TNF-alpha antagonism with etanercept decreases glucose and increases the proportion of high molecular weight adiponectin in obese subjects with features of the metabolic syndrome - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2011 Jan;96(1):E146-50.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-1170. Epub 2010 Nov 3.
Affiliations
- PMID: 21047923
- PMCID: PMC3038481
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2010-1170
Randomized Controlled Trial
TNF-alpha antagonism with etanercept decreases glucose and increases the proportion of high molecular weight adiponectin in obese subjects with features of the metabolic syndrome
Takara L Stanley et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Jan.
Abstract
Context and objective: Obesity is associated with activation of the TNF-α system, increased inflammatory markers, and insulin resistance. Although studies in rodents suggest that attenuation of TNF activity improves glucose homeostasis, the effect of prolonged inhibition of TNF-α with etanercept on inflammation and glucose homeostasis in a human model of obesity is not known.
Design and participants: Forty obese subjects with features of metabolic syndrome were randomized to etanercept or placebo, 50 mg twice weekly for 3 months, followed by 50 mg once weekly for 3 months.
Outcome measures: Subjects underwent oral glucose tolerance testing and measurement of serum inflammatory biomarkers and adipokines. Subcutaneous fat biopsy was performed in a subset for measurement of adipokine and TNF-α mRNA expression.
Results: Visceral adiposity was significantly associated with serum concentrations of TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1), TNFR2, and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and adipose tissue expression of TNF-α and SOCS-3 (all P < 0.05). Insulin resistance as assessed by homeostasis model assessment was significantly associated with TNFR1, C-reactive protein, IL-6, and soluble intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) (all P < 0.05). Etanercept significantly improved fasting glucose (treatment effect vs. placebo over 6 months, -10.8 ± 4.4%, P = 0.02). Etanercept also increased the ratio of high molecular weight adiponectin to total adiponectin (+22.1 ± 9.2% vs. placebo, P = 0.02), and decreased levels of sICAM-1 (-11 ± 2% vs. placebo, P < 0.0001). In contrast, body composition, lipids, C-reactive protein, and IL-6 were unchanged after 6 months.
Conclusions: Prolonged therapy with etanercept improved fasting glucose, increased the ratio of high molecular weight to total adiponectin, and decreased sICAM-1 in obese subjects with abnormal glucose homeostasis and significant subclinical inflammation.
Figures
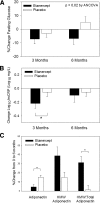
Figure 1
Effect of etanercept on glucose, hsCRP, and adiponectin: changes in etanercept (black bars) and placebo (white bars) groups. Error bars are
se
. A, Percent change in fasting glucose at 3 and 6 months; P = 0.02 for etanercept vs. placebo by repeated-measures ANCOVA. B, Change in log10 hsCRP at 3 and 6 months. *, P = 0.03 for change in etanercept vs. placebo at 3 months controlling for age and race. Change between groups is not significantly different at 6 months. C, Aggregate percent change in total adiponectin, HMW adiponectin, and ratio of HMW to total adiponectin over 6 months. *, P < 0.05 for etanercept vs. placebo by repeated-measures ANCOVA.
Similar articles
- Effects of TNF-alpha antagonism on E-selectin in obese subjects with metabolic dysregulation.
Zanni MV, Stanley TL, Makimura H, Chen CY, Grinspoon SK. Zanni MV, et al. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2010 Jul;73(1):48-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2009.03741.x. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2010. PMID: 19878508 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Effects of TNF-alpha neutralization on adipocytokines and skeletal muscle adiposity in the metabolic syndrome.
Lo J, Bernstein LE, Canavan B, Torriani M, Jackson MB, Ahima RS, Grinspoon SK. Lo J, et al. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Jul;293(1):E102-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00089.2007. Epub 2007 Mar 20. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 17374698 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Effects of etanercept in patients with the metabolic syndrome.
Bernstein LE, Berry J, Kim S, Canavan B, Grinspoon SK. Bernstein LE, et al. Arch Intern Med. 2006 Apr 24;166(8):902-8. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.8.902. Arch Intern Med. 2006. PMID: 16636217 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - TNF-alpha inhibitors for ankylosing spondylitis.
Maxwell LJ, Zochling J, Boonen A, Singh JA, Veras MM, Tanjong Ghogomu E, Benkhalti Jandu M, Tugwell P, Wells GA. Maxwell LJ, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 18;2015(4):CD005468. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005468.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25887212 Free PMC article. Review. - Adiponectin Resistance in Obesity: Adiponectin Leptin/Insulin Interaction.
Engin A. Engin A. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:431-462. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287861 Review.
Cited by
- Gene silencing in adipose tissue macrophages regulates whole-body metabolism in obese mice.
Aouadi M, Tencerova M, Vangala P, Yawe JC, Nicoloro SM, Amano SU, Cohen JL, Czech MP. Aouadi M, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 May 14;110(20):8278-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300492110. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23630254 Free PMC article. - Targeting adipose tissue in the treatment of obesity-associated diabetes.
Kusminski CM, Bickel PE, Scherer PE. Kusminski CM, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016 Sep;15(9):639-660. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.75. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27256476 Review. - Regulation of metabolism by the innate immune system.
Lackey DE, Olefsky JM. Lackey DE, et al. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016 Jan;12(1):15-28. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2015.189. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26553134 Review. - Neurogenic obesity and systemic inflammation following spinal cord injury: A review.
Farkas GJ, Gater DR. Farkas GJ, et al. J Spinal Cord Med. 2018 Jul;41(4):378-387. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2017.1357104. Epub 2017 Jul 30. J Spinal Cord Med. 2018. PMID: 28758554 Free PMC article. Review. - Transcriptome-wide Mendelian randomization during CD4+ T cell activation reveals immune-related drug targets for cardiometabolic diseases.
Wu X, Ying H, Yang Q, Yang Q, Liu H, Ding Y, Zhao H, Chen Z, Zheng R, Lin H, Wang S, Li M, Wang T, Zhao Z, Xu M, Chen Y, Xu Y, Vincent EE, Borges MC, Gaunt TR, Ning G, Wang W, Bi Y, Zheng J, Lu J. Wu X, et al. Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 28;15(1):9302. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53621-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39468075 Free PMC article.
References
- Kern PA, Ranganathan S, Li C, Wood L, Ranganathan G 2001 Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 280:E745–E751 - PubMed
- Dandona P, Weinstock R, Thusu K, Abdel-Rahman E, Aljada A, Wadden T 1998 Tumor necrosis factor-α in sera of obese patients: fall with weight loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:2907–2910 - PubMed
- Ofei F, Hurel S, Newkirk J, Sopwith M, Taylor R 1996 Effects of an engineered human anti-TNF-α antibody (CDP571) on insulin sensitivity and glycemic control in patients with NIDDM. Diabetes 45:881–885 - PubMed
- Paquot N, Castillo MJ, Lefèbvre PJ, Scheen AJ 2000 No increased insulin sensitivity after a single intravenous administration of a recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor: Fc fusion protein in obese insulin-resistant patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:1316–1319 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 DK089910/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK040561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK085969/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01-DK049210/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK085969-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK049210/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK064545-06/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK089910-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1 UL1 RR025758-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK080642-02/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK064545/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK087857/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK080642/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials