Caveolin-1: a critical regulator of lung injury - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Caveolin-1: a critical regulator of lung injury
Yang Jin et al. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 Feb.
Abstract
Caveolin-1 (cav-1), a 22-kDa transmembrane scaffolding protein, is the principal structural component of caveolae. Cav-1 regulates critical cell functions including proliferation, apoptosis, cell differentiation, and transcytosis via diverse signaling pathways. Abundant in almost every cell type in the lung, including type I epithelial cells, endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, macrophages, and neutrophils, cav-1 plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury (ALI). ALI and its severe form, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), are responsible for significant morbidity and mortality in intensive care units, despite improvement in ventilation strategies. The pathogenesis of ARDS is still poorly understood, and therapeutic options remain limited. In this article, we summarize recent data regarding the regulation and function of cav-1 in lung biology and pathology, in particular as it relates to ALI. We further discuss the potential molecular and cellular mechanisms by which cav-1 expression contributes to ALI. Investigating the cellular functions of cav-1 may provide new insights for understanding the pathogenesis of ALI and provide novel targets for therapeutic interventions in the future.
Figures
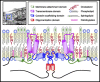
Fig. 1.
Structure of caveolin-1. Cav-1 contains a hydrophobic central domain with a hairpin-like conformation inserted in the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane. 14–16 Cav-1 monomers form a single cav-1 homooligomer. A simplified dimmer is illustrated here. Both the COOH and NH2 terminus of the cav-1 monomer face the cytoplasm. The caveolin scaffolding domain is located between amino acid residues 82–101 in the NH2-terminal region adjacent to the hydrophobic membrane-insertion domain. The COOH-terminal region of cav-1 contains 3 palmitoylated cysteine residues. Inset: caveolae viewed by electron microscopy (×50,000).
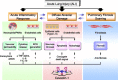
Fig. 2.
Scheme of proposed roles of caveolin-1 in acute lung injury.
Similar articles
- Deletion of caveolin-1 protects against oxidative lung injury via up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1.
Jin Y, Kim HP, Chi M, Ifedigbo E, Ryter SW, Choi AM. Jin Y, et al. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008 Aug;39(2):171-9. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0323OC. Epub 2008 Mar 6. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18323531 Free PMC article. - Genetic ablation of caveolin-2 sensitizes mice to bleomycin-induced injury.
de Almeida CJ, Jasmin JF, Del Galdo F, Lisanti MP. de Almeida CJ, et al. Cell Cycle. 2013 Jul 15;12(14):2248-54. doi: 10.4161/cc.25335. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 24067367 Free PMC article. - Pathogenesis of indirect (secondary) acute lung injury.
Perl M, Lomas-Neira J, Venet F, Chung CS, Ayala A. Perl M, et al. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2011 Feb;5(1):115-26. doi: 10.1586/ers.10.92. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2011. PMID: 21348592 Free PMC article. Review. - Inflammation-induced caveolin-1 and BMPRII depletion promotes endothelial dysfunction and TGF-β-driven pulmonary vascular remodeling.
Oliveira SDS, Castellon M, Chen J, Bonini MG, Gu X, Elliott MH, Machado RF, Minshall RD. Oliveira SDS, et al. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 May 1;312(5):L760-L771. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00484.2016. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28188225 Free PMC article. - Acute lung injury and ARDS in acute pancreatitis: mechanisms and potential intervention.
Zhou MT, Chen CS, Chen BC, Zhang QY, Andersson R. Zhou MT, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2010 May 7;16(17):2094-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i17.2094. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20440849 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Epithelial membrane protein 2 governs transepithelial migration of neutrophils into the airspace.
Lin WC, Gowdy KM, Madenspacher JH, Zemans RL, Yamamoto K, Lyons-Cohen M, Nakano H, Janardhan K, Williams CJ, Cook DN, Mizgerd JP, Fessler MB. Lin WC, et al. J Clin Invest. 2020 Jan 2;130(1):157-170. doi: 10.1172/JCI127144. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 31550239 Free PMC article. - Role of calcium-sensor proteins in cell membrane repair.
Li Z, Shaw GS. Li Z, et al. Biosci Rep. 2023 Feb 27;43(2):BSR20220765. doi: 10.1042/BSR20220765. Biosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36728029 Free PMC article. Review. - Antenatal inflammation reduces expression of caveolin-1 and influences multiple signaling pathways in preterm fetal lungs.
Kunzmann S, Collins JJ, Yang Y, Uhlig S, Kallapur SG, Speer CP, Jobe AH, Kramer BW. Kunzmann S, et al. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011 Nov;45(5):969-76. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0519OC. Epub 2011 May 11. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21562314 Free PMC article. - Caveolin-1 Deficiency Protects Mice Against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Injury Through Regulating Polarization of Hepatic Macrophages.
Yang Z, Zhang J, Wang Y, Lu J, Sun Q. Yang Z, et al. Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 9;12:713808. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.713808. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34434195 Free PMC article. - Caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptides enhance anti-inflammatory effect of heme oxygenase-1 through interrupting its interact with caveolin-1.
Weng P, Zhang XT, Sheng Q, Tian WF, Chen JL, Yuan JJ, Zhang JR, Pang QF. Weng P, et al. Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 20;8(25):40104-40114. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16676. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28402952 Free PMC article.
References
- Alonso MA, Millán J. The role of lipid rafts in signalling and membrane trafficking in T lymphocytes. J Cell Sci 114: 3957–3965, 2001. - PubMed
- Bento-Abreu A, Velasco A, Polo-Hernández E, Lillo C, Kozyraki R, Tabernero A, Medina JM. Albumin endocytosis via megalin in astrocytes is caveola- and Dab-1 dependent and is required for the synthesis of the neurotrophic factor oleic acid. J Neurochem 111: 49–60, 2009. - PubMed
- Buckley S, Barsky L, Driscoll B, Weinberg K, Anderson KD, Warburton D. Apoptosis and DNA damage in type 2 alveolar epithelial cells cultured from hyperoxic rats. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 274: L714–L720, 1998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources