Complete genome sequence of Sphaerobacter thermophilus type strain (S 6022) - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2010 Jan 28;2(1):49-56.
doi: 10.4056/sigs.601105.
Kurt Labutti, Rüdiger Pukall, Matt Nolan, Tijana Glavina Del Rio, Hope Tice, Jan-Fang Cheng, Susan Lucas, Feng Chen, Alex Copeland, Natalia Ivanova, Konstantinos Mavromatis, Natalia Mikhailova, Sam Pitluck, David Bruce, Lynne Goodwin, Miriam Land, Loren Hauser, Yun-Juan Chang, Cynthia D Jeffries, Amy Chen, Krishna Palaniappan, Patrick Chain, Thomas Brettin, Johannes Sikorski, Manfred Rohde, Markus Göker, Jim Bristow, Jonathan A Eisen, Victor Markowitz, Philip Hugenholtz, Nikos C Kyrpides, Hans-Peter Klenk, Alla Lapidus
- PMID: 21304677
- PMCID: PMC3035262
- DOI: 10.4056/sigs.601105
Complete genome sequence of Sphaerobacter thermophilus type strain (S 6022)
Amrita Pati et al. Stand Genomic Sci. 2010.
Abstract
Sphaerobacter thermophilus Demharter et al. 1989 is the sole and type species of the genus Sphaerobacter, which is the type genus of the family Sphaerobacteraceae, the order Sphaerobacterales and the subclass Sphaerobacteridae. Phylogenetically, it belongs to the genomically little studied class of the Thermomicrobia in the bacterial phylum Chloroflexi. Here, the genome of strain S 6022(T) is described which is an obligate aerobe that was originally isolated from an aerated laboratory-scale fermentor that was pulse fed with municipal sewage sludge. We describe the features of this organism, together with the complete genome and annotation. This is the first complete genome sequence of the thermomicrobial subclass Sphaerobacteridae, and the second sequence from the chloroflexal class Thermomicrobia. The 3,993,764 bp genome with its 3,525 protein-coding and 57 RNA genes is a part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project.
Keywords: GEBA; Sphaerobacteridae; Thermomicrobia; non-motile; non-sporeforming; obligate aerobic; pleomorphic; sewage sludge isolate; thermophile.
Figures
Figure 1
Phylogenetic tree of S. thermophilus strain S 6022T and all type strains of the phylum Chloroflexi, inferred from 1,304 aligned characters [5,6] of the 16S rRNA gene sequence under the maximum likelihood criterion [7]. The tree was rooted with the members of Anaerolineae and Caldilineae within the Chloroflexi. The branches are scaled in terms of the expected number of substitutions per site. Numbers above branches are support values from 1,000 bootstrap replicates if larger than 60%. Lineages with type strain genome sequencing projects registered in GOLD [8] are shown in blue, published genomes in bold.
Figure 2
Scanning electron micrograph of S. thermophilus S strain 6022T
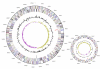
Figure 3
Graphical circular map of the genome. Chromosome (left), plasmid (right), drown not in scale. From outside to the center: Genes on forward strand (color by COG categories), Genes on reverse strand (color by COG categories), RNA genes (tRNAs green, rRNAs red, other RNAs black), GC content, GC skew.
Similar articles
- Complete genome sequence of 'Thermobaculum terrenum' type strain (YNP1).
Kiss H, Cleland D, Lapidus A, Lucas S, Del Rio TG, Nolan M, Tice H, Han C, Goodwin L, Pitluck S, Liolios K, Ivanova N, Mavromatis K, Ovchinnikova G, Pati A, Chen A, Palaniappan K, Land M, Hauser L, Chang YJ, Jeffries CD, Lu M, Brettin T, Detter JC, Göker M, Tindall BJ, Beck B, McDermott TR, Woyke T, Bristow J, Eisen JA, Markowitz V, Hugenholtz P, Kyrpides NC, Klenk HP, Cheng JF. Kiss H, et al. Stand Genomic Sci. 2010 Oct 27;3(2):153-62. doi: 10.4056/sigs.1153107. Stand Genomic Sci. 2010. PMID: 21304745 Free PMC article. - Complete genome sequence of Hydrogenobacter thermophilus type strain (TK-6).
Zeytun A, Sikorski J, Nolan M, Lapidus A, Lucas S, Han J, Tice H, Cheng JF, Tapia R, Goodwin L, Pitluck S, Liolios K, Ivanova N, Mavromatis K, Mikhailova N, Ovchinnikova G, Pati A, Chen A, Palaniappan K, Ngatchou-Djao OD, Land M, Hauser L, Jeffries CD, Han C, Detter JC, Ubler S, Rohde M, Tindall BJ, Göker M, Wirth R, Woyke T, Bristow J, Eisen JA, Markowitz V, Hugenholtz P, Klenk HP, Kyrpides NC. Zeytun A, et al. Stand Genomic Sci. 2011 Apr 29;4(2):131-43. doi: 10.4056/sigs.1463589. Stand Genomic Sci. 2011. PMID: 21677850 Free PMC article. - Complete genome sequence of Marivirga tractuosa type strain (H-43).
Pagani I, Chertkov O, Lapidus A, Lucas S, Del Rio TG, Tice H, Copeland A, Cheng JF, Nolan M, Saunders E, Pitluck S, Held B, Goodwin L, Liolios K, Ovchinikova G, Ivanova N, Mavromatis K, Pati A, Chen A, Palaniappan K, Land M, Hauser L, Jeffries CD, Detter JC, Han C, Tapia R, Ngatchou-Djao OD, Rohde M, Göker M, Spring S, Sikorski J, Woyke T, Bristow J, Eisen JA, Markowitz V, Hugenholtz P, Klenk HP, Kyrpides NC. Pagani I, et al. Stand Genomic Sci. 2011 Apr 29;4(2):154-62. doi: 10.4056/sigs.1623941. Stand Genomic Sci. 2011. PMID: 21677852 Free PMC article. - Complete genome sequence of Streptobacillus moniliformis type strain (9901).
Nolan M, Gronow S, Lapidus A, Ivanova N, Copeland A, Lucas S, Del Rio TG, Chen F, Tice H, Pitluck S, Cheng JF, Sims D, Meincke L, Bruce D, Goodwin L, Brettin T, Han C, Detter JC, Ovchinikova G, Pati A, Mavromatis K, Mikhailova N, Chen A, Palaniappan K, Land M, Hauser L, Chang YJ, Jeffries CD, Rohde M, Spröer C, Göker M, Bristow J, Eisen JA, Markowitz V, Hugenholtz P, Kyrpides NC, Klenk HP, Chain P. Nolan M, et al. Stand Genomic Sci. 2009 Dec 30;1(3):300-7. doi: 10.4056/sigs.48727. Stand Genomic Sci. 2009. PMID: 21304670 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Cu+-specific CopB transporter: Revising P1B-type ATPase classification.
Purohit R, Ross MO, Batelu S, Kusowski A, Stemmler TL, Hoffman BM, Rosenzweig AC. Purohit R, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Feb 27;115(9):2108-2113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1721783115. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29440418 Free PMC article. - Analysis of the SOS response of Vibrio and other bacteria with multiple chromosomes.
Sanchez-Alberola N, Campoy S, Barbé J, Erill I. Sanchez-Alberola N, et al. BMC Genomics. 2012 Feb 3;13:58. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-58. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22305460 Free PMC article. - Proteogenomic analysis of a thermophilic bacterial consortium adapted to deconstruct switchgrass.
D'haeseleer P, Gladden JM, Allgaier M, Chain PS, Tringe SG, Malfatti SA, Aldrich JT, Nicora CD, Robinson EW, Paša-Tolić L, Hugenholtz P, Simmons BA, Singer SW. D'haeseleer P, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Jul 19;8(7):e68465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068465. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23894306 Free PMC article. - Complete genome sequence of 'Thermobaculum terrenum' type strain (YNP1).
Kiss H, Cleland D, Lapidus A, Lucas S, Del Rio TG, Nolan M, Tice H, Han C, Goodwin L, Pitluck S, Liolios K, Ivanova N, Mavromatis K, Ovchinnikova G, Pati A, Chen A, Palaniappan K, Land M, Hauser L, Chang YJ, Jeffries CD, Lu M, Brettin T, Detter JC, Göker M, Tindall BJ, Beck B, McDermott TR, Woyke T, Bristow J, Eisen JA, Markowitz V, Hugenholtz P, Kyrpides NC, Klenk HP, Cheng JF. Kiss H, et al. Stand Genomic Sci. 2010 Oct 27;3(2):153-62. doi: 10.4056/sigs.1153107. Stand Genomic Sci. 2010. PMID: 21304745 Free PMC article. - The quest for a unified view of bacterial land colonization.
Wu H, Fang Y, Yu J, Zhang Z. Wu H, et al. ISME J. 2014 Jul;8(7):1358-69. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.247. Epub 2014 Jan 23. ISME J. 2014. PMID: 24451209 Free PMC article.
References
- Demharter W, Hensel R, Smida J, Stackebrandt E. Sphaerobacter thermophilus gen. nov., sp. nov. A deeply rooting member of the actinomycetes subdivision isolated from thermophilically treated sewage sludge. Syst Appl Microbiol 1989; 11:261-266
- Hensel R, Demharter W, Hilpert R. The microflora involved in aerobic-thermophilic sludge stabilization. Syst Appl Microbiol 1989; 11:312-319
- Jackson TJ, Ramaley RF, Meinschein WG. Thermomicrobium, a new genus of extremely thermophilic bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1973; 23:28-36
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases