Regulation of PGC-1α, a nodal regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Regulation of PGC-1α, a nodal regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis
Pablo J Fernandez-Marcos et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011 Apr.
Abstract
Mechanisms responsible for energy management in the cell and in the whole organism require a complex network of transcription factors and cofactors. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) has emerged as a master regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis and function, thus becoming a crucial metabolic node. We present an overview of the mechanisms by which PGC-1α is regulated, including the transcriptional regulation of PGC-1α expression and the fine-tuning of its final activity via posttranslational modifications.
Figures
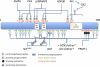
FIGURE 1.
Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) transcription. At the PGC-1α promoter, there are binding sites for transcription factors myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2), forkhead box class-O (FoxO1), activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2), and cAMP response element–binding protein (CREB), all of which enhance PGC-1α transcription. These factors, in turn, are modulated by different signaling pathways: insulin activates Akt, which leads to cytoplasmic sequestration and inhibition of FoxO1; cytokines and exercise activate p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK), which phosporylates and activates MEF2 and ATF2; exercise also stimulates Ca2+ signaling, which, through calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (CaMKIV) and calcineurin A (CnA), will induce CREB and MEF2-mediated PGC-1α transcription; and cold activates β3-adrenergic receptors (β3-AR) in muscle and brown fat, leading to protein kinase A (PKA)–mediated activation of CREB. IRS, insulin response sequence; GLGN-R, glucagon receptor; P, phosphate; CRE, cAMP response element.
FIGURE 2.
Posttranslational modifications of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α). Numerous modifications have been described to affect PGC-1α, modulating its levels and activity through phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, ubiquitination, and _O_-linked N_-acetylglucosylation. The respective residues or regions where these modifications occur are indicated. Certain modification sites are mapped in the mouse or the human PGC-1α protein (as indicated in the key). AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; PKA, protein kinase A; p38MAPK, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3_β; SCFCdc4, Skp1/Cullin/F-box cell division control 4; OGT, _O_-linked _N_-acetylglucosamine transferase; Clk2, Cdc2-like kinase 2; Ac, acetylation; CPD, Cdc4 phosphodegron; SR, serine-arginine domain; GCN5, general control of amino acid synthesis 5; Sirt1, silence information regulator 2-like 1; PRMT1, protein arginine methyltransferase 1.
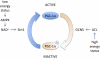
FIGURE 3.
Cellular sensing of energy status through acetylation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α). In situations of low energy status, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)–increased NAD+ amounts enhance Sirt1 activity and lead to the activating deacetylation of PGC-1α and increased mitochondrial biogenesis and function. When energy is abundant in the cell, GCN5 (general control of amino acid synthesis) acetylates and inhibits PGC-1α; the acetyl-CoA necessary for this reaction is provided by ATP-citrate lyase (ACL), which acts as a rate-liming factor for GCN5-mediated acetylation of PGC-1α. Ac, acetylation.
Similar articles
- Mitochondrial biogenesis and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) deacetylation by physical activity: intact adipocytokine signaling is required.
Li L, Pan R, Li R, Niemann B, Aurich AC, Chen Y, Rohrbach S. Li L, et al. Diabetes. 2011 Jan;60(1):157-67. doi: 10.2337/db10-0331. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 20929977 Free PMC article. - The diabetes medication canagliflozin promotes mitochondrial remodelling of adipocyte via the AMPK-Sirt1-Pgc-1α signalling pathway.
Yang X, Liu Q, Li Y, Tang Q, Wu T, Chen L, Pu S, Zhao Y, Zhang G, Huang C, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Huang Y, Zou M, Shi X, Jiang W, Wang R, He J. Yang X, et al. Adipocyte. 2020 Dec;9(1):484-494. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2020.1807850. Adipocyte. 2020. PMID: 32835596 Free PMC article. - Mutual exacerbation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α deregulation and α-synuclein oligomerization.
Eschbach J, von Einem B, Müller K, Bayer H, Scheffold A, Morrison BE, Rudolph KL, Thal DR, Witting A, Weydt P, Otto M, Fauler M, Liss B, McLean PJ, Spada AR, Ludolph AC, Weishaupt JH, Danzer KM. Eschbach J, et al. Ann Neurol. 2015 Jan;77(1):15-32. doi: 10.1002/ana.24294. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Ann Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25363075 Free PMC article. - Posttranslational regulation of PGC-1α and its implication in cancer metabolism.
Luo X, Liao C, Quan J, Cheng C, Zhao X, Bode AM, Cao Y. Luo X, et al. Int J Cancer. 2019 Sep 15;145(6):1475-1483. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32253. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30848477 Free PMC article. Review. - PGC-1α-mediated regulation of mitochondrial function and physiological implications.
Halling JF, Pilegaard H. Halling JF, et al. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020 Sep;45(9):927-936. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2020-0005. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020. PMID: 32516539 Review.
Cited by
- Cardioprotection in the aging, diabetic heart: the loss of protective Akt signalling.
Whittington HJ, Harding I, Stephenson CI, Bell R, Hausenloy DJ, Mocanu MM, Yellon DM. Whittington HJ, et al. Cardiovasc Res. 2013 Sep 1;99(4):694-704. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt140. Epub 2013 May 30. Cardiovasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23723063 Free PMC article. - Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and SIRT1: Impact on the Aging Process.
Salminen A, Kaarniranta K, Kauppinen A. Salminen A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Feb 11;14(2):3834-59. doi: 10.3390/ijms14023834. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23434668 Free PMC article. - An improvement in skeletal muscle mitochondrial capacity with short-term aerobic training is associated with changes in Tribbles 1 expression.
Vega RB, Brouwers B, Parsons SA, Stephens NA, Pino MF, Hodges A, Yi F, Yu G, Pratley RE, Smith SR, Sparks LM. Vega RB, et al. Physiol Rep. 2020 Jun;8(12):e14416. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14416. Physiol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32562350 Free PMC article. - Dysfunctional mitochondrial bioenergetics and the pathogenesis of hepatic disorders.
Auger C, Alhasawi A, Contavadoo M, Appanna VD. Auger C, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Jun 25;3:40. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2015.00040. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26161384 Free PMC article. Review. - Resveratrol is not as effective as physical exercise for improving reproductive and metabolic functions in rats with dihydrotestosterone-induced polycystic ovary syndrome.
Benrick A, Maliqueo M, Miao S, Villanueva JA, Feng Y, Ohlsson C, Duleba AJ, Stener-Victorin E. Benrick A, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:964070. doi: 10.1155/2013/964070. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23690868 Free PMC article.
References
- Chawla A, Repa JJ, Evans RM, Mangelsdorf DJ. Nuclear receptors and lipid physiology: opening the X-files. Science 2001;294:1866–70 - PubMed
- Francis GA, Fayard E, Picard F, Auwerx J. Nuclear receptors and the control of metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol 2003;65:261–311 - PubMed
- Spiegelman BM, Heinrich R. Biological control through regulated transcriptional coactivators. Cell 2004;119:157–67 - PubMed
- Puigserver P, Wu Z, Park CW, Graves R, Wright M, Spiegelman BM. A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell 1998;92:829–39 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources