The role of the antioxidant and longevity-promoting Nrf2 pathway in metabolic regulation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The role of the antioxidant and longevity-promoting Nrf2 pathway in metabolic regulation
Gerasimos P Sykiotis et al. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011 Jan.
Abstract
Purpose of review: The vertebrate cap'n'collar family transcription factor Nrf2 and its invertebrate homologues SKN-1 (in worms) and CncC (in flies) function as master mediators of antioxidant and detoxification responses and regulators of the cellular redox state. Nrf2 controls gene expression programs that defend various tissues against diverse electrophilic stressors and oxidative insults, thus protecting the organism from disorders that are caused or exacerbated by such stresses. Moreover, studies on model organisms implicate the Nrf2 pathway in the prevention of aging-related diseases and suggest that SKN-1-regulated and CncC-regulated gene expression can promote longevity. These facets of Nrf2 signaling have been thoroughly reviewed. This article discusses another aspect of the Nrf2 pathway's function that has not yet received the same degree of attention, but emerges as a topic of increasing interest and potential clinical impact: its role in metabolic regulation and its interaction with central signaling systems that respond to nutritional inputs.
Recent findings: Recent evidence identifies Nrf2 signaling as a mediator of the salutary effects of caloric restriction. Nrf2 signaling also crosstalks with metabolic signaling systems such as the insulin/Akt pathway as well as with the metabolism of lipids. Moreover, Nrf2 has a protective role in models of diabetic nephropathy.
Summary: The emerging role of Nrf2 as an effector of metabolic and longevity signals offers new therapeutic perspectives. The potential impact of pharmacological manipulation of Nrf2 signaling as a strategy for the prevention and treatment of metabolic disease can be envisioned.
Figures
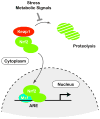
Figure 1. Schematic model of Nrf2 activation
In basal conditions the protein levels of Nrf2 are kept low due to the rapid proteasome-mediated turn-over facilitated by the Kelch family protein Keap1 which acts as a Nrf2-specific E3 ligase adaptor protein. In response to various extracellular signals the inhibitory effect of Keap1 on Nrf2 is interrupted, such that Nrf2 is stabilized and accumulates in the nucleus. There it dimerizes with a small Maf protein, binds to AREs (Antioxidant Response Elements) in the regulatory regions of its target genes and modulates their transcription.
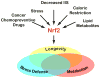
Figure 2. Model: Nrf2 as a convergence point for stress, metabolic, and longevity signals
Nrf2 can be activated by various types of oxidative and electrophile stress. Recent evidence reviewed in this article shows that Nrf2 function can also respond to Lipid Me metabolic and longevity signals such as CR, low levels of IIS, and lipid metabolites. We suggest that the transcriptome changes that occur in these conditions include different, but overlapping sets of Nrf2 target genes. The resulting Nrf2-induced genetic programs can contribute to stress protection, longevity, or changes in metabolism. A scientific challenge, or opportunity, arising from this model is to evaluate pharmacological options to evoke longevity programs, possibly by using Nrf2-activating drugs that have originally been identified as cancer chemopreventive agents.
Similar articles
- Sphingosine Kinase Regulates Neuropeptide Secretion During the Oxidative Stress-Response Through Intertissue Signaling.
Kim S, Sieburth D. Kim S, et al. J Neurosci. 2018 Sep 19;38(38):8160-8176. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0536-18.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 6. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30082417 Free PMC article. - Nrf2 Signaling and the Slowed Aging Phenotype: Evidence from Long-Lived Models.
Bruns DR, Drake JC, Biela LM, Peelor FF 3rd, Miller BF, Hamilton KL. Bruns DR, et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:732596. doi: 10.1155/2015/732596. Epub 2015 Oct 25. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26583062 Free PMC article. Review. - The rise of antioxidant signaling--the evolution and hormetic actions of Nrf2.
Maher J, Yamamoto M. Maher J, et al. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010 Apr 1;244(1):4-15. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2010.01.011. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20122947 Review. - Stress-activated cap'n'collar transcription factors in aging and human disease.
Sykiotis GP, Bohmann D. Sykiotis GP, et al. Sci Signal. 2010 Mar 9;3(112):re3. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.3112re3. Sci Signal. 2010. PMID: 20215646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The Roles of White Adipose Tissue and Liver NADPH in Dietary Restriction-Induced Longevity.
Jamerson LE, Bradshaw PC. Jamerson LE, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jul 8;13(7):820. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070820. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061889 Free PMC article. Review. - Impact of Polyphenolic-Food on Longevity: An Elixir of Life. An Overview.
Meccariello R, D'Angelo S. Meccariello R, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 24;10(4):507. doi: 10.3390/antiox10040507. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805092 Free PMC article. Review. - Willow bark extract increases antioxidant enzymes and reduces oxidative stress through activation of Nrf2 in vascular endothelial cells and Caenorhabditis elegans.
Ishikado A, Sono Y, Matsumoto M, Robida-Stubbs S, Okuno A, Goto M, King GL, Keith Blackwell T, Makino T. Ishikado A, et al. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:1506-1515. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.12.006. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23277146 Free PMC article. - Prevention of diabetic nephropathy by sulforaphane: possible role of Nrf2 upregulation and activation.
Cui W, Bai Y, Miao X, Luo P, Chen Q, Tan Y, Rane MJ, Miao L, Cai L. Cui W, et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012:821936. doi: 10.1155/2012/821936. Epub 2012 Sep 23. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012. PMID: 23050040 Free PMC article. - Norketamine, the Main Metabolite of Ketamine, Induces Mitochondria-Dependent and ER Stress-Triggered Apoptotic Death in Urothelial Cells via a Ca2+-Regulated ERK1/2-Activating Pathway.
Lin JW, Lin YC, Liu JM, Liu SH, Fang KM, Hsu RJ, Huang CF, Chang KY, Lee KI, Chang KC, Su CC, Chen YW. Lin JW, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 23;23(9):4666. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094666. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563057 Free PMC article.
References
- Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N, Biswal S. Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;47:89–116. - PubMed
- Kobayashi M, Yamamoto M. Nrf2-Keap1 regulation of cellular defense mechanisms against electrophiles and reactive oxygen species. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2006;46:113–140. - PubMed
- Lee JM, Li J, Johnson DA, Stein TD, Kraft AD, Calkins MJ, Jakel RJ, Johnson JA. Nrf2, a multi-organ protector? Faseb J. 2005;19(9):1061–1066. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous