Effects of vitamin E on stroke subtypes: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials - PubMed (original) (raw)
Meta-Analysis
Effects of vitamin E on stroke subtypes: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Markus Schürks et al. BMJ. 2010.
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effect of vitamin E supplementation on incident total, ischaemic, and haemorrhagic stroke.
Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised, placebo controlled trials published until January 2010.
Data sources: Electronic databases (Medline, Embase, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials) and reference lists of trial reports. Selection criteria Randomised, placebo controlled trials with ≥1 year of follow-up investigating the effect of vitamin E on stroke. Review methods and data extraction Two investigators independently assessed eligibility of identified trials. Disagreements were resolved by consensus. Two different investigators independently extracted data. Risk ratios (and 95% confidence intervals) were calculated for each trial based on the number of cases and non-cases randomised to vitamin E or placebo. Pooled effect estimates were then calculated.
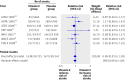
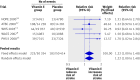
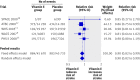
Results: Nine trials investigating the effect of vitamin E on incident stroke were included, totalling 118 765 participants (59 357 randomised to vitamin E and 59 408 to placebo). Among those, seven trials reported data for total stroke and five trials each for haemorrhagic and ischaemic stroke. Vitamin E had no effect on the risk for total stroke (pooled relative risk 0.98 (95% confidence interval 0.91 to 1.05), P=0.53). In contrast, the risk for haemorrhagic stroke was increased (pooled relative risk 1.22 (1.00 to 1.48), P=0.045), while the risk of ischaemic stroke was reduced (pooled relative risk 0.90 (0.82 to 0.99), P=0.02). There was little evidence for heterogeneity among studies. Meta-regression did not identify blinding strategy, vitamin E dose, or morbidity status of participants as sources of heterogeneity. In terms of absolute risk, this translates into one additional haemorrhagic stroke for every 1250 individuals taking vitamin E, in contrast to one ischaemic stroke prevented per 476 individuals taking vitamin E.
Conclusion: In this meta-analysis, vitamin E increased the risk for haemorrhagic stroke by 22% and reduced the risk of ischaemic stroke by 10%. This differential risk pattern is obscured when looking at total stroke. Given the relatively small risk reduction of ischaemic stroke and the generally more severe outcome of haemorrhagic stroke, indiscriminate widespread use of vitamin E should be cautioned against.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the Unified Competing Interest form at www.icmje.org/coi\_disclosure.pdf (available on request from the corresponding author) and declare: that for the specific matter of this research, no support from any organisation for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
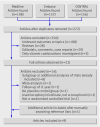
Fig 1 Flow chart of identifying and including trials
Fig 2 Relative risks of the effect of vitamin E on total stroke for individual trials and for the pooled population
Fig 3 Relative risks of the effect of vitamin E on haemorrhagic stroke for individual trials and for the pooled population
Fig 4 Relative risks of the effect of vitamin E on ischaemic stroke for individual trials and for the pooled population
Similar articles
- Antioxidant vitamin and mineral supplements for preventing age-related macular degeneration.
Evans JR, Lawrenson JG. Evans JR, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 30;7(7):CD000253. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000253.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28756617 Free PMC article. - Antioxidant vitamin and mineral supplements for slowing the progression of age-related macular degeneration.
Evans JR, Lawrenson JG. Evans JR, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 31;7(7):CD000254. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000254.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28756618 Free PMC article. Updated. - Nutritional interventions for survivors of childhood cancer.
Cohen JE, Wakefield CE, Cohn RJ. Cohen JE, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 22;2016(8):CD009678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27545902 Free PMC article. - Herbal and dietary therapies for primary and secondary dysmenorrhoea.
Proctor ML, Murphy PA. Proctor ML, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD002124. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002124. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. PMID: 11687013 Updated. - Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.
Sbidian E, Chaimani A, Afach S, Doney L, Dressler C, Hua C, Mazaud C, Phan C, Hughes C, Riddle D, Naldi L, Garcia-Doval I, Le Cleach L. Sbidian E, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
- Antioxidants and the risk of stroke: results from NHANES and two-sample Mendelian randomization study.
Chen R, Liu H, Zhang G, Zhang Q, Hua W, Zhang L, Lv N, Zhang Y, Dai D, Zhao R, Li Q, Huang Q, Xu Y, Yang P, Liu J, Zuo Q. Chen R, et al. Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jan 12;29(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01646-5. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38217043 Free PMC article. - NAFLD and liver transplantation: Current burden and expected challenges.
Pais R, Barritt AS 4th, Calmus Y, Scatton O, Runge T, Lebray P, Poynard T, Ratziu V, Conti F. Pais R, et al. J Hepatol. 2016 Dec;65(6):1245-1257. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.033. Epub 2016 Jul 30. J Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27486010 Free PMC article. Review. - Oral tocotrienols are transported to human tissues and delay the progression of the model for end-stage liver disease score in patients.
Patel V, Rink C, Gordillo GM, Khanna S, Gnyawali U, Roy S, Shneker B, Ganesh K, Phillips G, More JL, Sarkar A, Kirkpatrick R, Elkhammas EA, Klatte E, Miller M, Firstenberg MS, Chiocca EA, Nesaretnam K, Sen CK. Patel V, et al. J Nutr. 2012 Mar;142(3):513-9. doi: 10.3945/jn.111.151902. Epub 2012 Feb 1. J Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22298568 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - An automated framework for hypotheses generation using literature.
Abedi V, Zand R, Yeasin M, Faisal FE. Abedi V, et al. BioData Min. 2012 Aug 29;5(1):13. doi: 10.1186/1756-0381-5-13. BioData Min. 2012. PMID: 22931688 Free PMC article. - Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), Type 2 Diabetes, and Non-viral Hepatocarcinoma: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and New Therapeutic Strategies.
Vetrano E, Rinaldi L, Mormone A, Giorgione C, Galiero R, Caturano A, Nevola R, Marfella R, Sasso FC. Vetrano E, et al. Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 6;11(2):468. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020468. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36831004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Clarke MW, Burnett JR, Croft KD. Vitamin E in human health and disease. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 2008;45:417-50. - PubMed
- Navab M, Ananthramaiah GM, Reddy ST, Van Lenten BJ, Ansell BJ, Fonarow GC, et al. The oxidation hypothesis of atherogenesis: the role of oxidized phospholipids and HDL. J Lipid Res 2004;45:993-1007. - PubMed
- Kushi LH, Folsom AR, Prineas RJ, Mink PJ, Wu Y, Bostick RM. Dietary antioxidant vitamins and death from coronary heart disease in postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med 1996;334:1156-62. - PubMed
- Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Ascherio A, Giovannucci E, Colditz GA, Willett WC. Vitamin E consumption and the risk of coronary heart disease in men. N Engl J Med 1993;328:1450-6. - PubMed
- Stampfer MJ, Hennekens CH, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Rosner B, Willett WC. Vitamin E consumption and the risk of coronary disease in women. N Engl J Med 1993;328:1444-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical