Allele-selective inhibition of huntingtin expression by switching to an miRNA-like RNAi mechanism - PubMed (original) (raw)
Allele-selective inhibition of huntingtin expression by switching to an miRNA-like RNAi mechanism
Jiaxin Hu et al. Chem Biol. 2010.
Abstract
Inhibiting expression of huntingtin (HTT) protein is a promising strategy for treating Huntington's disease (HD), but indiscriminant inhibition of both wild-type and mutant alleles may lead to toxicity. An ideal silencing agent would block expression of mutant HTT while leaving expression of wild-type HTT intact. We observe that fully complementary duplex RNAs targeting the expanded CAG repeat within HTT mRNA block expression of both alleles. Switching the RNAi mechanism toward that used by miRNAs by introducing one or more mismatched bases into these duplex RNAs leads to potent (<10 nM) and highly selective (>30-fold relative to wild-type HTT) inhibition of mutant HTT expression in patient-derived cells. Potent, allele selective inhibition of HTT by mismatched RNAs provides a new option for developing HD therapeutics.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
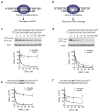
Figure 1. Allele-selective inhibition by mismatch-containing duplex RNAs
Schemes showing recognition of a (a) perfectly complementary duplex leading to cleavage of mRNA and (b) mismatch-containing duplex leading to inhibition of translation. Effect on HTT expression from adding duplex RNAs (c) P9, (d) REP (e) PM3 to GM04281 cells or f) P9 to GM04717 cells. Data describing the selectivities and potencies of other duplexes can be found in Table 1. See also Figure S1.
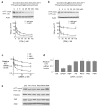
Figure 2. Mechanism of allele-selective RNAs
Effect on mutant and wild-type HTT expression after treatment with duplex RNAs that contain a mismatched base in either the (a) passenger strand, P9a, or (b) guide strand, P9b. (c) qPCR analysis of effect on HTT mRNA levels after treatment of increasing amount of siRNAs siHdh1, REP, and P9. (d) Effect of varied siRNAs (12 nM) on HTT mRNA levels measured by qPCR. (e) Effect of allele-selective duplex RNAs (25 nM) on expression of other genes containing regions with CAG repeats. CM: a duplex RNA not complementary to HTT mRNA. siHdh1: an siRNA that is complementary to HTT mRNA outside of the CAG repeat region (Omi et al., 2005). See also Figure S2.
Similar articles
- Exploring the effect of sequence length and composition on allele-selective inhibition of human huntingtin expression by single-stranded silencing RNAs.
Hu J, Liu J, Yu D, Aiba Y, Lee S, Pendergraff H, Boubaker J, Artates JW, Lagier-Tourenne C, Lima WF, Swayze EE, Prakash TP, Corey DR. Hu J, et al. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2014 Jun;24(3):199-209. doi: 10.1089/nat.2013.0476. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2014. PMID: 24694346 Free PMC article. - Mechanism of allele-selective inhibition of huntingtin expression by duplex RNAs that target CAG repeats: function through the RNAi pathway.
Hu J, Liu J, Yu D, Chu Y, Corey DR. Hu J, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Dec;40(22):11270-80. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks907. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 23042244 Free PMC article. - Allele-selective inhibition of expression of huntingtin and ataxin-3 by RNA duplexes containing unlocked nucleic acid substitutions.
Aiba Y, Hu J, Liu J, Xiang Q, Martinez C, Corey DR. Aiba Y, et al. Biochemistry. 2013 Dec 23;52(51):9329-38. doi: 10.1021/bi4014209. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 24266403 Free PMC article. - An insight into allele-selective approaches to lowering mutant huntingtin protein for Huntington's disease treatment.
Yao JY, Liu T, Hu XR, Sheng H, Chen ZH, Zhao HY, Li XJ, Wang Y, Hao L. Yao JY, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Nov;180:117557. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117557. Epub 2024 Oct 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39405896 Review. - Transcriptional dysregulation of coding and non-coding genes in cellular models of Huntington's disease.
Bithell A, Johnson R, Buckley NJ. Bithell A, et al. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Dec;37(Pt 6):1270-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0371270. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19909260 Review.
Cited by
- Recent advances in RNA interference therapeutics for CNS diseases.
Ramachandran PS, Keiser MS, Davidson BL. Ramachandran PS, et al. Neurotherapeutics. 2013 Jul;10(3):473-85. doi: 10.1007/s13311-013-0183-8. Neurotherapeutics. 2013. PMID: 23589092 Free PMC article. Review. - Mutant CAG Repeats Effectively Targeted by RNA Interference in SCA7 Cells.
Fiszer A, Wroblewska JP, Nowak BM, Krzyzosiak WJ. Fiszer A, et al. Genes (Basel). 2016 Dec 17;7(12):132. doi: 10.3390/genes7120132. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27999335 Free PMC article. - Suppression of MAPK11 or HIPK3 reduces mutant Huntingtin levels in Huntington's disease models.
Yu M, Fu Y, Liang Y, Song H, Yao Y, Wu P, Yao Y, Pan Y, Wen X, Ma L, Hexige S, Ding Y, Luo S, Lu B. Yu M, et al. Cell Res. 2017 Dec;27(12):1441-1465. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.113. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 29151587 Free PMC article. - Limits of using oligonucleotides for allele-selective inhibition at trinucleotide repeat sequences - targeting the CAG repeat within ataxin-1.
Hu J, Corey DR. Hu J, et al. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2020;39(1-3):185-194. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2019.1671592. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 31645175 Free PMC article. - Potent and sustained huntingtin lowering via AAV5 encoding miRNA preserves striatal volume and cognitive function in a humanized mouse model of Huntington disease.
Caron NS, Southwell AL, Brouwers CC, Cengio LD, Xie Y, Black HF, Anderson LM, Ko S, Zhu X, van Deventer SJ, Evers MM, Konstantinova P, Hayden MR. Caron NS, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jan 10;48(1):36-54. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz976. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31745548 Free PMC article.
References
- De Souza EB, Cload ST, Pendergrast PS, Sah DW. Novel therapeutic modalities to address nondrugable protein interaction targets. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009;34:142–158. - PubMed
- Drouet V, Perrin V, Hassig R, Dufour N, Auregan G, Alves S, Bonvento G, Brouillet E, Luthi-Carter R, Hantraye P, Deglon N. Sustained effects of nonallele-specific Huntingtin silencing. Ann Neurol. 2009;65:276–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources