The Parkinson disease protein α-synuclein inhibits autophagy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The Parkinson disease protein α-synuclein inhibits autophagy
Ashley R Winslow et al. Autophagy. 2011 Apr.
Abstract
Parkinson disease (PD) is the most common movement disorder affecting people. It is characterized by the accumulation of the protein α-synuclein in Lewy body inclusions in vulnerable neurons. α-Synuclein overexpression caused by gene multiplications is sufficient to cause this disease, suggesting that α-synuclein accumulation is toxic. Here we review our recent study showing that α-synuclein inhibits autophagy. We discuss our mechanistic understanding of this phenomenon and also speculate how a deficiency in autophagy may contribute to a range of pleiotropic features of PD biology.
Figures
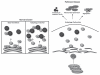
Figure 1
Autophagy inhibition by alpha-synuclein may contribute to Parkinson disease pathogenesis. In normal, healthy cells, Atg9 colocalizes with the trans-Golgi network and LC3-positive vesicles (shown in blue). Upon autophagy induction, Atg9 is mobilized away from the TGN to LC3-positive vesicles, which correlates with increased autophagosome synthesis. Our data show that overexpression of alpha-synuclein disrupts the normal localization and mobilization of Atg9 to LC3-positive vesicles, which correlates with decreased autophagosome synthesis and dysfunctional autophagy. This phenomenon may be a major contributor to PD pathogenesis, as inhibition of autophagy can increase aggregation, sensitivity to pro-apoptotic insults and mitochondrial dysfunction, all of which are associated with PD pathogenesis.
Similar articles
- α-Synuclein impairs macroautophagy: implications for Parkinson's disease.
Winslow AR, Chen CW, Corrochano S, Acevedo-Arozena A, Gordon DE, Peden AA, Lichtenberg M, Menzies FM, Ravikumar B, Imarisio S, Brown S, O'Kane CJ, Rubinsztein DC. Winslow AR, et al. J Cell Biol. 2010 Sep 20;190(6):1023-37. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201003122. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20855506 Free PMC article. - p62/SQSTM1-dependent autophagy of Lewy body-like α-synuclein inclusions.
Watanabe Y, Tatebe H, Taguchi K, Endo Y, Tokuda T, Mizuno T, Nakagawa M, Tanaka M. Watanabe Y, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52868. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052868. Epub 2012 Dec 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300799 Free PMC article. - Aggregate clearance of α-synuclein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae depends more on autophagosome and vacuole function than on the proteasome.
Petroi D, Popova B, Taheri-Talesh N, Irniger S, Shahpasandzadeh H, Zweckstetter M, Outeiro TF, Braus GH. Petroi D, et al. J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 10;287(33):27567-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.361865. Epub 2012 Jun 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22722939 Free PMC article. - Ubiquitination of alpha-synuclein and autophagy in Parkinson's disease.
Engelender S. Engelender S. Autophagy. 2008 Apr;4(3):372-4. doi: 10.4161/auto.5604. Epub 2008 Jan 18. Autophagy. 2008. PMID: 18216494 Review. - Alpha-synuclein, autophagy-lysosomal pathway, and Lewy bodies: Mutations, propagation, aggregation, and the formation of inclusions.
Bayati A, McPherson PS. Bayati A, et al. J Biol Chem. 2024 Oct;300(10):107742. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107742. Epub 2024 Sep 2. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39233232 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- α-Synuclein: Multiple pathogenic roles in trafficking and proteostasis pathways in Parkinson's disease.
Zalon AJ, Quiriconi DJ, Pitcairn C, Mazzulli JR. Zalon AJ, et al. Neuroscientist. 2024 Oct;30(5):612-635. doi: 10.1177/10738584241232963. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Neuroscientist. 2024. PMID: 38420922 Review. - Autophagy Activation Is Involved in Acidic Fibroblast Growth Factor Ameliorating Parkinson's Disease via Regulating Tribbles Homologue 3.
Zhong X, Wang B, Zhang G, Yuan Y, Hu X, Xiong J, Zheng P, Liu Y, Xu K, Xiao J, Wu Y, Ye J. Zhong X, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2019 Dec 2;10:1428. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01428. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31849673 Free PMC article. - Is There a Place for Lewy Bodies before and beyond Alpha-Synuclein Accumulation? Provocative Issues in Need of Solid Explanations.
Lenzi P, Lazzeri G, Ferrucci M, Scotto M, Frati A, Puglisi-Allegra S, Busceti CL, Fornai F. Lenzi P, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 1;25(7):3929. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073929. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612739 Free PMC article. Review. - Autophagy modulation as a potential therapeutic target for diverse diseases.
Rubinsztein DC, Codogno P, Levine B. Rubinsztein DC, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 Sep;11(9):709-30. doi: 10.1038/nrd3802. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22935804 Free PMC article. Review. - Singular value decomposition analysis of the secondary structure features contributing to the circular dichroism spectra of model proteins.
Shiratori T, Goto S, Sakaguchi T, Kasai T, Otsuka Y, Higashi K, Makino K, Takahashi H, Komatsu K. Shiratori T, et al. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Oct 18;28:101153. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101153. eCollection 2021 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 34712848 Free PMC article.
References
- J Cell Biol. 2010 Sep 20;190(6):1023-37 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical