Harmine is an ATP-competitive inhibitor for dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (Dyrk1A) - PubMed (original) (raw)
Harmine is an ATP-competitive inhibitor for dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (Dyrk1A)
Tatyana Adayev et al. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2011.
Abstract
Harmine is a β-carboline alkaloid. The compound is a potent inhibitor of dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (Dyrk1A), a kinase implicated in Down syndrome. In this study, we show that harmine functions as an ATP-competitive inhibitor against Dyrk1A. Our conclusion is supported by kinetic analysis of harmine inhibition as well as by the characterization of a Dyrk1A mutation conferring significant resistance to harmine. The mutation, V306A, is located next to the highly conserved D307 residue in kinases known to coordinate the phosphate groups of ATP through a Mg²+ ion. The V306A mutation offers harmine resistance by differentially altering Dyrk1A affinity for harmine and ATP. The V306A mutation causes no apparent alteration to Dyrk1A activity except for the reduction in ATP affinity. This deficiency could be fully compensated by supplying ATP with a concentration in the physiological range. Our results reveal that harmine inhibits Dyrk1A activity by interacting with residues in the ATP-binding pocket and displacing ATP. Our results also suggest that harmine will be a good lead compound for further designing of selective ATP-competitive Dyrk1A inhibitors through exploration of the ATP-binding pocket of Dyrk1A.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
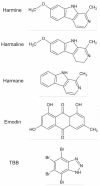
Fig. 1
Harmine derivatives, emodin, and TBB.
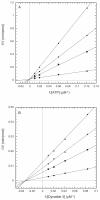
Fig. 2. Inhibition of Dyrk1A by harmine
A. Competition of harmine against ATP. Harmine and ATP competition was performed with varied ATP (10-100 μM) and harmine (0 - 0.4 μM) at a constant dynatide 3 (24 μM) as described in the Materials and Methods. The initial rate (V) obtained from three independent trials was averaged and plotted as 1/V vs 1/[ATP]. KI was calculated from the secondary plot of apparent Km vs. [harmine]. B. Competition of harmine against dynatide 3. The reaction was performed with varied dynatide 3 (12-96 μM) and harmine (0 - 0.4 μM) at a constant ATP (50 μM) similarly as described above. The initial rate (V) obtained from three independent trials was averaged and was plotted as 1/V vs 1/[dynatide 3]. KI was calculated from the secondary plot of apparent Vmax vs. [harmine]. Harmine concentrations used in the reactions: (●) 0, (■) 0.1 μM, (◆) 0.2 μM, (▲) 0.4 μM.
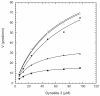
Fig. 3. Activity of the V306A mutant with high concentrations of ATP in vitro
Dynatide 3 concentration-dependent reactions were performed with 6-96 μM peptide in the presence of a constant ATP as described in Materials and Methods. Data (reaction rate) from three independent assays were averaged and used for plotting against [dynatide 3] followed by curve fitting using the Michaelis-Menten equation (v = Vmax*[dynatide 3]/(Km+[dynatide 3]). WT with 250 μM (□), 500 μM (not shown), and 1000 μM (○) ATP. The V306A mutant with 250 μM (■), 500 μM (◆), and 1000 μM (●) ATP.
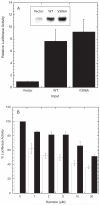
Fig. 4. Activity and harmine sensitivity of the V306A mutant in NIH 3T3 cells
A. Kinase activity. Dyrk1A activity in 3T3 cells was measured by using Gli 1-dependent transcription of luciferase as the reporter as described in Materials and Methods. The reaction was driven either by empty pCMV (vector), wild-type (WT) or mutant V306A (306) Dyrk1A. After correcting for the internal control, the luciferase output was normalized to the reactions promoted by empty pCMV(set as 1) before plotting. The data represent the average (± standard error) of four independent trials. The level of Dyrk1A expression (insert) in transfected cells was detected as described in Materials and Methods. A typical result was shown. B. Harmine sensitivity. WT and mutant V306A-driven luciferase synthesis was set up similarly as described above. After transfection, cells were incubated for 20 hours to allow Dyrk1A expression before treating with the indicated concentrations of harmine for 24-hour until luciferase determination. The luciferase activity at each harmine concentration was calculated as the percent of activity relative to each respective luciferase output for the no harmine control (set as 100%). The data represent the average (± standard error) of four independent trials. WT, open column and mutant V306A, solid column.
Similar articles
- Harmine specifically inhibits protein kinase DYRK1A and interferes with neurite formation.
Göckler N, Jofre G, Papadopoulos C, Soppa U, Tejedor FJ, Becker W. Göckler N, et al. FEBS J. 2009 Nov;276(21):6324-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07346.x. Epub 2009 Oct 1. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 19796173 - Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of harmine derivatives as potent GSK-3β/DYRK1A dual inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Liu W, Liu X, Tian L, Gao Y, Liu W, Chen H, Jiang X, Xu Z, Ding H, Zhao Q. Liu W, et al. Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Oct 15;222:113554. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113554. Epub 2021 May 29. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34098466 - Rational Design and Identification of Harmine-Inspired, N-Heterocyclic DYRK1A Inhibitors Employing a Functional Genomic In Vivo Drosophila Model System.
Huizar FJ, Hill HM, Bacher EP, Eckert KE, Gulotty EM, Rodriguez KX, Tucker ZD, Banerjee M, Liu H, Wiest O, Zartman J, Ashfeld BL. Huizar FJ, et al. ChemMedChem. 2022 Feb 16;17(4):e202100512. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202100512. Epub 2022 Jan 27. ChemMedChem. 2022. PMID: 34994084 Free PMC article. - Dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A) inhibitors: a survey of recent patent literature.
Nguyen TL, Fruit C, Hérault Y, Meijer L, Besson T. Nguyen TL, et al. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Nov;27(11):1183-1199. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2017.1360285. Epub 2017 Aug 2. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017. PMID: 28766366 Review. - Activation, regulation, and inhibition of DYRK1A.
Becker W, Sippl W. Becker W, et al. FEBS J. 2011 Jan;278(2):246-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07956.x. Epub 2010 Dec 3. FEBS J. 2011. PMID: 21126318 Review.
Cited by
- DYRK1A: a down syndrome-related dual protein kinase with a versatile role in tumorigenesis.
Laham AJ, Saber-Ayad M, El-Awady R. Laham AJ, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jan;78(2):603-619. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03626-4. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32870330 Free PMC article. Review. - A dual specificity kinase, DYRK1A, as a potential therapeutic target for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Radhakrishnan A, Nanjappa V, Raja R, Sathe G, Puttamallesh VN, Jain AP, Pinto SM, Balaji SA, Chavan S, Sahasrabuddhe NA, Mathur PP, Kumar MM, Prasad TS, Santosh V, Sukumar G, Califano JA, Rangarajan A, Sidransky D, Pandey A, Gowda H, Chatterjee A. Radhakrishnan A, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 31;6:36132. doi: 10.1038/srep36132. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27796319 Free PMC article. - Ayahuasca: Psychological and Physiologic Effects, Pharmacology and Potential Uses in Addiction and Mental Illness.
Hamill J, Hallak J, Dursun SM, Baker G. Hamill J, et al. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2019;17(2):108-128. doi: 10.2174/1570159X16666180125095902. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2019. PMID: 29366418 Free PMC article. Review. - A review on medicinal importance, pharmacological activity and bioanalytical aspects of beta-carboline alkaloid ''Harmine''.
Patel K, Gadewar M, Tripathi R, Prasad SK, Patel DK. Patel K, et al. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2012 Aug;2(8):660-4. doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(12)60116-6. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2012. PMID: 23569990 Free PMC article. Review. - Influence of prenatal EGCG treatment and Dyrk1a dosage reduction on craniofacial features associated with Down syndrome.
McElyea SD, Starbuck JM, Tumbleson-Brink DM, Harrington E, Blazek JD, Ghoneima A, Kula K, Roper RJ. McElyea SD, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Nov 15;25(22):4856-4869. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw309. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 28172997 Free PMC article.
References
- Tejedor FJ, Hämmerle B. FEBS J. 2010;277 doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07954.x. - PubMed
- Marti E, Altafaj X, Dierssen M, de la Luna S, Fotaki V, Alvarez M, Perez-Riba M, Ferrer I, Estivill X. Brain Res. 2003;964:250–263. - PubMed
- Wegiel J, Kuchna I, Nowicki K, Frackowiak J, Dowjat K, Silverman WP, Reisberg B, DeLeon M, Wisniewski T, Adayev T, Chen-Hwang MC, Hwang YW. Brain Res. 2004;1010:69–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD043960/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD043960-05/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01HD043960/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources