Transcriptome analysis of embryonic and adult sensory axons reveals changes in mRNA repertoire localization - PubMed (original) (raw)
Transcriptome analysis of embryonic and adult sensory axons reveals changes in mRNA repertoire localization
Laura F Gumy et al. RNA. 2011 Jan.
Abstract
mRNAs are transported, localized, and translated in axons of sensory neurons. However, little is known about the full repertoire of transcripts present in embryonic and adult sensory axons and how this pool of mRNAs dynamically changes during development. Here, we used a compartmentalized chamber to isolate mRNA from pure embryonic and adult sensory axons devoid of non-neuronal or cell body contamination. Genome-wide microarray analysis reveals that a previously unappreciated number of transcripts are localized in sensory axons and that this repertoire changes during development toward adulthood. Embryonic axons are enriched in transcripts encoding cytoskeletal-related proteins with a role in axonal outgrowth. Surprisingly, adult axons are enriched in mRNAs encoding immune molecules with a role in nociception. Additionally, we show Tubulin-beta3 (Tubb3) mRNA is present only in embryonic axons, with Tubb3 locally synthesized in axons of embryonic, but not adult neurons where it is transported, thus validating our experimental approach. In summary, we provide the first complete catalog of embryonic and adult sensory axonal mRNAs. In addition we show that this pool of axonal mRNAs dynamically changes during development. These data provide an important resource for studies on the role of local protein synthesis in axon regeneration and nociception during neuronal development.
Figures
FIGURE 1.
Venn diagrams comparing the three different analyses: GCOS, GC-RMA, and RMA in embryonic and adult DRG axons. (A) The 2627 genes present in embryonic axons, (B) the 2924 genes present in adult axons. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of genes as determined by either the GCOS, RMA, or GCRMA algorithms (see Materials and Methods).
FIGURE 2.
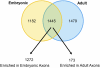
Embryonic and adult sensory axons contain different repertoires of mRNAs. Venn diagram showing overlapping (1445) and uniquely localized mRNAs in embryonic (1182) and adult (1479) DRG axons. Of the overlapping mRNAs, 1272 were up-regulated (enriched) in embryonic axons while 173 were enriched in adult ones.
FIGURE 3.
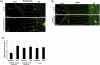
Tubb3 is locally translated in embryonic DRG axons. (A) Fluorescent micrograph of Tubb3 immunolabeled embryonic DRG neurons cultured in the compartmentalized microfluidic chamber. Cycloheximide treatment (25 μM) for 3 h significantly decreased Tubb3 immunoreactivity in distal axons. CB indicates the cell body compartment. Scale bar = 100 μm. (B) Fluorescent micrograph of Tubb3 immunolabeled adult DRG neurons cultured in the compartmentalized microfluidic chamber. Cycloheximide treatment (25 μM) for 3 h of distal axons had no effect on Tubb3 levels. CB indicates the cell body compartment. Scale bar = 100 μm. (C) Quantification of the raw intensity levels of Tubb3 immunofluorescence in cycloheximide-treated and untreated distal axons proximal axons in the cell body compartment. Tubb3 intensity levels in distal axons decreased significantly following cycloheximide treatment compared to untreated controls (*P = 0.010; two-tailed Student's _t_-test). Error bars indicate SD.
Similar articles
- mRNAs and Protein Synthetic Machinery Localize into Regenerating Spinal Cord Axons When They Are Provided a Substrate That Supports Growth.
Kalinski AL, Sachdeva R, Gomes C, Lee SJ, Shah Z, Houle JD, Twiss JL. Kalinski AL, et al. J Neurosci. 2015 Jul 15;35(28):10357-70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1249-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26180210 Free PMC article. - Axonal mRNAs: characterisation and role in the growth and regeneration of dorsal root ganglion axons and growth cones.
Vogelaar CF, Gervasi NM, Gumy LF, Story DJ, Raha-Chowdhury R, Leung KM, Holt CE, Fawcett JW. Vogelaar CF, et al. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2009 Oct;42(2):102-115. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2009.06.002. Epub 2009 Jun 9. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19520167 Free PMC article. - Limited availability of ZBP1 restricts axonal mRNA localization and nerve regeneration capacity.
Donnelly CJ, Willis DE, Xu M, Tep C, Jiang C, Yoo S, Schanen NC, Kirn-Safran CB, van Minnen J, English A, Yoon SO, Bassell GJ, Twiss JL. Donnelly CJ, et al. EMBO J. 2011 Sep 30;30(22):4665-77. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.347. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21964071 Free PMC article. - Changes in cytoskeletal protein synthesis following axon injury and during axon regeneration.
Bisby MA, Tetzlaff W. Bisby MA, et al. Mol Neurobiol. 1992 Summer-Fall;6(2-3):107-23. doi: 10.1007/BF02780547. Mol Neurobiol. 1992. PMID: 1476674 Review. - New insights into neuronal regeneration: the role of axonal protein synthesis in pathfinding and axonal extension.
Twiss JL, van Minnen J. Twiss JL, et al. J Neurotrauma. 2006 Mar-Apr;23(3-4):295-308. doi: 10.1089/neu.2006.23.295. J Neurotrauma. 2006. PMID: 16629617 Review.
Cited by
- Intra-axonal synthesis of eukaryotic translation initiation factors regulates local protein synthesis and axon growth in rat sympathetic neurons.
Kar AN, MacGibeny MA, Gervasi NM, Gioio AE, Kaplan BB. Kar AN, et al. J Neurosci. 2013 Apr 24;33(17):7165-74. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2040-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23616526 Free PMC article. - Axonal mRNA translation in neurological disorders.
Lin JQ, van Tartwijk FW, Holt CE. Lin JQ, et al. RNA Biol. 2021 Jul;18(7):936-961. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1822638. Epub 2020 Sep 29. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 32988274 Free PMC article. Review. - Detection of Axonally Localized mRNAs in Brain Sections Using High-Resolution In Situ Hybridization.
Baleriola J, Jean Y, Troy C, Hengst U. Baleriola J, et al. J Vis Exp. 2015 Jun 17;(100):e52799. doi: 10.3791/52799. J Vis Exp. 2015. PMID: 26131922 Free PMC article. - Alterations in DNA methylation associate with reduced migraine and headache days after medication withdrawal treatment in chronic migraine patients: a longitudinal study.
Mehta D, de Boer I, Sutherland HG, Pijpers JA, Bron C, Bainomugisa C, Haupt LM, van den Maagdenberg AMJM, Griffiths LR, Nyholt DR, Terwindt GM. Mehta D, et al. Clin Epigenetics. 2023 Dec 12;15(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s13148-023-01604-8. Clin Epigenetics. 2023. PMID: 38087366 Free PMC article. - Subcellular RNA-seq for the Analysis of the Dendritic and Somatic Transcriptomes of Single Neurons.
Perez JD, Schuman EM. Perez JD, et al. Bio Protoc. 2022 Jan 5;12(1):e4278. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4278. eCollection 2022 Jan 5. Bio Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35118171 Free PMC article.
References
- Abbadie C 2005. Chemokines, chemokine receptors and pain. Trends Immunol 26: 529–534 - PubMed
- Andreassi C, Zimmermann C, Mitter R, Fusco S, Devita S, Saiardi A, Riccio A 2010. An NGF-responsive element targets myo-inositol monophosphatase-1 mRNA to sympathetic neuron axons. Nat Neurosci 13: 291–301 - PubMed
- Baron R 2006. Mechanisms of disease: neuropathic pain—a clinical perspective. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2: 95–106 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases