Investigation of the influence of EPs® 7630, a herbal drug preparation from Pelargonium sidoides, on replication of a broad panel of respiratory viruses - PubMed (original) (raw)
Investigation of the influence of EPs® 7630, a herbal drug preparation from Pelargonium sidoides, on replication of a broad panel of respiratory viruses
Martin Michaelis et al. Phytomedicine. 2011.
Abstract
The Pelargonium sidoides extract EPs® 7630 is an approved drug for the treatment of acute bronchitis in Germany. The postulated mechanisms underlying beneficial effects of EPs® 7630 in bronchitis patients include immunomodulatory and cytoprotective effects, inhibition of interaction between bacteria and host cells, and increase of cilliary beat frequency on respiratory cells. Here, we investigated the influence of EPs® 7630 on replication of a panel of respiratory viruses. Determination of virus-induced cytopathogenic effects and virus titres revealed that EPs® 7630 at concentrations up to 100 μg/ml interfered with replication of seasonal influenza A virus strains (H1N1, H3N2), respiratory syncytial virus, human coronavirus, parainfluenza virus, and coxsackie virus but did not affect replication of highly pathogenic avian influenza A virus (H5N1), adenovirus, or rhinovirus. Therefore, antiviral effects may contribute to the beneficial effects exerted by EPs® 7630 in acute bronchitis patients.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier GmbH. All rights reserved.
Figures
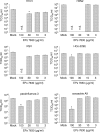
Fig. 1
Influence of EPs® 7630 on infectious virus titres indicated as 50% tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50/ml). EPs® 7630 was continuously present in cell culture media beginning with a 1 h pre-incubation period. Cells were infected with the respective viruses in the absence (Mock) or presence of EPs® 7630 at the following MOIs: influenza A virus H1N1, 0.005 (titres were determined 24 h post infection, cell line MDCK); influenza A virus H3N2, 0.005 (24 h, MDCK); coxsackie virus A9 (coxsackie A9), MOI 0.005 (24 h, human foreskin fibroblasts); parainfluenza virus type 3 (parainfluenza 3), 0.01 (72 h, LLC-MK2); respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), 0.01 (72 h, Vero); human coronavirus strain 229E (HCo-229E), 0.01 (72 h, Caco-2). *P < 0.05 relative to Mock (as determined by ANOVA with subsequent Student-Newmam–Keuls test); n.d. = not detectable.
Similar articles
- Medicinal properties and conservation of Pelargonium sidoides DC.
Moyo M, Van Staden J. Moyo M, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Mar 14;152(2):243-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.01.009. Epub 2014 Jan 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24463034 Free PMC article. Review. - EPs® 7630 (Umckaloabo®), an extract from Pelargonium sidoides roots, exerts anti-influenza virus activity in vitro and in vivo.
Theisen LL, Muller CP. Theisen LL, et al. Antiviral Res. 2012 May;94(2):147-56. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.03.006. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Antiviral Res. 2012. PMID: 22475498 - Comparative in vitro analysis of inhibition of rhinovirus and influenza virus replication by mucoactive secretolytic agents and plant extracts.
Walther C, Döring K, Schmidtke M. Walther C, et al. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Dec 23;20(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-03173-2. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 33357221 Free PMC article. - Evaluation of pharmacodynamic activities of EPs® 7630, a special extract from roots of Pelargonium sidoides, in animals models of cough, secretolytic activity and acute bronchitis.
Bao Y, Gao Y, Koch E, Pan X, Jin Y, Cui X. Bao Y, et al. Phytomedicine. 2015 Apr 15;22(4):504-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Phytomedicine. 2015. PMID: 25925973 Free PMC article. - Antimicrobial, Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Activity Studies of Pelargonium sidoides (EPs® 7630) in the Context of Health Promotion.
Kolodziej H. Kolodziej H. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2011 Oct 10;4(10):1295-1314. doi: 10.3390/ph4101295. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2011. PMID: 27721327 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Multi-Omics Approach in the Identification of Potential Therapeutic Biomolecule for COVID-19.
Singh R, Singh PK, Kumar R, Kabir MT, Kamal MA, Rauf A, Albadrani GM, Sayed AA, Mousa SA, Abdel-Daim MM, Uddin MS. Singh R, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 12;12:652335. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.652335. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34054532 Free PMC article. Review. - Glycyrrhizic acid as the antiviral component of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. against coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus 71 of hand foot and mouth disease.
Wang J, Chen X, Wang W, Zhang Y, Yang Z, Jin Y, Ge HM, Li E, Yang G. Wang J, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 May 2;147(1):114-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.02.017. Epub 2013 Feb 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23454684 Free PMC article. - Medicinal properties and conservation of Pelargonium sidoides DC.
Moyo M, Van Staden J. Moyo M, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Mar 14;152(2):243-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.01.009. Epub 2014 Jan 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24463034 Free PMC article. Review. - Chronobiological Efficacy of Combined Therapy of Pelargonium Sidoides and Melatonin in Acute and Persistent Cases of COVID-19: A Hypothetical Approach.
Taner N, Haskologlu IC, Erdag E, Mercan M, Chuckwunyere U, Ulker D, Sehirli AO, Abacioglu N. Taner N, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1412:427-442. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-28012-2_23. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37378781 Review. - A Review on Plant Bioactive Compounds and Their Modes of Action Against Coronavirus Infection.
Remali J, Aizat WM. Remali J, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 11;11:589044. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.589044. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33519449 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Agbabiaka T.B., Guo R., Ernst E. Pelargonium sidoides for acute bronchitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytomedicine. 2008;15:378–385. - PubMed
- Brendler T., van Wyk B.E. A historical, scientific and commercial perspective on the medicinal use of Pelargonium sidoides (Geraniaceae) J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008;119:420–433. - PubMed
- Cernik C., Gallina K., Brodell R.T. The treatment of herpes simplex infections: an evidence-based review. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008;168:1137–1144. - PubMed
- Cinatl J., Jr., Cinatl J., Rabenau H., Gümbel H.O., Kornhuber B., Doerr H.W. In vitro inhibition of human cytomegalovirus replication by desferrioxamine. Antiviral Res. 1994;25:73–77. - PubMed
- Conrad A., Kolodziej H., Schulz V. Pelargonium sidoides-Extrakt (Eps® 7630): Zulassung bestätigt Wirksamkeit und Verträglichkeit. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2007;157:331–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources