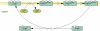EcoCyc: a comprehensive database of Escherichia coli biology - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2011 Jan;39(Database issue):D583-90.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1143. Epub 2010 Nov 21.
Julio Collado-Vides, Alberto Santos-Zavaleta, Martin Peralta-Gil, Socorro Gama-Castro, Luis Muñiz-Rascado, César Bonavides-Martinez, Suzanne Paley, Markus Krummenacker, Tomer Altman, Pallavi Kaipa, Aaron Spaulding, John Pacheco, Mario Latendresse, Carol Fulcher, Malabika Sarker, Alexander G Shearer, Amanda Mackie, Ian Paulsen, Robert P Gunsalus, Peter D Karp
Affiliations
- PMID: 21097882
- PMCID: PMC3013716
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq1143
EcoCyc: a comprehensive database of Escherichia coli biology
Ingrid M Keseler et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan.
Abstract
EcoCyc (http://EcoCyc.org) is a comprehensive model organism database for Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655. From the scientific literature, EcoCyc captures the functions of individual E. coli gene products; their regulation at the transcriptional, post-transcriptional and protein level; and their organization into operons, complexes and pathways. EcoCyc users can search and browse the information in multiple ways. Recent improvements to the EcoCyc Web interface include combined gene/protein pages and a Regulation Summary Diagram displaying a graphical overview of all known regulatory inputs to gene expression and protein activity. The graphical representation of signal transduction pathways has been updated, and the cellular and regulatory overviews were enhanced with new functionality. A specialized undergraduate teaching resource using EcoCyc is being developed.
Figures
Figure 1.
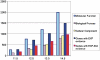
Growth of experimental GO term annotations in EcoCyc over time. Data is grouped by database version, beginning with release 11.5 (August 2007) and ending with release 14.5 (September 2010). The first three bars in each group report the number of assignments of a GO term from each of the three primary GO categories with an EXP_IDA (inferred by direct assay) evidence code. In contrast, the last two bars report the number of genes that have at least one GO term annotation with an EXP or an EXP-IDA evidence code. EXP includes the EXP-IDA evidence codes as well as others such as EXP-IMP (inferred by mutant phenotype).
Figure 2.
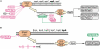
The Regulation Summary Diagram. Colors indicate the overall effect on the production of the functional protein. (A) Regulation Summary Diagram for the oppD gene. Transcription initiation is influenced by a variety of TFs, which are themselves regulated by small molecules. The operon containing oppD is transcribed by RNA polymerase containing the alternative sigma factor Sigma 28. Translation is regulated by a small molecule, spermidine, the small RNA GcvB, and Hfq. The OppD protein can be part of two different heteromultimeric complexes. (B) Regulation Summary Diagram for the trpA gene. Transcription initiation is regulated by TrpR. In the presence of the charged tryptophanyl-tRNATrp, transcription is attenuated due to formation of a stem-loop structure in the mRNA. Pyridoxal-phosphate is a cofactor for the tryptophan synthase enzyme.
Figure 3.
New graphic representation of the EvgSA two-component signal transduction pathway.
Figure 4.
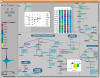
Omics Data Graphing.
Similar articles
- EcoCyc: a comprehensive database resource for Escherichia coli.
Keseler IM, Collado-Vides J, Gama-Castro S, Ingraham J, Paley S, Paulsen IT, Peralta-Gil M, Karp PD. Keseler IM, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jan 1;33(Database issue):D334-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki108. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15608210 Free PMC article. - EcoCyc: fusing model organism databases with systems biology.
Keseler IM, Mackie A, Peralta-Gil M, Santos-Zavaleta A, Gama-Castro S, Bonavides-Martínez C, Fulcher C, Huerta AM, Kothari A, Krummenacker M, Latendresse M, Muñiz-Rascado L, Ong Q, Paley S, Schröder I, Shearer AG, Subhraveti P, Travers M, Weerasinghe D, Weiss V, Collado-Vides J, Gunsalus RP, Paulsen I, Karp PD. Keseler IM, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(Database issue):D605-12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1027. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23143106 Free PMC article. - The EcoCyc database: reflecting new knowledge about Escherichia coli K-12.
Keseler IM, Mackie A, Santos-Zavaleta A, Billington R, Bonavides-Martínez C, Caspi R, Fulcher C, Gama-Castro S, Kothari A, Krummenacker M, Latendresse M, Muñiz-Rascado L, Ong Q, Paley S, Peralta-Gil M, Subhraveti P, Velázquez-Ramírez DA, Weaver D, Collado-Vides J, Paulsen I, Karp PD. Keseler IM, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 4;45(D1):D543-D550. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1003. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27899573 Free PMC article. - The EcoCyc Database.
Karp PD, Ong WK, Paley S, Billington R, Caspi R, Fulcher C, Kothari A, Krummenacker M, Latendresse M, Midford PE, Subhraveti P, Gama-Castro S, Muñiz-Rascado L, Bonavides-Martinez C, Santos-Zavaleta A, Mackie A, Collado-Vides J, Keseler IM, Paulsen I. Karp PD, et al. EcoSal Plus. 2018 Nov;8(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0006-2018. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0006-2018. EcoSal Plus. 2018. PMID: 30406744 Free PMC article. Review. - The EcoCyc Database (2023).
Karp PD, Paley S, Caspi R, Kothari A, Krummenacker M, Midford PE, Moore LR, Subhraveti P, Gama-Castro S, Tierrafria VH, Lara P, Muñiz-Rascado L, Bonavides-Martinez C, Santos-Zavaleta A, Mackie A, Sun G, Ahn-Horst TA, Choi H, Covert MW, Collado-Vides J, Paulsen I. Karp PD, et al. EcoSal Plus. 2023 Dec 12;11(1):eesp00022023. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.esp-0002-2023. Epub 2023 May 11. EcoSal Plus. 2023. PMID: 37220074 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A flood-based information flow analysis and network minimization method for gene regulatory networks.
Pavlogiannis A, Mozhayskiy V, Tagkopoulos I. Pavlogiannis A, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013 Apr 24;14:137. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-137. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23617932 Free PMC article. - Dynamic knockdown of E. coli central metabolism for redirecting fluxes of primary metabolites.
Brockman IM, Prather KLJ. Brockman IM, et al. Metab Eng. 2015 Mar;28:104-113. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2014.12.005. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Metab Eng. 2015. PMID: 25542851 Free PMC article. - Constrained Allocation Flux Balance Analysis.
Mori M, Hwa T, Martin OC, De Martino A, Marinari E. Mori M, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Jun 29;12(6):e1004913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004913. eCollection 2016 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27355325 Free PMC article. - Genome-scale engineering for systems and synthetic biology.
Esvelt KM, Wang HH. Esvelt KM, et al. Mol Syst Biol. 2013;9:641. doi: 10.1038/msb.2012.66. Mol Syst Biol. 2013. PMID: 23340847 Free PMC article. Review. - Word-based GWAS harnesses the rich potential of genomic data for E. coli quinolone resistance.
Malekian N, Sainath S, Al-Fatlawi A, Schroeder M. Malekian N, et al. Front Microbiol. 2023 Dec 13;14:1276332. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1276332. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38152371 Free PMC article.
References
- Gama-Castro S, Jimenez-Jacinto V, Peralta-Gil M, Santos-Zavaleta A, Penaloza-Spinola MI, Contreras-Moreira B, Segura-Salazar J, Muniz-Rascado L, Martinez-Flores I, Salgado H, et al. RegulonDB (version 6.0): gene regulation model of Escherichia coli K-12 beyond transcription, active (experimental) annotated promoters and Textpresso navigation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:D120–D124. - PMC - PubMed
- Jorgensen CI, Kallipolitis BH, Valentin-Hansen P. DNA-binding characteristics of the Escherichia coli CytR regulator: a relaxed spacing requirement between operator half-sites is provided by a flexible, unstructured interdomain linker. Mol. Microbiol. 1998;27:41–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GU24GM077678/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM071962/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GU24GM077678-20/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 GM077678/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071962/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 GM077678-19/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources