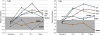Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in ischemic stroke: outcome and therapeutic values - PubMed (original) (raw)
Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in ischemic stroke: outcome and therapeutic values
David Brea et al. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011 Jun.
Abstract
Stroke triggers an intense inflammatory response that could be a consequence of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) activation. However, the clinical significance and the therapeutic possibilities of TLR in stroke is not completely clear. In this study, we analyze the association between the expression of TLR2 and TLR4, inflammatory molecules and endogenous ligands, and clinical outcome of ischemic stroke patients, and we test the potential of TLR2/TLR4 and their endogenous ligands as therapeutic targets. For this purpose, we included 110 patients with ischemic stroke finding that TLR2 and TLR4 are independently associated to poor outcome and correlated with higher serum levels of interleukin (IL)1β, IL6, tumor necrosis factor α, and VCAM1, and that TLR4 was independently associated to lesion volume. In addition, we have developed an in vitro model to test the potential therapeutic value of blocking TLR2/TLR4 or their endogenous ligands. Cultured cells (monocytes and human umbilical vein endothelial cells) were treated with serum from ischemic stroke patients, showing a strong inflammatory response that was blocked when TLR2/4 or cellular fibronectin (cFN) or HSP60 were blocked. In conclusion, TLR2 and TLR4 are associated to outcome in stroke patients and TLR2/4 or their endogenous ligands, cFN/HSP60 could be new therapeutic targets for ischemic stroke.
Figures
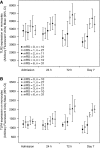
Figure 1
TLR2 (A) and TLR4 (B) expression by the score of the Rankin scale evaluated at 3 months. CI, confidence interval; mRs, Modified Rankin Scale; TLR, Toll-like receptor.
Figure 2
Graphic representations of Pearson coefficients between the expression of TLR2 and 4 on admission (n_=110 patients), and levels of inflammatory (interleukin (IL)1_β, tumor necrosis factor α (TNF_α_), IL6, and matrix metalloproteinases 9 (MMP9)) and adhesion molecules (VCAM1 and ICAM1) at baseline, 24 hours, 72 hours, and 7 days. Gray-shadowed points represent coefficients that were not statistically significant. Hollowed points represent statistically significant coefficients. ICAM1, Intercellular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1; TLR, Toll-like receptor; VCAM1, Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1.
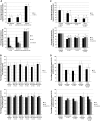
Figure 3
Graphical representation of levels of inflammatory markers in the supernatant of monocytes (left graphic) and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) (right graphic) cultured during 18 hours. (A) With culture medium (left bars labeled as ‘only medium'), with culture medium plus serum from healthy control subjects (bars on the center of the chart, labeled as ‘negative control') and with culture medium plus serum from ischemic patients (bars on the right of the chart, labeled as ‘positive control'); (B) with culture medium without any treatment (only medium), with culture medium with anti-TLR2 (medium+anti-TLR2), with culture medium with anti-TLR4 (medium+anti-TLR4), with culture medium with anti-cFN (medium+anti-cFN), with culture medium with anti-HSP60 (medium+anti-HSP60), and with culture medium with anti-HSP70 (medium+anti-HSP70); (C) with culture medium without pretreatment (positive control), and previously treated with anti-TLR2 (TLR2 blockade) anti-TLR4 (TLR4 blockade) and anti-TLR2 and 4 (TLR2/4 blockade); (D) with culture medium and serum from patients (positive control) and culture medium and serum from patients treated to block cFN blockade), HSP60 (HSP60 blockade), HSP70 (HSP70 blockade) and the three ligands at once (three ligands blockade) (*P<0.01). cFN, cellular fibronectin; IL, interleukin; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Similar articles
- Synergism of toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), TLR4, and TLR6 ligation on the production of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha in a spontaneous arthritis animal model of interleukin (IL)-1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice.
Jung YO, Cho ML, Lee SY, Oh HJ, Park JS, Park MK, Park MJ, Ju JH, Kim SI, Park SH, Kim HY, Min JK. Jung YO, et al. Immunol Lett. 2009 Apr 27;123(2):138-43. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2009.03.004. Epub 2009 Mar 21. Immunol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19428561 - Increased toll-like receptor (TLR) activation and TLR ligands in recently diagnosed type 2 diabetic subjects.
Dasu MR, Devaraj S, Park S, Jialal I. Dasu MR, et al. Diabetes Care. 2010 Apr;33(4):861-8. doi: 10.2337/dc09-1799. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Diabetes Care. 2010. PMID: 20067962 Free PMC article. - Salvianolic acid A alleviated inflammatory response mediated by microglia through inhibiting the activation of TLR2/4 in acute cerebral ischemia-reperfusion.
Ling Y, Jin L, Ma Q, Huang Y, Yang Q, Chen M, Shou Q. Ling Y, et al. Phytomedicine. 2021 Jul;87:153569. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153569. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33985878 - Toll-like receptors 2 and 4: initiators of non-septic inflammation in critical care medicine?
Lorne E, Dupont H, Abraham E. Lorne E, et al. Intensive Care Med. 2010 Nov;36(11):1826-35. doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-1983-5. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Intensive Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20689929 Free PMC article. Review. - The regulatory role of Toll-like receptors after ischemic stroke: neurosteroids as TLR modulators with the focus on TLR2/4.
Tajalli-Nezhad S, Karimian M, Beyer C, Atlasi MA, Azami Tameh A. Tajalli-Nezhad S, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Feb;76(3):523-537. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2953-2. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30377701 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Neuroprotection during Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Review of Future Therapies.
Dammavalam V, Lin S, Nessa S, Daksla N, Stefanowski K, Costa A, Bergese S. Dammavalam V, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 10;25(2):891. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020891. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255965 Free PMC article. Review. - Blood microRNAs in low or no risk ischemic stroke patients.
Tan JR, Tan KS, Koo YX, Yong FL, Wang CW, Armugam A, Jeyaseelan K. Tan JR, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jan 22;14(1):2072-84. doi: 10.3390/ijms14012072. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23340648 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - TLR7 rs2897827 Polymorphism Affects TLR7 Gene mRNA Expression and Serum Apolipoprotein A1 Level of Ischemic Stroke Patients in a Chinese Han Population.
Gu L, Zhou J, Tan J, Su L, Wei Q, Jiang H, Liang B, Tang Q. Gu L, et al. J Mol Neurosci. 2016 Jul;59(3):397-403. doi: 10.1007/s12031-016-0773-0. Epub 2016 Jul 18. J Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27427388 - Combination Therapy with Low-Dose IVIG and a C1-esterase Inhibitor Ameliorates Brain Damage and Functional Deficits in Experimental Ischemic Stroke.
Chen X, Arumugam TV, Cheng YL, Lee JH, Chigurupati S, Mattson MP, Basta M. Chen X, et al. Neuromolecular Med. 2018 Mar;20(1):63-72. doi: 10.1007/s12017-017-8474-6. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Neuromolecular Med. 2018. PMID: 29299869 Free PMC article. - Emerging Roles of microRNAs in Ischemic Stroke: As Possible Therapeutic Agents.
Khoshnam SE, Winlow W, Farbood Y, Moghaddam HF, Farzaneh M. Khoshnam SE, et al. J Stroke. 2017 May;19(2):166-187. doi: 10.5853/jos.2016.01368. Epub 2017 May 8. J Stroke. 2017. PMID: 28480877 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Adams HP, Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE., III Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993;24:35–41. - PubMed
- Adams HP, Jr, Davis PH, Leira EC, Chang KC, Bendixen BH, Clarke WR, Woolson RF, Hansen MD. Baseline NIH Stroke Scale score strongly predicts outcome after stroke: a report of the Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) Neurology. 1999;53:126–131. - PubMed
- Akira S. TLR signaling. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;311:1–16. - PubMed
- Cao CX, Yang QW, Lv FL, Cui J, Fu HB, Wang JZ. Reduced cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in Toll-like receptor 4 deficient mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;353:509–514. - PubMed
- Caso JR, Pradillo JM, Hurtado O, Leza JC, Moro MA, Lizasoain I. Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in subacute stress-induced neuroinflammation and in the worsening of experimental stroke. Stroke. 2008;39:1314–1320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous