Autosomal-dominant Alzheimer's disease: a review and proposal for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Autosomal-dominant Alzheimer's disease: a review and proposal for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease
Randall J Bateman et al. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2011.
Abstract
Autosomal-dominant Alzheimer's disease has provided significant understanding of the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease. The present review summarizes clinical, pathological, imaging, biochemical, and molecular studies of autosomal-dominant Alzheimer's disease, highlighting the similarities and differences between the dominantly inherited form of Alzheimer's disease and the more common sporadic form of Alzheimer's disease. Current developments in autosomal-dominant Alzheimer's disease are presented, including the international Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network and this network's initiative for clinical trials. Clinical trials in autosomal-dominant Alzheimer's disease may test the amyloid hypothesis, determine the timing of treatment, and lead the way to Alzheimer's disease prevention.
Figures
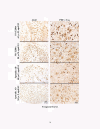
Figure 1
Principal neuropathological changes in autosomal-dominant Alzheimer's disease. Sections showing amyloid-beta (Aβ)42 and PHF-1 tau detection (top to bottom): presenilin 1 (PS1) E280A (male, 62 years old, disease duration 8 years, apolipoprotein E3/3); PS1 E280A (male, 50 years old, disease duration 5 years, apolipoprotein E3/3); sporadic Alzheimer's disease (SAD) (female, 80 years old, disease duration 7 years, apolipoprotein E3/3); SAD (female, 84 years old, disease duration 13 years, apolipoprotein E4/4). All brain tissues were routinely fixed in formalin and were paraffin-embedded. Sections were 12 μm thick. Aβ42 was detected using polyclonal antibody C42 (with formic acid pretreatment), kindly provided by Dr Takaomi Saido (RIKEN Brain Science Institute, Tokyo, Japan). PHF-1 tau was detected using PHF-1 monoclonal antibody (with microwave pretreatment), kindly provided by Dr Peter Davies (Feinstein Institute of Medical Research, New York, USA).
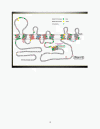
Figure 2
Overview of dominantly inherited mutations in the amyloid precursor protein. Amyloid precursor protein (APP) is a type I integral membrane protein inserted in the cell membrane (upper part). The APP mutations are all clustered in or around the amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptide sequence, and this region is therefore displayed enlarged using the single amino acid code. White circles, mutations found; red font, resulting amino acid substitutions. Mutations cluster around the α-secretase, β-secretase and γ-secretase sites as indicated. They have various effects on the generation of Aβ as indicated, but their overall effect is an increased tendency to generate toxic species.
Figure 3
Overview of dominantly inherited mutations in presenilin 1. Presenilin contains nine transmembrane domains. The presenilin 1 mutations (red circles) are scattered over the protein, but most are in the hydrophobic domains of the protein. Green and yellow circles indicate whether the effect of the mutation on amyloid-beta (Aβ) production has been investigated: green, mutations that decrease Aβ40 production; yellow, mutations that increase Aβ42 production. In all cases, an increase of the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio has been found.
Similar articles
- Autosomal dominant and sporadic late onset Alzheimer's disease share a common in vivo pathophysiology.
Morris JC, Weiner M, Xiong C, Beckett L, Coble D, Saito N, Aisen PS, Allegri R, Benzinger TLS, Berman SB, Cairns NJ, Carrillo MC, Chui HC, Chhatwal JP, Cruchaga C, Fagan AM, Farlow M, Fox NC, Ghetti B, Goate AM, Gordon BA, Graff-Radford N, Day GS, Hassenstab J, Ikeuchi T, Jack CR, Jagust WJ, Jucker M, Levin J, Massoumzadeh P, Masters CL, Martins R, McDade E, Mori H, Noble JM, Petersen RC, Ringman JM, Salloway S, Saykin AJ, Schofield PR, Shaw LM, Toga AW, Trojanowski JQ, Vöglein J, Weninger S, Bateman RJ, Buckles VD. Morris JC, et al. Brain. 2022 Oct 21;145(10):3594-3607. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac181. Brain. 2022. PMID: 35580594 Free PMC article. - Differentiating amyloid beta spread in autosomal dominant and sporadic Alzheimer's disease.
Levitis E, Vogel JW, Funck T, Hachinski V, Gauthier S, Vöglein J, Levin J, Gordon BA, Benzinger T, Iturria-Medina Y, Evans AC; Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Levitis E, et al. Brain Commun. 2022 Apr 13;4(3):fcac085. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac085. eCollection 2022. Brain Commun. 2022. PMID: 35602652 Free PMC article. - Comparison of tau spread in people with Down syndrome versus autosomal-dominant Alzheimer's disease: a cross-sectional study.
Wisch JK, McKay NS, Boerwinkle AH, Kennedy J, Flores S, Handen BL, Christian BT, Head E, Mapstone M, Rafii MS, O'Bryant SE, Price JC, Laymon CM, Krinsky-McHale SJ, Lai F, Rosas HD, Hartley SL, Zaman S, Lott IT, Tudorascu D, Zammit M, Brickman AM, Lee JH, Bird TD, Cohen A, Chrem P, Daniels A, Chhatwal JP, Cruchaga C, Ibanez L, Jucker M, Karch CM, Day GS, Lee JH, Levin J, Llibre-Guerra J, Li Y, Lopera F, Roh JH, Ringman JM, Supnet-Bell C, van Dyck CH, Xiong C, Wang G, Morris JC, McDade E, Bateman RJ, Benzinger TLS, Gordon BA, Ances BM; Alzheimer's Biomarker Consortium-Down syndrome; Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network. Wisch JK, et al. Lancet Neurol. 2024 May;23(5):500-510. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(24)00084-X. Lancet Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38631766 Free PMC article. - Biological and Cognitive Markers of Presenilin1 E280A Autosomal Dominant Alzheimer's Disease: A Comprehensive Review of the Colombian Kindred.
Fuller JT, Cronin-Golomb A, Gatchel JR, Norton DJ, Guzmán-Vélez E, Jacobs HIL, Hanseeuw B, Pardilla-Delgado E, Artola A, Baena A, Bocanegra Y, Kosik KS, Chen K, Tariot PN, Johnson K, Sperling RA, Reiman EM, Lopera F, Quiroz YT. Fuller JT, et al. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2019;6(2):112-120. doi: 10.14283/jpad.2019.6. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 30756118 Free PMC article. Review. - Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network: facilitating research and clinical trials.
Moulder KL, Snider BJ, Mills SL, Buckles VD, Santacruz AM, Bateman RJ, Morris JC. Moulder KL, et al. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2013 Oct 17;5(5):48. doi: 10.1186/alzrt213. eCollection 2013. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 24131566 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The PANoptosis-related hippocampal molecular subtypes and key biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease patients.
Li CL, Wang Q, Wu L, Hu JY, Gao QC, Jiao XL, Zhang YX, Tang S, Yu Q, He PF. Li CL, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 11;14(1):23851. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75377-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39394418 Free PMC article. - Appraisal of cognition in preclinical Alzheimer's disease: a conceptual review.
Knopman DS, Caselli RJ. Knopman DS, et al. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2012;2(2):183-195. doi: 10.2217/NMT.12.5. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2012. PMID: 22798965 Free PMC article. - Effect of BDNFVal66Met on disease markers in dominantly inherited Alzheimer's disease.
Lim YY, Hassenstab J, Goate A, Fagan AM, Benzinger TLS, Cruchaga C, McDade E, Chhatwal J, Levin J, Farlow MR, Graff-Radford NR, Laske C, Masters CL, Salloway S, Schofield P, Morris JC, Maruff P, Bateman RJ; Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network. Lim YY, et al. Ann Neurol. 2018 Sep;84(3):424-435. doi: 10.1002/ana.25299. Epub 2018 Aug 25. Ann Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30014553 Free PMC article. - Plasma biomarker profiles in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease.
Johansson C, Thordardottir S, Laffita-Mesa J, Rodriguez-Vieitez E, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Graff C. Johansson C, et al. Brain. 2023 Mar 1;146(3):1132-1140. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac399. Brain. 2023. PMID: 36626935 Free PMC article. - Emergence of distinct and heterogeneous strains of amyloid beta with advanced Alzheimer's disease pathology in Down syndrome.
Maxwell AM, Yuan P, Rivera BM, Schaaf W, Mladinov M, Prasher VP, Robinson AC, DeGrado WF, Condello C. Maxwell AM, et al. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021 Dec 27;9(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s40478-021-01298-0. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021. PMID: 34961556 Free PMC article.
References
- Ferri CP, Prince M, Brayne C, Brodaty H, Fratiglioni L, Ganguli M, Hall K, Hasegawa K, Hendrie H, Huang Y, Jorm A, Mathers C, Menezes PR, Rimmer E, Scazufca M. Global prevalence of dementia: a Delphi consensus study. Lancet. 2005;366:2112–2117. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67889-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Lowenberg K, Waggoner RW. Familial organic psychosis (Alzheimer's type) Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1934;31:737–754.
- Flugel FE. Zur Diagnostik der Alzheimershen Krankheit. Zentralbl Gesamte Neurol Psychiatr. 1929;120:783–787. doi: 10.1007/BF02864478. - DOI
- Lauter H. Genealogical findings in a family with Alzheimer's disease. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr Z Gesamte Neurol Psychiatr. 1961;202:126–139. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources