Why do T cells express the vitamin D receptor? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Why do T cells express the vitamin D receptor?
Margherita T Cantorna. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011 Jan.
Abstract
Vitamin D is an important regulator of immune function. T cells express the vitamin D receptor (VDR) and have been shown to be direct and indirect vitamin D targets. Why should T cells be responsive to vitamin D? The data suggest that expression of the VDR is required for the development of two cell types, NKT cells and CD8αα T cells, which inhibit autoimmunity. In addition, effector T cell cytokine production is regulated by vitamin D. Available evidence suggests that NKT and CD8αα T cells express the VDR as part of the selection process to protect against the generation of autoimmunity, particularly in the gut.
© 2010 New York Academy of Sciences.
Figures
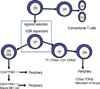
Figure 1
The role of vitamin D and the VDR in development of iNKT cells and TCRαβ CD8αα T cells. VDR KO mice have normal numbers of conventional CD4 and CD8 positive T cells. Conversely, VDR KO mice develop fewer less mature iNKT cells and TCRαβ CD8αα T cells. iNKT cells and TCRαβ CD8αα T cells diverge from conventional T cells at the DP stage when they undergo agonist selection under the influence of non-classical MHC class I molecules. Following selection the iNKT cells and TCRαβ CD8αα T cells diverge. It is likely that there is a common and vitamin D regulated step that occurs at this point in the development of these cell types.
Similar articles
- Vitamin D regulation of immune function in the gut: why do T cells have vitamin D receptors?
Ooi JH, Chen J, Cantorna MT. Ooi JH, et al. Mol Aspects Med. 2012 Feb;33(1):77-82. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2011.10.014. Epub 2011 Nov 6. Mol Aspects Med. 2012. PMID: 22079836 Free PMC article. Review. - Intrinsic requirement for the vitamin D receptor in the development of CD8αα-expressing T cells.
Bruce D, Cantorna MT. Bruce D, et al. J Immunol. 2011 Mar 1;186(5):2819-25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003444. Epub 2011 Jan 26. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21270396 Free PMC article. - ZBTB7B (Th-POK) regulates the development of IL-17-producing CD1d-restricted mouse NKT cells.
Enders A, Stankovic S, Teh C, Uldrich AP, Yabas M, Juelich T, Altin JA, Frankenreiter S, Bergmann H, Roots CM, Kyparissoudis K, Goodnow CC, Godfrey DI. Enders A, et al. J Immunol. 2012 Dec 1;189(11):5240-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201486. Epub 2012 Oct 26. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23105140 Free PMC article. - Control of T cell effector functions by miRNAs.
Inácio DP, Amado T, Silva-Santos B, Gomes AQ. Inácio DP, et al. Cancer Lett. 2018 Jul 28;427:63-73. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.04.011. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 29679611 Review.
Cited by
- Modulation of the immune system by UV radiation: more than just the effects of vitamin D?
Hart PH, Gorman S, Finlay-Jones JJ. Hart PH, et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011 Aug 19;11(9):584-96. doi: 10.1038/nri3045. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21852793 Review. - Metabolic profiling of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: influence of vitamin d status and gender.
Stepien M, Nugent AP, Brennan L. Stepien M, et al. Metabolites. 2014 Apr 22;4(2):248-59. doi: 10.3390/metabo4020248. Metabolites. 2014. PMID: 24957025 Free PMC article. - Vitamin D Levels as a Potential Modifier of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Severity in Adults.
Cameron BA, Anderson CW, Jensen ET, Dellon ES. Cameron BA, et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2024 Apr;69(4):1287-1292. doi: 10.1007/s10620-023-08264-x. Epub 2024 Jan 6. Dig Dis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38183560 - The Anti-Inflammatory Roles of Vitamin D for Improving Human Health.
Fenercioglu AK. Fenercioglu AK. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Nov 26;46(12):13514-13525. doi: 10.3390/cimb46120807. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39727935 Free PMC article. Review. - Vitamin d deficiency is associated with ulcerative colitis disease activity.
Blanck S, Aberra F. Blanck S, et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2013 Jun;58(6):1698-702. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2531-7. Epub 2013 Jan 19. Dig Dis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23334382
References
- Bhalla AK, Amento EP, Clemens TL, Holick MF, Krane SM. Specific high-affinity receptors for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: presence in monocytes and induction in T lymphocytes following activation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983;57:1308–1310. - PubMed
- Provvedini DM, Tsoukas CD, Deftos LJ, Manolagas SC. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors in human leukocytes. Science. 1983;221:1181–1183. - PubMed
- Muller K, Odum N, Bendtzen K. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 selectively reduces interleukin-2 levels and proliferation of human T cell lines in vitro. Immunol Lett. 1993;35:177–182. - PubMed
- Tsoukas CD, et al. Inhibition of interleukin-1 production by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989;69:127–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AT005378/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- AT005378/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- DK070781/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK070781/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS067563/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources