Genetic evaluation of the nine component features of hip score in UK Labrador Retrievers - PubMed (original) (raw)
Genetic evaluation of the nine component features of hip score in UK Labrador Retrievers
Thomas W Lewis et al. PLoS One. 2010.
Abstract
The aim of this study was to explore the genetic relationship between the nine component traits comprising the British Veterinary Association (BVA) total hip score in UK registered Labrador Retrievers. Data consisted of 11,928 single records of trait scores of dogs aged between one and four years (365-1459 days) old, from radiographs evaluated between 2000 and 2007. Pedigree information was provided by the UK Kennel Club. The distribution of trait scores showed only small numbers of dogs with visible malformation in the six traits that were scored according to the severity of osteoarthritis. Linear mixed models were fitted using ASREML. Estimates of heritability ranged from 0.15 to 0.38, and litter effects from 0.04 to 0.10. Genetic correlations between all nine traits were extremely high ranging from 0.71 to 1.0, implying considerable genetic similarity. The decomposition demonstrated that aggregate scores of only the 3 traits indicative of laxity in one year old dogs was predictive of the phenotype of the remaining six scored on osteoarthritic severity in dogs at 4+ years old. The application of selection index methodology in selecting against hip dysplasia using the trait scores was explored and potential improvements in accuracy (directly related to response to selection) of over 10% are reported compared to the current total hip score. This study demonstrates that traits descriptive of joint laxity are valuable early-age predictors of osteoarthritis and shows that there is scope for improvement in the way data from the UK hip score scheme are used for selection against hip dysplasia in Labradors. This was verified via use of selection indices, which identified substantial increases in accuracy, not only via optimum coefficients, but also through an easily applicable aggregate of scores of just two or three traits only compared with the current total hip score.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: Hip score and pedigree data was collated and provided by the Kennel Club.
Figures
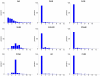
Figure 1. Distribution of total score.
Left + right hip score for the 9 traits contributing to total hip score.
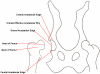
Figure 2. Diagrammatical representation of the skeletal features of the hip joint.
Features pertinent to those graded by the BVA/KC hip score scheme.
Similar articles
- Heritability and epidemiology of canine hip-dysplasia score and its components in Labrador retrievers in the United Kingdom.
Wood JL, Lakhani KH, Rogers K. Wood JL, et al. Prev Vet Med. 2002 Sep 30;55(2):95-108. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5877(02)00090-9. Prev Vet Med. 2002. PMID: 12350314 - Genetic evaluation of hip score in UK Labrador Retrievers.
Lewis TW, Blott SC, Woolliams JA. Lewis TW, et al. PLoS One. 2010 Oct 22;5(10):e12797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012797. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21042573 Free PMC article. - Genetic evaluation of elbow scores and the relationship with hip scores in UK Labrador retrievers.
Lewis TW, Ilska JJ, Blott SC, Woolliams JA. Lewis TW, et al. Vet J. 2011 Aug;189(2):227-33. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2011.06.024. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Vet J. 2011. PMID: 21737324 - Canine hip and elbow dysplasia in UK Labrador retrievers.
Woolliams JA, Lewis TW, Blott SC. Woolliams JA, et al. Vet J. 2011 Aug;189(2):169-76. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2011.06.015. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Vet J. 2011. PMID: 21737322 Review. - Genetics of canine hip dysplasia.
Leighton EA. Leighton EA. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1997 May 15;210(10):1474-9. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1997. PMID: 9154200 Review.
Cited by
- Genetic correlations among canine hip dysplasia radiographic traits in a cohort of Australian German Shepherd Dogs, and implications for the design of a more effective genetic control program.
Wilson BJ, Nicholas FW, James JW, Wade CM, Raadsma HW, Thomson PC. Wilson BJ, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Nov 7;8(11):e78929. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078929. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24244386 Free PMC article. - Quantitative trait loci mapping for canine hip dysplasia and its related traits in UK Labrador Retrievers.
Sánchez-Molano E, Woolliams JA, Pong-Wong R, Clements DN, Blott SC, Wiener P. Sánchez-Molano E, et al. BMC Genomics. 2014 Oct 1;15(1):833. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-833. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25270232 Free PMC article. - Comparative analyses of genetic trends and prospects for selection against hip and elbow dysplasia in 15 UK dog breeds.
Lewis TW, Blott SC, Woolliams JA. Lewis TW, et al. BMC Genet. 2013 Mar 2;14:16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-14-16. BMC Genet. 2013. PMID: 23452300 Free PMC article. - Joint Genomic Prediction of Canine Hip Dysplasia in UK and US Labrador Retrievers.
Edwards SM, Woolliams JA, Hickey JM, Blott SC, Clements DN, Sánchez-Molano E, Todhunter RJ, Wiener P. Edwards SM, et al. Front Genet. 2018 Mar 28;9:101. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00101. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 29643866 Free PMC article. - Heritability and phenotypic variation of canine hip dysplasia radiographic traits in a cohort of Australian German shepherd dogs.
Wilson BJ, Nicholas FW, James JW, Wade CM, Tammen I, Raadsma HW, Castle K, Thomson PC. Wilson BJ, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39620. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039620. Epub 2012 Jun 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22761846 Free PMC article.
References
- Malm S, Fikse WF, Danell B, Strandberg E. Genetic variation and genetic trends in hip and elbow dysplasia in Swedish Rottweiler and Bernese Mountain Dog. J Anim Breed Genet. 2008;125:403–412. - PubMed
- Willis MB. A review of the progress in canine hip dysplasia control in Britain. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1997;210:1480–1482. - PubMed
- Leppanen M, Saloniemi H. Controlling canine hip dysplasia in Finland. Prev Vet Med. 1999;42:121–131. - PubMed
- Brass W. Hip dysplasia in dogs. Journal of small animal practice. 1989;30:166–170.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical