Single mimivirus particles intercepted and imaged with an X-ray laser - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2011 Feb 3;470(7332):78-81.
doi: 10.1038/nature09748.
Tomas Ekeberg, Filipe R N C Maia, Martin Svenda, Jakob Andreasson, Olof Jönsson, Duško Odić, Bianca Iwan, Andrea Rocker, Daniel Westphal, Max Hantke, Daniel P DePonte, Anton Barty, Joachim Schulz, Lars Gumprecht, Nicola Coppola, Andrew Aquila, Mengning Liang, Thomas A White, Andrew Martin, Carl Caleman, Stephan Stern, Chantal Abergel, Virginie Seltzer, Jean-Michel Claverie, Christoph Bostedt, John D Bozek, Sébastien Boutet, A Alan Miahnahri, Marc Messerschmidt, Jacek Krzywinski, Garth Williams, Keith O Hodgson, Michael J Bogan, Christina Y Hampton, Raymond G Sierra, Dmitri Starodub, Inger Andersson, Saša Bajt, Miriam Barthelmess, John C H Spence, Petra Fromme, Uwe Weierstall, Richard Kirian, Mark Hunter, R Bruce Doak, Stefano Marchesini, Stefan P Hau-Riege, Matthias Frank, Robert L Shoeman, Lukas Lomb, Sascha W Epp, Robert Hartmann, Daniel Rolles, Artem Rudenko, Carlo Schmidt, Lutz Foucar, Nils Kimmel, Peter Holl, Benedikt Rudek, Benjamin Erk, André Hömke, Christian Reich, Daniel Pietschner, Georg Weidenspointner, Lothar Strüder, Günter Hauser, Hubert Gorke, Joachim Ullrich, Ilme Schlichting, Sven Herrmann, Gerhard Schaller, Florian Schopper, Heike Soltau, Kai-Uwe Kühnel, Robert Andritschke, Claus-Dieter Schröter, Faton Krasniqi, Mario Bott, Sebastian Schorb, Daniela Rupp, Marcus Adolph, Tais Gorkhover, Helmut Hirsemann, Guillaume Potdevin, Heinz Graafsma, Björn Nilsson, Henry N Chapman, Janos Hajdu
Affiliations
- PMID: 21293374
- PMCID: PMC4038304
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09748
Single mimivirus particles intercepted and imaged with an X-ray laser
M Marvin Seibert et al. Nature. 2011.
Abstract
X-ray lasers offer new capabilities in understanding the structure of biological systems, complex materials and matter under extreme conditions. Very short and extremely bright, coherent X-ray pulses can be used to outrun key damage processes and obtain a single diffraction pattern from a large macromolecule, a virus or a cell before the sample explodes and turns into plasma. The continuous diffraction pattern of non-crystalline objects permits oversampling and direct phase retrieval. Here we show that high-quality diffraction data can be obtained with a single X-ray pulse from a non-crystalline biological sample, a single mimivirus particle, which was injected into the pulsed beam of a hard-X-ray free-electron laser, the Linac Coherent Light Source. Calculations indicate that the energy deposited into the virus by the pulse heated the particle to over 100,000 K after the pulse had left the sample. The reconstructed exit wavefront (image) yielded 32-nm full-period resolution in a single exposure and showed no measurable damage. The reconstruction indicates inhomogeneous arrangement of dense material inside the virion. We expect that significantly higher resolutions will be achieved in such experiments with shorter and brighter photon pulses focused to a smaller area. The resolution in such experiments can be further extended for samples available in multiple identical copies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Figure 1. The experimental arrangement
Mimivirus particles were injected into the pulse train of the LCLS at the AMO experimental station with a sample injector built in Uppsala. The injector was mounted into the CAMP instrument. The aerodynamic lens stack is visible in the centre of the injector body, on the left. Particles leaving the injector enter the vacuum chamber and are intercepted randomly by the LCLS pulses. The far-field diffraction pattern of each particle hit by an X-ray pulse is recorded on a pair of fast p–n junction charge-coupled device (pnCCD) detectors. The intense, direct beam passes through an opening in the centre of the detector assembly and is absorbed harmlessly behind the sensitive detectors. Some of the low-resolution data also go through this gap and are lost in the current set-up.
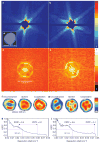
Figure 2. Single-shot diffraction patterns on single virus particles give interpretable results
a, b, Experimentally recorded far-field diffraction patterns (in false-colour representation) from individual virus particles captured in two different orientations. c, Transmission electron micrograph of an unstained Mimivirus particle, showing pseudo-icosahedral appearance. d, e, Autocorrelation functions for a (d) and b (e). The shape and size of each autocorrelation correspond to those of a single virus particle after high-pass filtering due to missing low-resolution data. f, g, Reconstructed images after iterative phase retrieval with the Hawk software package. The size of a pixel corresponds to 9 nm in the images. Three different reconstructions are shown for each virus particle: an averaged reconstruction with unconstrained Fourier modes and two averaged images after fitting unconstrained low-resolution modes to a spherical or an icosahedral profile, respectively. The orientation of the icosahedron was determined from the diffraction data. The results show small differences between the spherical and icosahedral fits. h, i, The PRTF for reconstructions where the unconstrained low-resolution modes were fitted to an icosahedron. All reconstructions gave similar resolutions. We characterize resolution by the point where the PRTF drops to 1/e (ref. 20). This corresponds to 32-nm full-period resolution in both exposures. Arrows mark the resolution range with other cut-off criteria found in the literature (Methods). Resolution can be substantially extended for samples available in multiple identical copies,–.
Comment in
- Diffraction before destruction.
Doerr A. Doerr A. Nat Methods. 2011 Apr;8(4):283. doi: 10.1038/nmeth0411-283. Nat Methods. 2011. PMID: 21574275 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Single-shot diffraction data from the Mimivirus particle using an X-ray free-electron laser.
Ekeberg T, Svenda M, Seibert MM, Abergel C, Maia FR, Seltzer V, DePonte DP, Aquila A, Andreasson J, Iwan B, Jönsson O, Westphal D, Odić D, Andersson I, Barty A, Liang M, Martin AV, Gumprecht L, Fleckenstein H, Bajt S, Barthelmess M, Coppola N, Claverie JM, Loh ND, Bostedt C, Bozek JD, Krzywinski J, Messerschmidt M, Bogan MJ, Hampton CY, Sierra RG, Frank M, Shoeman RL, Lomb L, Foucar L, Epp SW, Rolles D, Rudenko A, Hartmann R, Hartmann A, Kimmel N, Holl P, Weidenspointner G, Rudek B, Erk B, Kassemeyer S, Schlichting I, Strüder L, Ullrich J, Schmidt C, Krasniqi F, Hauser G, Reich C, Soltau H, Schorb S, Hirsemann H, Wunderer C, Graafsma H, Chapman H, Hajdu J. Ekeberg T, et al. Sci Data. 2016 Aug 1;3:160060. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2016.60. Sci Data. 2016. PMID: 27479754 Free PMC article. - X-Ray Free-Electron Lasers for the Structure and Dynamics of Macromolecules.
Chapman HN. Chapman HN. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019 Jun 20;88:35-58. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-013118-110744. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30601681 Review. - Emerging opportunities in structural biology with X-ray free-electron lasers.
Schlichting I, Miao J. Schlichting I, et al. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2012 Oct;22(5):613-26. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2012.07.015. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22922042 Free PMC article. Review. - Three-dimensional reconstruction of the giant mimivirus particle with an x-ray free-electron laser.
Ekeberg T, Svenda M, Abergel C, Maia FR, Seltzer V, Claverie JM, Hantke M, Jönsson O, Nettelblad C, van der Schot G, Liang M, DePonte DP, Barty A, Seibert MM, Iwan B, Andersson I, Loh ND, Martin AV, Chapman H, Bostedt C, Bozek JD, Ferguson KR, Krzywinski J, Epp SW, Rolles D, Rudenko A, Hartmann R, Kimmel N, Hajdu J. Ekeberg T, et al. Phys Rev Lett. 2015 Mar 6;114(9):098102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.098102. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Phys Rev Lett. 2015. PMID: 25793853 - Diffraction data from aerosolized Coliphage PR772 virus particles imaged with the Linac Coherent Light Source.
Li H, Nazari R, Abbey B, Alvarez R, Aquila A, Ayyer K, Barty A, Berntsen P, Bielecki J, Pietrini A, Bucher M, Carini G, Chapman HN, Contreras A, Daurer BJ, DeMirci H, Flűckiger L, Frank M, Hajdu J, Hantke MF, Hogue BG, Hosseinizadeh A, Hunter MS, Jönsson HO, Kirian RA, Kurta RP, Loh D, Maia FRNC, Mancuso AP, Morgan AJ, McFadden M, Muehlig K, Munke A, Reddy HKN, Nettelblad C, Ourmazd A, Rose M, Schwander P, Marvin Seibert M, Sellberg JA, Sierra RG, Sun Z, Svenda M, Vartanyants IA, Walter P, Westphal D, Williams G, Xavier PL, Yoon CH, Zaare S. Li H, et al. Sci Data. 2020 Nov 19;7(1):404. doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-00745-2. Sci Data. 2020. PMID: 33214568 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Opportunities in multidimensional trace metal imaging: taking copper-associated disease research to the next level.
Vogt S, Ralle M. Vogt S, et al. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013 Feb;405(6):1809-20. doi: 10.1007/s00216-012-6437-1. Epub 2012 Oct 19. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013. PMID: 23079951 Free PMC article. Review. - Imaging transient melting of a nanocrystal using an X-ray laser.
Clark JN, Beitra L, Xiong G, Fritz DM, Lemke HT, Zhu D, Chollet M, Williams GJ, Messerschmidt MM, Abbey B, Harder RJ, Korsunsky AM, Wark JS, Reis DA, Robinson IK. Clark JN, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jun 16;112(24):7444-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417678112. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26034277 Free PMC article. - Single-particle structure determination by correlations of snapshot X-ray diffraction patterns.
Starodub D, Aquila A, Bajt S, Barthelmess M, Barty A, Bostedt C, Bozek JD, Coppola N, Doak RB, Epp SW, Erk B, Foucar L, Gumprecht L, Hampton CY, Hartmann A, Hartmann R, Holl P, Kassemeyer S, Kimmel N, Laksmono H, Liang M, Loh ND, Lomb L, Martin AV, Nass K, Reich C, Rolles D, Rudek B, Rudenko A, Schulz J, Shoeman RL, Sierra RG, Soltau H, Steinbrener J, Stellato F, Stern S, Weidenspointner G, Frank M, Ullrich J, Strüder L, Schlichting I, Chapman HN, Spence JC, Bogan MJ. Starodub D, et al. Nat Commun. 2012;3:1276. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2288. Nat Commun. 2012. PMID: 23232406 - Single-pulse enhanced coherent diffraction imaging of bacteria with an X-ray free-electron laser.
Fan J, Sun Z, Wang Y, Park J, Kim S, Gallagher-Jones M, Kim Y, Song C, Yao S, Zhang J, Zhang J, Duan X, Tono K, Yabashi M, Ishikawa T, Fan C, Zhao Y, Chai Z, Gao X, Earnest T, Jiang H. Fan J, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 23;6:34008. doi: 10.1038/srep34008. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27659203 Free PMC article. - Laser science: Even harder X-rays.
Marangos J. Marangos J. Nature. 2012 Jan 25;481(7382):452-3. doi: 10.1038/481452a. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22281590 No abstract available.
References
- Neutze R, et al. Potential for biomolecular imaging with femtosecond X-ray pulses. Nature. 2000;406:752–757. - PubMed
- Chapman HN, et al. Femtosecond diffractive imaging with a soft-X-ray free-electron laser. Nature Phys. 2006;2:839–843.
- Bergh M, et al. Feasibility of imaging living cells at sub-nanometer resolution by ultrafast X-ray diffraction. Q Rev Biophys. 2008;41:181–204. - PubMed
- Nagler B, et al. Turning solid aluminium transparent by intense soft X-ray photoionization. Nature Phys. 2009;5:693–696.
- Emma P, et al. First lasing and operation of an ångstrom-wavelength free-electron laser. Nature Photon. 2010;4:641–647.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources