miR-200b precursor can ameliorate renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2010 Oct 25;5(10):e13614.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013614.
Shintaro Kumano, Etsu Suzuki, Hiroaki Nishimatsu, Masao Takahashi, Hajime Takamori, Masatoshi Kasuya, Yousuke Ogawa, Kenichiro Sato, Kenjiro Kimura, Yukio Homma, Yasunobu Hirata, Toshiro Fujita
Affiliations
- PMID: 21049046
- PMCID: PMC2963611
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013614
miR-200b precursor can ameliorate renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis
Shigeyoshi Oba et al. PLoS One. 2010.
Abstract
Members of the miR-200 family of micro RNAs (miRNAs) have been shown to inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). EMT of tubular epithelial cells is the mechanism by which renal fibroblasts are generated. Here we show that miR-200 family members inhibit transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta)-induced EMT of tubular cells. Unilateral ureter obstruction (UUO) is a common model of EMT of tubular cells and subsequent tubulointerstitial fibrosis. In order to examine the role of miR-200 family members in tubulointerstitial fibrosis, their expression was investigated in the kidneys of UUO mice. The expression of miR-200 family miRNAs was increased in a time-dependent manner, with induction of miR-200b most pronounced. To clarify the effect of miR-200b on tubulointerstitial fibrosis, we injected miR-200b precursor intravenously. A single injection of 0.5 nM miR-200b precursor was sufficient to inhibit the increase of collagen types I, III and fibronectin in obstructed kidneys, and amelioration of fibrosis was confirmed by observation of the kidneys with Azan staining. miR-200 family members have been previously shown to inhibit EMT by reducing the expression of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2 which are known repressors of E-cadherin. We demonstrated that expression of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2 was increased after ureter obstruction and that administration of the miR-200b precursor reversed this effect. In summary, these results indicate that miR-200 family is up-regulated after ureter obstruction, miR-200b being strongly induced, and that miR-200b ameliorates tubulointerstitial fibrosis in obstructed kidneys. We suggest that members of the miR-200 family, and miR-200b specifically, might constitute novel therapeutic targets in kidney disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
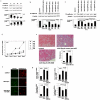
Figure 1. miR-200 family members can ameliorate EMT and tubulointerstitial fibrosis in UUO model mouse kidneys.
a, Western blotting analysis confirms down-regulation of E-cadherin and up-regulation of N-cadherin during EMT. b,c, Western blotting of E-cadherin and N-cadherin in HK-2 cells treated with TGF-beta and transfected with control miR or miR-200 members precursors individually. In western blotting, each band has been quantitated and subjected to densitometry to determine if statistically significant difference exists between groups d, Changes in miR-200 family levels in UUO model mice kidneys, as measured by TaqMan qRT-PCR and normalized to U6 expression. The data are means from a representative time course experiment measured in triplicate and are presented as mean±S.E. e, Azan staining of intact Balbc mouse kidney, UUO day-6 kidneys after transfection of negative control pre-miR or miR-200b precursor. Fibrosis score; The tubulointerstitial fibrosis score in kidneys of miR-200b precursor injected group was significantly lower than of control group: P<0.05, The data are means from experiment measured in triplicate and are presented as mean±S.E (n = 8) f, Immunofluorescence studies of vimentin and cytokeratin 18 in the kidneys of UUO day6 mice and UUO day6 mice injected by miR-200b precursor. miR-200b ameliorates up-regulation of vimentin and down-regulation of cytokeratin 18. g, real-time PCR confirms that miR-200b precursor reverses up-regulation of type I,III collagen and fibronectin of UUO day-6 kidneys. The data are normalized to beta-actin mRNA and shown as mean±S.E.(n = 8).
Figure 2. Injected miR-200b precursor can be converted to mature miR-200b in kidneys.
a. Laser microscopy images of kidney, frozen sections at 24 hr after intravenously administration of Cy3 dye-labeled Pre-miR control. b. Changes in miR-200 family levels in Balbc mice kidneys 12, 24, 48 hours after intravenously administration of miR-200b precursor, as measured by TaqMan qRT-PCR and normalized to U6 expression. The data are means from experiment measured in triplicate and are presented as mean±S.E. P<0.05: kidneys 12, 24 hours after intravenously administration of miR-200b precursor compared with 0 hour.
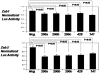
Figure 3. miR-200 family members target the transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2.
Normalized activity of luciferase reporter with the ZEB1 or ZEB2 3′UTR in HK-2 cells in the presence of co-transfected negative control pre-miR or miR-200 family individually. Luciferase activity was measured after 24 hours. The data are mean±S.E. of triplicates and are shown as the ratio of firefly to Renilla luciferase activity. P<0.05: HK-2 cells in the presence of co-transfected miR-200 family compared with negative control pre-miR
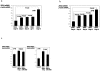
Figure 4. ZEB1 and ZEB2 expression in UUO model mice.
a,b, Real time PCR analysis of ZEB1 or ZEB2 mRNA in kidneys obstructed for 2,4,6 or 8 days. The data are normalized to beta-actin mRNA and shown as mean±S.E.(n = 8). P<0.05: kidneys obstructed for 2,4,6 and 8 compared with 0 day c, Real time PCR analysis of ZEB1 or ZEB2 mRNA in obstructed for 6 days after i.v. administration of miR-200b precursor. The data are normalized to beta-actin mRNA and shown as mean±S.E.(n = 8). P<0.05: obstructed for 6 days after i.v. administration of miR-200b precursor compared with negative control pre-miR.
Similar articles
- MiR-200b/c family inhibits renal fibrosis through modulating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via targeting fascin-1/CD44 axis.
Fu H, Gu YH, Yang YN, Liao S, Wang GH. Fu H, et al. Life Sci. 2020 Jul 1;252:117589. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117589. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32220622 - microRNA-29b prevents renal fibrosis by attenuating renal tubular epithelial cell-mesenchymal transition through targeting the PI3K/AKT pathway.
Hu S, Hu H, Wang R, He H, Shui H. Hu S, et al. Int Urol Nephrol. 2021 Sep;53(9):1941-1950. doi: 10.1007/s11255-021-02836-4. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Int Urol Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33742315 Free PMC article. - The miR-200 family regulates TGF-β1-induced renal tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition through Smad pathway by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2 expression.
Xiong M, Jiang L, Zhou Y, Qiu W, Fang L, Tan R, Wen P, Yang J. Xiong M, et al. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Feb 1;302(3):F369-79. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00268.2011. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22012804 - miR-141 regulates TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through repression of HIPK2 expression in renal tubular epithelial cells.
Huang Y, Tong J, He F, Yu X, Fan L, Hu J, Tan J, Chen Z. Huang Y, et al. Int J Mol Med. 2015 Feb;35(2):311-8. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.2008. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25421593 Free PMC article. - miRNA and mRNA expression profiling identifies members of the miR-200 family as potential regulators of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pterygium.
Engelsvold DH, Utheim TP, Olstad OK, Gonzalez P, Eidet JR, Lyberg T, Trøseid AM, Dartt DA, Raeder S. Engelsvold DH, et al. Exp Eye Res. 2013 Oct;115:189-98. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Exp Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23872359 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- MicroRNAs and fibrosis.
Patel V, Noureddine L. Patel V, et al. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012 Jul;21(4):410-6. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e328354e559. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012. PMID: 22622653 Free PMC article. Review. - Inhibiting microRNA-192 ameliorates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy.
Putta S, Lanting L, Sun G, Lawson G, Kato M, Natarajan R. Putta S, et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Mar;23(3):458-69. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011050485. Epub 2012 Jan 5. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22223877 Free PMC article. - Revisiting the miR-200 Family: A Clan of Five Siblings with Essential Roles in Development and Disease.
Sundararajan V, Burk UC, Bajdak-Rusinek K. Sundararajan V, et al. Biomolecules. 2022 Jun 3;12(6):781. doi: 10.3390/biom12060781. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35740906 Free PMC article. Review. - Stromal miR-200s contribute to breast cancer cell invasion through CAF activation and ECM remodeling.
Tang X, Hou Y, Yang G, Wang X, Tang S, Du YE, Yang L, Yu T, Zhang H, Zhou M, Wen S, Xu L, Liu M. Tang X, et al. Cell Death Differ. 2016 Jan;23(1):132-45. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.78. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 26068592 Free PMC article. - MicroRNA-324-3p promotes renal fibrosis and is a target of ACE inhibition.
Macconi D, Tomasoni S, Romagnani P, Trionfini P, Sangalli F, Mazzinghi B, Rizzo P, Lazzeri E, Abbate M, Remuzzi G, Benigni A. Macconi D, et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Sep;23(9):1496-505. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011121144. Epub 2012 Jul 19. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22822076 Free PMC article.
References
- Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A, et al. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1and SIP1. Nature cell biology. 2008;10:593–601. - PubMed
- Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, Bert AG, Wang J, et al. A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2008;68:7846–7854. - PubMed
- Duband JL, Monier F, Delannet M, Newgreen D. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition during neural crest development. Acta Anat. 1995;154:63–78. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials