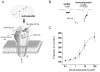Neurosteroids: endogenous role in the human brain and therapeutic potentials - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Neurosteroids: endogenous role in the human brain and therapeutic potentials
Doodipala Samba Reddy. Prog Brain Res. 2010.
Abstract
This chapter provides an overview of neurosteroids, especially their impact on the brain, sex differences and their therapeutic potentials. Neurosteroids are synthesized within the brain and rapidly modulate neuronal excitability. They are classified as pregnane neurosteroids, such as allopregnanolone and allotetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone, androstane neurosteroids, such as androstanediol and etiocholanolone, and sulfated neurosteroids such as pregnenolone sulfate. Neurosteroids such as allopregnanolone are positive allosteric modulators of GABA-A receptors with powerful anti-seizure activity in diverse animal models. Neurosteroids increase both synaptic and tonic inhibition. They are endogenous regulators of seizure susceptibility, anxiety, and stress. Sulfated neurosteroids such as pregnenolone sulfate, which are negative GABA-A receptor modulators, are memory-enhancing agents. Sex differences in susceptibility to brain disorders could be due to neurosteroids and sexual dimorphism in specific structures of the human brain. Synthetic neurosteroids that exhibit better bioavailability and efficacy and drugs that enhance neurosteroid synthesis have therapeutic potential in anxiety, epilepsy, and other brain disorders. Clinical trials with the synthetic neurosteroid analog ganaxolone in the treatment of epilepsy have been encouraging. Neurosteroidogenic agents that lack benzodiazepine-like side effects show promise in the treatment of anxiety and depression.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
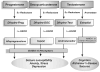
Figure 1. Biosynthetic pathways of neurosteroids in the human brain and their impact on brain function
5α-Reductase converts progesterone, testosterone and deoxycorticosterone into 5α-dihydro reduced steroids, which are then reduced further to 3α-hydroxylated neurosteroids by 3α-HSOR. Testosterone is converted into 17β-estradiol by the aromatase enzyme. These and related enzymes involved in neurosteroid biosynthesis and metabolism are present in the human brain.
Figure 2. Biosynthesis of progesterone- and testosterone-derived neurosteroids in the brain
Androstanediol (5α-androstan-3α,17β-diol) is synthesized from testosterone by reduction at the 5-and 3-positions of the steroid A-ring. Allopregnanolone (5α-pregnan-3α-ol-20-one) is derived from progesterone by reduction at the 5- and 3-positions of the steroid A-ring. Androstanediol differs from allopregnanolone by a 17β-hydroxyl group instead of 17β-methyl-carbonyl group.
Figure 3. Neurosteroid potentiation of GABA-A receptor-mediated currents
(A) Neurosteroids have specific allosteric binding site on the GABA-A receptors, which are pentameric structures made of 2α, 2β,1γ or δ subunit that form chloride ion channel. The binding site(s) for the neurosteroids is separate from that of the benzodiazepine and barbiturate sites. (B) The neurosteroid androstanediol causes an increase in GABA-gated chloride currents in acutely dissociated hippocampal CA1 neurons in the whole-cell patch-clamp electrophysiological recordings. (C) The concentration-dependent increase in GABA potentiation by androstanediol in CA1 neurons.
Similar articles
- Neurosteroid interactions with synaptic and extrasynaptic GABA(A) receptors: regulation of subunit plasticity, phasic and tonic inhibition, and neuronal network excitability.
Carver CM, Reddy DS. Carver CM, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Nov;230(2):151-88. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3276-5. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 24071826 Free PMC article. Review. - Extrasynaptic γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor-mediated sex differences in the antiseizure activity of neurosteroids in status epilepticus and complex partial seizures.
Reddy DS, Carver CM, Clossen B, Wu X. Reddy DS, et al. Epilepsia. 2019 Apr;60(4):730-743. doi: 10.1111/epi.14693. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Epilepsia. 2019. PMID: 30895610 Free PMC article. - Isobolographic Analysis of Antiseizure Activity of the GABA Type A Receptor-Modulating Synthetic Neurosteroids Brexanolone and Ganaxolone with Tiagabine and Midazolam.
Chuang SH, Reddy DS. Chuang SH, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020 Mar;372(3):285-298. doi: 10.1124/jpet.119.261735. Epub 2019 Dec 16. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020. PMID: 31843812 Free PMC article. - Clinical Potential of Neurosteroids for CNS Disorders.
Reddy DS, Estes WA. Reddy DS, et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Jul;37(7):543-561. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 May 5. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27156439 Free PMC article. Review. - The role of GABA-A and mitochondrial diazepam-binding inhibitor receptors on the effects of neurosteroids on food intake in mice.
Reddy DS, Kulkarni SK. Reddy DS, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1998 Jun;137(4):391-400. doi: 10.1007/s002130050635. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1998. PMID: 9676900
Cited by
- Neuroendocrine aspects of catamenial epilepsy.
Reddy DS. Reddy DS. Horm Behav. 2013 Feb;63(2):254-66. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2012.04.016. Epub 2012 May 2. Horm Behav. 2013. PMID: 22579656 Free PMC article. Review. - The 5α-reductase inhibitor finasteride reduces opioid self-administration in animal models of opioid use disorder.
Bosse GD, Cadeddu R, Floris G, Farero RD, Vigato E, Lee SJ, Zhang T, Gaikwad NW, Keefe KA, Phillips PE, Bortolato M, Peterson RT. Bosse GD, et al. J Clin Invest. 2021 May 17;131(10):e143990. doi: 10.1172/JCI143990. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33848264 Free PMC article. - Mechanism-based novel antidotes for organophosphate neurotoxicity.
Reddy DS. Reddy DS. Curr Opin Toxicol. 2019 Apr;14:35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.cotox.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Curr Opin Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 32856007 Free PMC article. - A synthetic pregnenolone analog promotes microtubule dynamics and neural development.
Kolas V, Bandonil JSA, Wali N, Hsia KC, Shie JJ, Chung BC. Kolas V, et al. Cell Biosci. 2022 Dec 1;12(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00923-2. Cell Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36456994 Free PMC article. - Regulation of neurosteroid biosynthesis by neurotransmitters and neuropeptides.
Do Rego JL, Seong JY, Burel D, Leprince J, Vaudry D, Luu-The V, Tonon MC, Tsutsui K, Pelletier G, Vaudry H. Do Rego JL, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012 Jan 24;3:4. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2012.00004. eCollection 2012. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012. PMID: 22654849 Free PMC article.
References
- Aird RB. The effect of desoxycorticosterone in epilepsy. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disorders. 1944;99:501–510.
- Aird RB, Gordan GS. Anticonvulsive properties of desoxycorticosterone. Journal of the American Medical Association. 1951;145:715–719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS071597/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS052158/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS051398/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS052158-03/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS051398-04/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS071597/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS052158/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS071597-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS051398/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources