Crystal structure of XMRV protease differs from the structures of other retropepsins - PubMed (original) (raw)
Crystal structure of XMRV protease differs from the structures of other retropepsins
Mi Li et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Feb.
Abstract
Using energy and density guided Rosetta refinement to improve molecular replacement, we determined the crystal structure of the protease encoded by xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus (XMRV). Despite overall similarity of XMRV protease to other retropepsins, the topology of its dimer interface more closely resembles those of the monomeric, pepsin-like enzymes. Thus, XMRV protease may represent a distinct branch of the aspartic protease family.
Figures
Figure 1
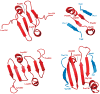
The structure of XMRV PR and a comparison with the fold of typical retroviral proteases. a) A dimer of XMRV PR in cartoon representation, with the two monomers colored cyan and blue and the catalytic aspartates shown as sticks. b) A superposition based on Cα coordinates of XMRV PR (cyan) and the apoenzyme of HIV-1 PR (green, PDB code 3hvp), shown in cartoon representation. c) Structure-based sequence alignment of the XMRV, HIV-1, and EIAV PRs, as well as Ddi1 RP. Secondary structure elements and residue numbers are marked above for XMRV PR and below for HIV-1 PR. Residues identical in all four enzymes are boxed. Panels a and b were prepared with PyMol.
Figure 2
Dimer interface regions in aspartic proteases. Strands belonging to the N-terminal regions of the molecules (or domains in pepsin) are blue, and the C-terminal regions are red. a) XMRV PR; b) HIV-1 PR; c) Ddi1 RP; d) pepsin.
Similar articles
- Inhibition of XMRV and HIV-1 proteases by pepstatin A and acetyl-pepstatin.
Matúz K, Mótyán J, Li M, Wlodawer A, Tőzsér J. Matúz K, et al. FEBS J. 2012 Sep;279(17):3276-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08714.x. Epub 2012 Aug 17. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22804908 Free PMC article. - NMR study of xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus protease in a complex with amprenavir.
Furukawa A, Okamura H, Morishita R, Matsunaga S, Kobayashi N, Ikegami T, Kodaki T, Takaori-Kondo A, Ryo A, Nagata T, Katahira M. Furukawa A, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Aug 24;425(2):284-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.07.083. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22842568 - Structural and biochemical characterization of the inhibitor complexes of xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus protease.
Li M, Gustchina A, Matúz K, Tözsér J, Namwong S, Goldfarb NE, Dunn BM, Wlodawer A. Li M, et al. FEBS J. 2011 Nov;278(22):4413-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08364.x. Epub 2011 Oct 10. FEBS J. 2011. PMID: 21951660 Free PMC article. - Lack of evidence for a role of xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer and/or chronic fatigue syndrome.
Hong P, Li J. Hong P, et al. Virus Res. 2012 Jul;167(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2012.04.004. Epub 2012 Apr 15. Virus Res. 2012. PMID: 22531412 Review. - Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus (XMRV) and the Safety of the Blood Supply.
Johnson AD, Cohn CS. Johnson AD, et al. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016 Oct;29(4):749-57. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00086-15. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27358491 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- RC1339/APRc from Rickettsia conorii is a novel aspartic protease with properties of retropepsin-like enzymes.
Cruz R, Huesgen P, Riley SP, Wlodawer A, Faro C, Overall CM, Martinez JJ, Simões I. Cruz R, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2014 Aug 21;10(8):e1004324. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004324. eCollection 2014 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25144529 Free PMC article. - High-resolution structure of a retroviral protease folded as a monomer.
Gilski M, Kazmierczyk M, Krzywda S, Zábranská H, Cooper S, Popović Z, Khatib F, DiMaio F, Thompson J, Baker D, Pichová I, Jaskolski M. Gilski M, et al. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2011 Nov;67(Pt 11):907-14. doi: 10.1107/S0907444911035943. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2011. PMID: 22101816 Free PMC article. - Crystal structures of the reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H domain of xenotropic murine leukemia-virus related virus.
Zhou D, Chung S, Miller M, Grice SF, Wlodawer A. Zhou D, et al. J Struct Biol. 2012 Mar;177(3):638-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2012.02.006. Epub 2012 Feb 16. J Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22366278 Free PMC article. - phenix.mr_rosetta: molecular replacement and model rebuilding with Phenix and Rosetta.
Terwilliger TC, Dimaio F, Read RJ, Baker D, Bunkóczi G, Adams PD, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Afonine PV, Echols N. Terwilliger TC, et al. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2012 Jun;13(2):81-90. doi: 10.1007/s10969-012-9129-3. Epub 2012 Mar 15. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22418934 Free PMC article. - Inhibition of XMRV and HIV-1 proteases by pepstatin A and acetyl-pepstatin.
Matúz K, Mótyán J, Li M, Wlodawer A, Tőzsér J. Matúz K, et al. FEBS J. 2012 Sep;279(17):3276-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08714.x. Epub 2012 Aug 17. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22804908 Free PMC article.
References
- Lombardi VC, et al. Science. 2009;326:585–589. - PubMed
- Wlodawer A, Vondrasek J. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1998;27:249–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN261200800001C/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM092802/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA BC010348-10/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials