Indole and 7-hydroxyindole diminish Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence - PubMed (original) (raw)
Indole and 7-hydroxyindole diminish Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence
Jintae Lee et al. Microb Biotechnol. 2009 Jan.
Abstract
Indole is an extracellular biofilm signal for Escherichia coli, and many bacterial oxygenases readily convert indole to various oxidized compounds including 7-hydroxyindole (7HI). Here we investigate the impact of indole and 7HI on Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 virulence and quorum sensing (QS)-regulated phenotypes; this strain does not synthesize these compounds but degrades them rapidly. Indole and 7HI both altered extensively gene expression in a manner opposite that of acylhomoserine lactones; the most repressed genes encode the mexGHI-opmD multidrug efflux pump and genes involved in the synthesis of QS-regulated virulence factors including pyocyanin (phz operon), 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolone (PQS) signal (pqs operon), pyochelin (pch operon) and pyoverdine (pvd operon). Corroborating these microarray results, indole and 7HI decreased production of pyocyanin, rhamnolipid, PQS and pyoverdine and enhanced antibiotic resistance. In addition, indole affected the utilization of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus, and 7HI abolished swarming motility. Furthermore, 7HI reduced pulmonary colonization of P. aeruginosa in guinea pigs and increased clearance in lungs. Hence, indole-related compounds have potential as a novel antivirulence approach for the recalcitrant pathogen P. aeruginosa.
© 2008 The Authors; Journal compilation © 2008 Society for Applied Microbiology and Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
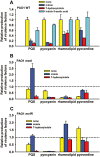
Figure 1
Reduction of virulence factors by indole and 7HI. Production of virulence factors with 1.0 mM indole, 0.5 mM 7HI and 1.0 mM IAA (negative control) with P. aeruginosa PAO1 (A), with P. aeruginosa PAO1 mexI (B) and P. aeruginosa PAO1 mvfR (C). For clarity, wild‐type values are not shown in (B) and (C) so bars indicate the relative amount of each compound made compared with the wild‐type strain without indole or 7HI added. Each experiment was performed with at least two independent cultures. Data show the average of the replicates, and one standard deviation is shown.
Figure 2
Inhibition of swarming motility by indole and 7HI. Swarming motility of P. aeruginosa on BM2 medium with 0.5% agar with 1.0 mM indole and 0.5 mM 7HI after 28 h. Each experiment was performed with at least two independent cultures and one representative data set is shown.
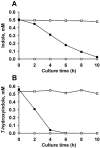
Figure 3
Degradation of indole and 7HI by P. aeruginosa. Pseudomonas aeruginosa degrades 0.5 mM indole (A) and 0.5 mM 7HI (B) in LB. The initial turbidity of cells was 1.0 at 600 nm. Closed square data (▪) are from live cells, open square data (□) are from autoclaved cells (dead cell control) and open circle data (○) are from live cells that lack added indole or 7HI. Each experiment was performed using two independent cultures, and one representative data set is shown.
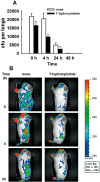
Figure 4
Reduction of virulence of P. aeruginosa in guinea pigs. A. Colonization and clearance of P. aeruginosa pre‐treated with 7HI or solvent (DMF) prior to infection of guinea pigs by aerosol with ∼2 × 105 cfu. Average of five replicates, and one standard deviation is shown. B. Real‐time analysis of P. aeruginosa pre‐treated with 7HI or solvent (DMF) in the acute guinea pig infection model (representative guinea pigs are shown for each group and are imaged laterally) using the Xenogen IVIS CCD camera. Colour bar represents the intensity of luminescent signal in photons s−1 cm−2 from low (blue) to high (red).
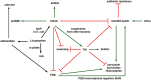
Figure 5
Summary of indole‐affected processes in _P. aeruginosa_→ indicates induction of gene expression or stimulation of a phenotype, ? indicates repression of gene expression or repression of a phenotype, and black arrows indicate reactions.
Similar articles
- Interference with Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing and Virulence by the Mycobacterial Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal Dioxygenase AqdC in Combination with the _N_-Acylhomoserine Lactone Lactonase QsdA.
Birmes FS, Säring R, Hauke MC, Ritzmann NH, Drees SL, Daniel J, Treffon J, Liebau E, Kahl BC, Fetzner S. Birmes FS, et al. Infect Immun. 2019 Sep 19;87(10):e00278-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00278-19. Print 2019 Oct. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31308081 Free PMC article. - 3-indolylacetonitrile decreases Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilm formation and Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence.
Lee JH, Cho MH, Lee J. Lee JH, et al. Environ Microbiol. 2011 Jan;13(1):62-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02308.x. Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 20649646 - Uncoupled Quorum Sensing Modulates the Interplay of Virulence and Resistance in a Multidrug-Resistant Clinical Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolate Belonging to the MLST550 Clonal Complex.
Cao H, Xia T, Li Y, Xu Z, Bougouffa S, Lo YK, Bajic VB, Luo H, Woo PCY, Yan A. Cao H, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Mar 27;63(4):e01944-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01944-18. Print 2019 Apr. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 30670423 Free PMC article. - Relationship between Pyochelin and Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Direction for Future Research.
Ma X, Zeng J, Xiao W, Li W, Cheng J, Lin J. Ma X, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 7;25(16):8611. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168611. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201297 Free PMC article. Review. - Quorum sensing by 2-alkyl-4-quinolones in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacterial species.
Dubern JF, Diggle SP. Dubern JF, et al. Mol Biosyst. 2008 Sep;4(9):882-8. doi: 10.1039/b803796p. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Mol Biosyst. 2008. PMID: 18704225 Review.
Cited by
- Downregulation of Klebsiella pneumoniae RND efflux pump genes following indole signal produced by Escherichia coli.
Salama GG, El-Mahdy TS, Moustafa WH, Emara M. Salama GG, et al. BMC Microbiol. 2024 Aug 24;24(1):312. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03443-w. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39182027 Free PMC article. - Interkingdom adenosine signal reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenicity.
Sheng L, Pu M, Hegde M, Zhang Y, Jayaraman A, Wood TK. Sheng L, et al. Microb Biotechnol. 2012 Jul;5(4):560-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2012.00338.x. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Microb Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22414222 Free PMC article. - Metagenomic approaches to understanding phylogenetic diversity in quorum sensing.
Kimura N. Kimura N. Virulence. 2014 Apr 1;5(3):433-42. doi: 10.4161/viru.27850. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Virulence. 2014. PMID: 24429899 Free PMC article. Review. - Highly active modulators of indole signaling alter pathogenic behaviors in Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.
Minvielle MJ, Eguren K, Melander C. Minvielle MJ, et al. Chemistry. 2013 Dec 16;19(51):17595-602. doi: 10.1002/chem.201303510. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Chemistry. 2013. PMID: 24243627 Free PMC article. - Commensal bacteria-dependent indole production enhances epithelial barrier function in the colon.
Shimada Y, Kinoshita M, Harada K, Mizutani M, Masahata K, Kayama H, Takeda K. Shimada Y, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Nov 20;8(11):e80604. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080604. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24278294 Free PMC article.
References
- Aendekerk S., Ghysels B., Cornelis P., Baysse C. Characterization of a new efflux pump, MexGHI‐OpmD, from Pseudomonas aeruginosa that confers resistance to vanadium. Microbiology. 2002;148:2371–2381. - PubMed
- Aendekerk S., Diggle S.P., Song Z., Høiby N., Cornelis P., Williams P. The MexGHI‐OpmD multidrug efflux pump controls growth, antibiotic susceptibility and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa via 4‐quinolone‐dependent cell‐to‐cell communication. Microbiology. 2005;151:1113–1125. et al. - PubMed
- Andrews J.M. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2001;48(1):5–16. - PubMed
- Attila C., Ueda A., Wood T.K. PA2663 (PpyR) increases biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 through the psl operon and stimulates virulence and quorum‐sensing phenotypes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008a;78:293–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources