European guidelines on managing adverse effects of medication for ADHD - PubMed (original) (raw)
Practice Guideline
doi: 10.1007/s00787-010-0140-6. Epub 2010 Nov 3.
T Banaschewski, J Buitelaar, D Coghill, M Danckaerts, R W Dittmann, M Döpfner, R Hamilton, C Hollis, M Holtmann, M Hulpke-Wette, M Lecendreux, E Rosenthal, A Rothenberger, P Santosh, J Sergeant, E Simonoff, E Sonuga-Barke, I C K Wong, A Zuddas, H-C Steinhausen, E Taylor; European Guidelines Group
Affiliations
- PMID: 21042924
- PMCID: PMC3012210
- DOI: 10.1007/s00787-010-0140-6
Practice Guideline
European guidelines on managing adverse effects of medication for ADHD
J Graham et al. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2011 Jan.
Abstract
The safety of ADHD medications is not fully known. Concerns have arisen about both a lack of contemporary-standard information about medications first licensed several decades ago, and signals of possible harm arising from more recently developed medications. These relate to both relatively minor adverse effects and extremely serious issues such as sudden cardiac death and suicidality. A guidelines group of the European Network for Hyperkinetic Disorders (EUNETHYDIS) has therefore reviewed the literature, recruited renowned clinical subspecialists and consulted as a group to examine these concerns. Some of the effects examined appeared to be minimal in impact or difficult to distinguish from risk to untreated populations. However, several areas require further study to allow a more precise understanding of these risks.
Figures
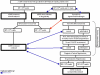
Fig. 1
Recommendation for blood pressure (BP) monitoring and management in ADHD patients
Similar articles
- ADHD update: new data on the risks of medication.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] Harv Ment Health Lett. 2006 Oct;23(4):3-5. Harv Ment Health Lett. 2006. PMID: 17183739 No abstract available. - Atomoxetine: a review of its use in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents.
Garnock-Jones KP, Keating GM. Garnock-Jones KP, et al. Paediatr Drugs. 2009;11(3):203-26. doi: 10.2165/00148581-200911030-00005. Paediatr Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19445548 Review. - Pharmacologic treatment of ADHD: road conditions in driving patients to successful outcomes.
Manos MJ. Manos MJ. Medscape J Med. 2008 Jan 8;10(1):5. Medscape J Med. 2008. PMID: 18324315 Free PMC article. Review. - Sleep disturbances and ADHD medications.
Rostain AL. Rostain AL. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2007 Oct;9(5):399-400. doi: 10.1007/s11920-007-0051-5. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2007. PMID: 17915079 No abstract available. - Priapism associated with the use of stimulant medications and atomoxetine for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children.
Eiland LS, Bell EA, Erramouspe J. Eiland LS, et al. Ann Pharmacother. 2014 Oct;48(10):1350-5. doi: 10.1177/1060028014541791. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Ann Pharmacother. 2014. PMID: 24982313 Review.
Cited by
- Association between ADHD drug use and injuries among children and adolescents.
van den Ban E, Souverein P, Meijer W, van Engeland H, Swaab H, Egberts T, Heerdink E. van den Ban E, et al. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014 Feb;23(2):95-102. doi: 10.1007/s00787-013-0432-8. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 23733150 - Amfetamine and methylphenidate medications for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: complementary treatment options.
Hodgkins P, Shaw M, Coghill D, Hechtman L. Hodgkins P, et al. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Sep;21(9):477-92. doi: 10.1007/s00787-012-0286-5. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22763750 Free PMC article. Review. - Is Physical Activity Causally Associated With Symptoms of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder?
Rommel AS, Lichtenstein P, Rydell M, Kuja-Halkola R, Asherson P, Kuntsi J, Larsson H. Rommel AS, et al. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2015 Jul;54(7):565-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2015.04.011. Epub 2015 May 5. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26088661 Free PMC article. - ADHD in children and youth: Part 1-Etiology, diagnosis, and comorbidity.
Bélanger SA, Andrews D, Gray C, Korczak D. Bélanger SA, et al. Paediatr Child Health. 2018 Nov;23(7):447-453. doi: 10.1093/pch/pxy109. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Paediatr Child Health. 2018. PMID: 30681669 Free PMC article. Review. - Differential Efficacy of Neurofeedback in Children with ADHD Presentations.
Cueli M, Rodríguez C, Cabaleiro P, García T, González-Castro P. Cueli M, et al. J Clin Med. 2019 Feb 7;8(2):204. doi: 10.3390/jcm8020204. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 30736419 Free PMC article.
References
- (1999) A 14-month randomized clinical trial of treatment strategies for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. The MTA Cooperative Group. Multimodal Treatment Study of Children with ADHD. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56:1073–1086 - PubMed
- (2001) Methylphenidate and narcolepsy: new indication. When modafinil fails. Prescrire Int 10:7–9 - PubMed
- (2002) Treatment of ADHD in children with tics: a randomized controlled trial. Neurology 58:527–536 - PubMed
- (2004) The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 114:555–576 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical