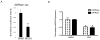Identification of SR3335 (ML-176): a synthetic RORα selective inverse agonist - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2011 Mar 18;6(3):218-22.
doi: 10.1021/cb1002762. Epub 2010 Dec 6.
Affiliations
- PMID: 21090593
- PMCID: PMC3076127
- DOI: 10.1021/cb1002762
Identification of SR3335 (ML-176): a synthetic RORα selective inverse agonist
Naresh Kumar et al. ACS Chem Biol. 2011.
Abstract
Several nuclear receptors (NRs) are still character-ized as orphan receptors because ligands have not yet been identified for these proteins. The retinoic acid receptor-related receptors (RORs) have no well-defined physiological ligands. Here, we describe the identification of a selective RORα synthetic ligand, SR3335 (ML-176). SR3335 directly binds to RORα, but not other RORs, and functions as a selective partial inverse agonist of RORα in cell-based assays. Furthermore, SR3335 suppresses the expression of endogenous RORα target genes in HepG2 involved in hepatic gluconeogenesis including glucose-6-phosphatase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. Pharmacokinetic studies indicate that SR3335 displays reasonable exposure following an ip injection into mice. We assess the ability of SR3335 to suppress gluconeogenesis in vivo using a diet-induced obesity (DIO) mouse model where the mice where treated with 15 mg/kg b.i.d., ip for 6 days followed by a pyruvate tolerance test. SR3335-treated mice displayed lower plasma glucose levels following the pyruvate challenge consistent with suppression of gluconeogenesis. Thus, we have identified the first selective synthetic RORα inverse agonist, and this compound can be utilized as a chemical tool to probe the function of this receptor both in vitro and in vivo. Additionally, our data suggests that RORα inverse agonists may hold utility for suppression of elevated hepatic glucose production in type 2 diabetics.
Figures
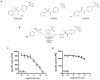
Figure 1
Identification of a selective RORα synthetic ligand, SR3335. A) Comparison of the chemical structure of T0901317 to SR3335 and SR1078. B) Scheme illustrating the synthesis of SR3335. C) Competition radioligand binding assay illustrating the ability of SR3335 to displace radiolabeled 25-hydroxycholesterol from RORα LBD. D) Competition radioligand binding assay illustrating the inability of SR3335 to displace radiolabeled 25-hydroxycholesterol from RORγ LBD.
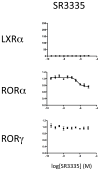
Figure 2
SR3335 is a selective RORα partial inverse agonist. Cotransfection of HEK293 cells with RORα, RORγ or LXRα LBD fused to a GAL4 DNA binding domain and a reporter containing 5 copies of the GAL4 UAS upstream of a luciferase reporter. The effect of T1317 is compared to SR3335 in each assay.
Figure 3
SR3335 suppresses the expression of RORα target genes. A) Treatment of HepG2 cells with 5 μM SR3335 results in suppression of transcription in a full-length RORα, G6Pase promoter-luciferase reporter cotransfection assay. G6Pase expression was normalized to cyclophilin. B) Treatment of HepG2 cells with 5 μM SR3335 results in suppression of G6Pase and PEPCK mRNA expression. *, indicates p<0.05.
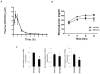
Figure 4
SR3335 suppresses gluconeogenesis in vivo. A) Pharmcokinetic profile SR3335 following a single injection of 10 mg/kg i.p. B) Pyruvate tolerance test in diet induced obese (DIO) mice (C57Bl/6) following 1 week of b.i.d. dosing (i.p.) 15 mg/kg. C) Gene expression in mice following administration of SR3335 as inidicated in 4B. Gene expression was normalized to cyclophilin. *, indicates p<0.05.
Similar articles
- Identification of a novel selective inverse agonist probe and analogs for the Retinoic acid receptor-related Orphan Receptor Alpha (RORα).
Kumar N, Nuhant P, Solt LA, Conkright JJ, Wang Y, Istrate MA, Busby SA, Ruben DGO, Burris TP, Cameron M, Mercer BA, Hodder P, Roush WR, Rosen H, Griffin PR. Kumar N, et al. 2010 Sep 1 [updated 2013 Mar 14]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. 2010 Sep 1 [updated 2013 Mar 14]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. PMID: 23762959 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Discovery and Optimization of a Series of Sulfonamide Inverse Agonists for the Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor-α.
Doebelin C, He Y, Campbell S, Nuhant P, Kumar N, Koenig M, Garcia-Ordonez R, Chang MR, Roush WR, Lin L, Kahn S, Cameron MD, Griffin PR, Solt LA, Kamenecka TM. Doebelin C, et al. Med Chem. 2019;15(6):676-684. doi: 10.2174/1573406415666190222124745. Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30799793 - Identification of SR1078, a synthetic agonist for the orphan nuclear receptors RORα and RORγ.
Wang Y, Kumar N, Nuhant P, Cameron MD, Istrate MA, Roush WR, Griffin PR, Burris TP. Wang Y, et al. ACS Chem Biol. 2010 Nov 19;5(11):1029-34. doi: 10.1021/cb100223d. ACS Chem Biol. 2010. PMID: 20735016 Free PMC article. - Pharmacological modulation of RORα controls fat browning, adaptive thermogenesis, and body weight in mice.
Auclair M, Roblot N, Capel E, Fève B, Antoine B. Auclair M, et al. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Feb 1;320(2):E219-E233. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00131.2020. Epub 2020 Nov 30. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33252251 Free PMC article. - Identification of a novel selective inverse agonist probe and analogs for the Retinoic acid receptor-related Orphan Receptor Gamma (RORγ).
Kumar N, Kamenecka T, Lyda B, Khan P, Chang MR, Garcia-Ordonez RD, Cameron M, Ferguson J, Mercer BA, Hodder P, Rosen H, Griffin PR. Kumar N, et al. 2012 Apr 16 [updated 2013 Mar 14]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. 2012 Apr 16 [updated 2013 Mar 14]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. PMID: 23762937 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
- Small molecule amides as potent ROR-γ selective modulators.
Khan PM, El-Gendy Bel-D, Kumar N, Garcia-Ordonez R, Lin L, Ruiz CH, Cameron MD, Griffin PR, Kamenecka TM. Khan PM, et al. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Jan 15;23(2):532-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.11.025. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013. PMID: 23232056 Free PMC article. - Emerging Role of Nuclear Receptors for the Treatment of NAFLD and NASH.
Welch RD, Billon C, Losby M, Bedia-Diaz G, Fang Y, Avdagic A, Elgendy B, Burris TP, Griffett K. Welch RD, et al. Metabolites. 2022 Mar 11;12(3):238. doi: 10.3390/metabo12030238. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35323681 Free PMC article. Review. - Inverse Agonist of Retinoid-Related Orphan Receptor-Alpha Prevents Apoptosis and Degeneration in Nucleus Pulposus Cells via Upregulation of YAP.
Liang T, Qiu J, Li S, Deng Z, Qiu X, Hu W, Li P, Chen T, Liang Z, Zhou H, Gao B, Huang D, Liang A, Gao W. Liang T, et al. Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Jul 28;2021:9954909. doi: 10.1155/2021/9954909. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34366712 Free PMC article. - Therapeutic Effect of a Synthetic RORα/γ Agonist in an Animal Model of Autism.
Wang Y, Billon C, Walker JK, Burris TP. Wang Y, et al. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016 Feb 17;7(2):143-8. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00159. Epub 2015 Dec 3. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26625251 Free PMC article. - Targeting nuclear receptors for NASH/MASH: From bench to bedside.
Sinha RA. Sinha RA. Liver Res. 2024 Mar;8(1):34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2024.03.002. Liver Res. 2024. PMID: 38544909 Free PMC article.
References
- Kallen J, Schlaeppi JM, Bitsch F, Delhon I, Fournier B. Crystal structure of the human ROR alpha ligand binding domain in complex with cholesterol sulfate at 2.2 angstrom. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279:14033–14038. - PubMed
- Kallen JA, Schlaeppi JM, Bitsch F, Geisse S, Geiser M, Delhon I, Fournier B. X-ray structure of the hROR alpha LBD at 1.63 angstrom: Structural and functional data that cholesterol or a cholesterol derivative is the natural ligand of ROR alpha. Structure. 2002;10:1697–1707. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH092769/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- GM084041/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080201-05/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54MH074404/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080201/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MH074404/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH092769-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK089984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK080201/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK089984-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM084041/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080201-06/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources