SLAMF6-driven co-stimulation of human peripheral T cells is defective in SLE T cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
SLAMF6-driven co-stimulation of human peripheral T cells is defective in SLE T cells
Madhumouli Chatterjee et al. Autoimmunity. 2011 May.
Abstract
The CD28 co-stimulatory pathway is well established for T cell activation. However, there is evidence suggesting the existence of additional co-stimulatory pathways. Here we report that a member of the SLAM superfamily, SLAMF6, or CD352 plays an important role in T cell co-stimulation. Cross-linking of SLAMF6 with anti-CD3 primes human T cell to secrete Th1 cytokines. Among the T cell subsets, CD8(+) and CD3(+)CD4(-)CD8(-) cells display the highest Th1 production responses. Engagement of SLAMF6 mobilizes the modulation of the same set of NF-κB-associated genes. Although the expression of SLAMF6 on the surface of T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) T cells is comparable to that on the normal T cells, engagement of SLAMF6 results in severely reduced Th1 and IL-2 cytokine production. Our results suggest the existence of an additional co-stimulatory pathway in human T cells, which is defective in SLE T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest: The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
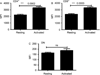
Figure 1
Cell-surface expression of SLAMF6 is upregulated in activated human T cells. Expression was detected on resting and activated T cells by flow cytometry using a PE-labeled monoclonal antibody against SLAMF6. SLAMF6 expression on (A) CD4+, (B) CD8+ and (C) DN T cells.
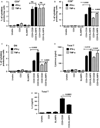
Figure 2
SLAMF6 co-stimulation leads to production of Th1 cytokines and IL-2 by total T cells. SLAMF6 co-stimulation induces the intracellular production of IFN-γ and TNF-α in (A) CD4+, (B) CD8+ and (C) DN T cells. (D) SLAMF6 co-stimulation leads to IFN-γ and TNF-α secretion by total T cells. Black graphs: IFN-γ; striped graphs: TNF-α. (E) SLAMF6 co-stimulation leads to IL-2 secretion by total T cells.
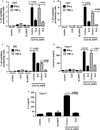
Figure 3
Cytokine production after SLAMF6 co-stimulation of SLE T cells. SLAMF6 co-stimulation induces the intracellular production of IFN-γ and TNF-α in (A) CD4+, (B) CD8+ and (C) DNSLE T cells. (D) SLAMF6 co-stimulation leads to IFN-γ and TNF-α secretion by total SLE T cells. Black graphs: IFN-γ; striped graphs: TNF-α. (E) SLAMF6 co-stimulation leads to IL-2 secretion by total SLE T cells.
Similar articles
- CD3-T cell receptor co-stimulation through SLAMF3 and SLAMF6 receptors enhances RORγt recruitment to the IL17A promoter in human T lymphocytes.
Chatterjee M, Hedrich CM, Rauen T, Ioannidis C, Terhorst C, Tsokos GC. Chatterjee M, et al. J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 2;287(45):38168-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.415067. Epub 2012 Sep 18. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22989874 Free PMC article. - Expansion of an osteopontin-expressing T follicular helper cell subset correlates with autoimmunity in B6.Sle1b mice and is suppressed by the H1-isoform of the Slamf6 receptor.
Keszei M, Detre C, Castro W, Magelky E, O'Keeffe M, Kis-Toth K, Tsokos GC, Wang N, Terhorst C. Keszei M, et al. FASEB J. 2013 Aug;27(8):3123-31. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-226951. Epub 2013 Apr 29. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23629864 Free PMC article. - Abnormal CTLA-4 function in T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Jury EC, Flores-Borja F, Kalsi HS, Lazarus M, Isenberg DA, Mauri C, Ehrenstein MR. Jury EC, et al. Eur J Immunol. 2010 Feb;40(2):569-78. doi: 10.1002/eji.200939781. Eur J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19950182 - SLAM family receptors and the SLAM-associated protein (SAP) modulate T cell functions.
Detre C, Keszei M, Romero X, Tsokos GC, Terhorst C. Detre C, et al. Semin Immunopathol. 2010 Jun;32(2):157-71. doi: 10.1007/s00281-009-0193-0. Epub 2010 Feb 10. Semin Immunopathol. 2010. PMID: 20146065 Free PMC article. Review. - Consequence of the SLAM-SAP signaling pathway in innate-like and conventional lymphocytes.
Veillette A, Dong Z, Latour S. Veillette A, et al. Immunity. 2007 Nov;27(5):698-710. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.11.005. Immunity. 2007. PMID: 18031694 Review.
Cited by
- B cell-intrinsic CD84 and Ly108 maintain germinal center B cell tolerance.
Wong EB, Soni C, Chan AY, Domeier PP, Shwetank, Abraham T, Limaye N, Khan TN, Elias MJ, Chodisetti SB, Wakeland EK, Rahman ZS. Wong EB, et al. J Immunol. 2015 May 1;194(9):4130-43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403023. Epub 2015 Mar 23. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25801429 Free PMC article. - SLE-Associated Defects Promote Altered T Cell Function.
Crispin JC, Hedrich CM, Suárez-Fueyo A, Comte D, Tsokos GC. Crispin JC, et al. Crit Rev Immunol. 2017;37(1):39-58. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2018025213. Crit Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29431078 Free PMC article. Review. - Decreased SAP Expression in T Cells from Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Contributes to Early Signaling Abnormalities and Reduced IL-2 Production.
Karampetsou MP, Comte D, Kis-Toth K, Terhorst C, Kyttaris VC, Tsokos GC. Karampetsou MP, et al. J Immunol. 2016 Jun 15;196(12):4915-24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501523. Epub 2016 May 11. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27183584 Free PMC article. - Association of IL-10 Gene Polymorphisms and Human T Lymphotropic Virus Type I-Associated Myelopathy/tropical Spastic Paraparesis in North-East of Iran (Mashhad).
Shirdel A, Azarpazhooh MR, Sahebari M, Ghanbari M, Mirfeizi SZ, Hutchinson I, Ziaee A, Rafatpanah H. Shirdel A, et al. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2013 Mar;16(3):258-63. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 24470873 Free PMC article. - Proliferating Transitory T Cells with an Effector-like Transcriptional Signature Emerge from PD-1+ Stem-like CD8+ T Cells during Chronic Infection.
Hudson WH, Gensheimer J, Hashimoto M, Wieland A, Valanparambil RM, Li P, Lin JX, Konieczny BT, Im SJ, Freeman GJ, Leonard WJ, Kissick HT, Ahmed R. Hudson WH, et al. Immunity. 2019 Dec 17;51(6):1043-1058.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.11.002. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Immunity. 2019. PMID: 31810882 Free PMC article.
References
- Greenwald RJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. The B7 family revisited. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:515–548. - PubMed
- Teft WA, Kirchhof MG, Madrenas J. A molecular perspective of CTLA-4 function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:65–97. - PubMed
- Valdez PA, Wang H, Seshasayee D, van Lookeren Campagne M, Gurney A, Lee WP, Grewal IS. NTB-A, a new activating receptor in T cells that regulates autoimmune disease. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:18662–18669. - PubMed
- Tsokos GC, Balow JE. Cellular immune responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Prog Allergy. 1984;35:93–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AI065687/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI042269/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01AI065687/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI42269/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials