, Wang C. Yin A, et al. J Androl. 2012 Nov-Dec;33(6):1282-90. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.112.017020. Epub 2012 Jul 12. J Androl. 2012. PMID: 22790645 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Importance of measuring testosterone in enzyme-inhibited plasma for oral testosterone undecanoate androgen replacement therapy clinical trials.
Lachance S, Dhingra O, Bernstein J, Gagnon S, Savard C, Pelletier N, Boudreau N, Lévesque A. Lachance S, et al. Future Sci OA. 2015 Nov 1;1(4):FSO55. doi: 10.4155/fso.15.55. eCollection 2015 Nov. Future Sci OA. 2015. PMID: 28031910 Free PMC article.
References
- Amory JK, Bremner WJ. Oral testosterone in oil plus dutasteride: a pharmacokinetic study in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:2610–2617. - PubMed
- Amory JK, Page ST, Bremner WJ. Oral testosterone in oil: pharmacokinetic effects of 5α-reduction with finasteride or dutasteride and food intake in men. J Androl. 2006;27:72–78. - PubMed
- Amory JK, Wang C, Swerdloff RS, Anawalt BD, Matsumoto AM, Bremner WJ, Walker SE, Haberer LJ, Clark RV. The effect of 5α-reductase inhibition with dutasteride and finasteride on semen parameters and serum hormones in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:1659–1665. - PubMed
- Andriole GL, Bostwick DG, Brawley OW, Gomella LG, Marberger M, Montorsi F, et al. Effect of dutasteride on the risk of prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1192–1202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 HD42454/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD060488/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025014/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000425/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD042454/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-025014/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR-00425/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources