Biology, risk stratification, and therapy of pediatric acute leukemias: an update - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Biology, risk stratification, and therapy of pediatric acute leukemias: an update
Ching-Hon Pui et al. J Clin Oncol. 2011.
Erratum in
- J Clin Oncol. 2011 Dec 20;29(36):4847
Abstract
Purpose: We review recent advances in the biologic understanding and treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML), identify therapeutically challenging subgroups, and suggest future directions of research.
Methods: A review of English literature on childhood acute leukemias from the past 5 years was performed.
Results: Contemporary treatments have resulted in 5-year event-free survival rates of approximately 80% for childhood ALL and almost 60% for pediatric AML. The advent of high-resolution genome-wide analyses has provided new insights into leukemogenesis and identified many novel subtypes of leukemia. Virtually all ALL and the vast majority of AML cases can be classified according to specific genetic abnormalities. Cooperative mutations involved in cell differentiation, cell cycle regulation, tumor suppression, drug responsiveness, and apoptosis have also been identified in many cases. The development of new formulations of existing drugs, molecularly targeted therapy, and immunotherapies promises to further advance the cure rates and improve quality of life of patients.
Conclusion: The application of new high-throughput sequencing techniques to define the complete DNA sequence of leukemia and host normal cells and the development of new agents targeted to leukemogenic pathways promise to further improve outcome in the coming decade.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
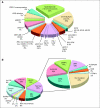
Fig 1.
Estimated frequency of specific genotypes in childhood leukemias. (A) Genetic abnormalities in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Data were modified from Pui et al by including recently identified genotypes. The genetic lesions that are exclusively seen in cases of T-cell ALL are indicated in purple. (B) Genetic abnormalities in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Panel to the left demonstrates the most common karyotypic alterations. Eighty percent of all children have disease-associated genomic structural alterations. Mutation profile in those without cytogenetic abnormalities (normal karyotype) is shown in the right panel. Seventy-six percent of those in the normal karyotype population have one of the known mutations; thus, more than 95% of all children with AML have at least one known genomic abnormality. (With permission from Reaman and Smith).
Similar articles
- [Therapeutic strategies for childhood high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia].
Lu XT. Lu XT. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013 Apr 18;45(2):327-32. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013. PMID: 23591360 Review. Chinese. - Driving Toward Precision Medicine for Acute Leukemias: Are We There Yet?
Chung C, Ma H. Chung C, et al. Pharmacotherapy. 2017 Sep;37(9):1052-1072. doi: 10.1002/phar.1977. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Pharmacotherapy. 2017. PMID: 28654205 Review. - Childhood and adolescent lymphoid and myeloid leukemia.
Pui CH, Schrappe M, Ribeiro RC, Niemeyer CM. Pui CH, et al. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2004:118-45. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2004.1.118. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2004. PMID: 15561680 Review. - How new advances in genetic analysis are influencing the understanding and treatment of childhood acute leukemia.
Roberts KG, Mullighan CG. Roberts KG, et al. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2011 Feb;23(1):34-40. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e3283426260. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2011. PMID: 21169835 Review. - Childhood leukemias--current status and future perspective.
Pui CH. Pui CH. Zhonghua Min Guo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1995 Sep-Oct;36(5):322-7. Zhonghua Min Guo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1995. PMID: 8607355 Review.
Cited by
- DNA methylation-based subtype prediction for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Nordlund J, Bäcklin CL, Zachariadis V, Cavelier L, Dahlberg J, Öfverholm I, Barbany G, Nordgren A, Övernäs E, Abrahamsson J, Flaegstad T, Heyman MM, Jónsson ÓG, Kanerva J, Larsson R, Palle J, Schmiegelow K, Gustafsson MG, Lönnerholm G, Forestier E, Syvänen AC. Nordlund J, et al. Clin Epigenetics. 2015 Feb 17;7(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13148-014-0039-z. eCollection 2015. Clin Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 25729447 Free PMC article. - Untargeted metabolomics of newborn dried blood spots reveals sex-specific associations with pediatric acute myeloid leukemia.
Petrick L, Imani P, Perttula K, Yano Y, Whitehead T, Metayer C, Schiffman C, Dolios G, Dudoit S, Rappaport S. Petrick L, et al. Leuk Res. 2021 Jul;106:106585. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2021.106585. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Leuk Res. 2021. PMID: 33971561 Free PMC article. - Improvement of the Outcome of Relapsed or Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children Using a Risk-Based Treatment Strategy.
Ceppi F, Duval M, Leclerc JM, Laverdiere C, Delva YL, Cellot S, Teira P, Bittencourt H. Ceppi F, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Sep 15;11(9):e0160310. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160310. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27632202 Free PMC article. - Targeted drug discovery for pediatric leukemia.
Napper AD, Watson VG. Napper AD, et al. Front Oncol. 2013 Jul 8;3:170. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00170. eCollection 2013. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23847761 Free PMC article. - Gastric carcinoma subsequent to myelodysplastic syndrome with t (1; 19) chromosome translocation: A rare case report and its potential mechanisms.
Yu W, Chen G, Sun Y, Gao S, Li W, Cui J, Sun J. Yu W, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jul;97(30):e11535. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011535. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30045276 Free PMC article.
References
- Conter V, Aricò M, Basso G, et al. Long-term results of the Italian Association of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology (AIEOP) Studies 82, 87, 88, 91 and 95 for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2010;24:255–264. - PubMed
- Möricke A, Zimmermann M, Reiter A, et al. Long-term results of five consecutive trials in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia performed by the ALL-BFM study group from 1981 to 2000. Leukemia. 2010;24:265–284. - PubMed
- Escherich G, Horstmann MA, Zimmermann M, et al. Cooperative study group for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (COALL): Long-term results of trials 82,85,89,92 and 97. Leukemia. 2010;24:298–308. - PubMed
- Stary J, Jabali Y, Trka J, et al. Long-term results of treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the Czech Republic. Leukemia. 2010;24:425–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous