Chromosome-wide analysis of parental allele-specific chromatin and DNA methylation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Chromosome-wide analysis of parental allele-specific chromatin and DNA methylation
Purnima Singh et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Apr.
Abstract
To reveal the extent of domain-wide epigenetic features at imprinted gene clusters, we performed a high-resolution allele-specific chromatin analysis of over 100 megabases along the maternally or paternally duplicated distal chromosome 7 (Chr7) and Chr15 in mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs). We found that reciprocal allele-specific features are limited to imprinted genes and their differentially methylated regions (DMRs), whereas broad local enrichment of H3K27me3 (BLOC) is a domain-wide feature at imprinted clusters. We uncovered novel allele-specific features of BLOCs. A maternally biased BLOC was found along the H19-Igf2 domain. A paternal allele-specific gap was found along Kcnq1ot1, interrupting a biallelic BLOC in the Kcnq1-Cdkn1c domain. We report novel allele-specific chromatin marks at the Peg13 and Slc38a4 DMRs, Cdkn1c upstream region, and Inpp5f_v2 DMR and paternal allele-specific CTCF binding at the Peg13 DMR. Additionally, we derived an imprinted gene predictor algorithm based on our allele-specific chromatin mapping data. The binary predictor H3K9ac and CTCF or H3K4me3 in one allele and H3K9me3 in the reciprocal allele, using a sliding-window approach, recognized with precision the parental allele specificity of known imprinted genes, H19, Igf2, Igf2as, Cdkn1c, Kcnq1ot1, and Inpp5f_v2 on Chr7 and Peg13 and Slc38a4 on Chr15. Chromatin features, therefore, can unequivocally identify genes with imprinted expression.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Uniparental duplication of distal chromosome 7 allows chromosome-wide analysis of allele-specific epigenetic features of two imprinted domains. (A) Normal embryos inherit one set of chromosomes from each parent. Maternally and paternally inherited alleles of chromosomes 7 (red and blue) and Chr15 (pink and light blue) are shown. (B) In MatDup.dist7 embryos, two copies of the distal Chr7 segment, telomeric to the T9H translocation breakpoint, are inherited from the mother, and two copies of distal Chr15 are inherited from the father. (C) In PatDup.dist7 embryos, two copies of distal Chr7 are inherited from the father, and two copies of distal Chr15 are inherited from the mother. Hyper- and hypomethylated alleles of known DMRs are marked by closed and open circles, respectively. (D) Two clusters of imprinted genes in distal chromosome 7 are regulated by reciprocal germ line methylation and different imprinting mechanisms. Imprinted expression of the H19-Igf2 imprinted domain (to the left) is regulated by a paternally (P) methylated (closed circles) DMR. The unmethylated (open circles) allele is specifically bound by a CTCF insulator protein (yellow ovals) that blocks Igf2 activation by the shared enhancers (gray circles) in the maternal chromosome (M). H19 is expressed from the maternal chromosome (red). Igf2as and Ins2 are paternally expressed (blue), the latter exhibiting imprinted expression in the yolk sac. (B) The Cdkn1c1-Kcnq1 imprinted domain (to the right) is telomeric to the H19-Igf2 domain. It is under the control of the maternally methylated KvDMR1, which overlaps the promoter of the noncoding RNA, Kcnq1ot1 (orange line). Cdkn1c is expressed from the maternal chromosome. Kcnq1ot1 is expressed from the paternal chromosome. Transcription of a set of imprinted genes, Th, Ascl2, Tspan32, Cd81, Tssc4, Slc22a18, Phlda2, Napl14, Tnfrsf23, Osbpl5, and Dhcr7, in the placenta is repressed in the paternal chromosome by Kcnq1ot1 expression from the paternal allele. Imprinted expression of Kcnq1 and Slc22a18 is developmentally regulated. The embryonic lethality phenotype of PatDup.dist7 embryos was rescued by an Ascl2 transgene, integrated at another chromosome. The overlap of the P1 clone with the endogenous locus is indicated. Map is not to scale.
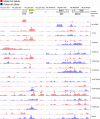
Fig. 2.
High-resolution allele-specific analysis of the H19, Igf2, and Igf2as imprinted genes. The chromatin (with the antibodies indicated to the right) and methylation (MIRA) signals are plotted along the chromosome as −log10 P value scores for the maternal allele in MatDup.dist7 (red bars) and for the paternal allele in PatDup.dist7 (blue bars) MEFs. The P value score was obtained by NimbleScan software and is derived from the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test comparing the log2 ratios (ChIP or MIRA versus input) within a 750-bp window centered at each probe and the rest of the data on the array. Transcripts are marked by rectangles, with arrows indicating the direction of transcription. The H19-Igf2 ICR and the Igf2 DMRs are labeled with yellow rectangles. Significant allele-specific peaks located at −5 kb to +2 kb from the transcription start sites (TSS) are marked by asterisks. Additionally, significant maternal H3K27me3 peaks are marked along the imprinted domain in this figure and in Fig. S3B in the supplemental material. Genomic coordinates are indicated on the top according to UCSC Genome Browser mouse genome version mm8.
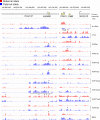
Fig. 3.
High-resolution allele-specific chromatin analysis along the Kcnq1ot1 and Cdkn1c-Slc22a18 imprinted genes. Kcnq1ot1 ncRNA and Cdkn1c are paternally and maternally expressed in MEFs, respectively. The KvDMR1, the Cdkn1c DMR, and the Slc22a18 DMR (47) (yellow rectangles) are very clearly marked by allele-specific chromatin. The H3K27me3 peaks in the bracketed area and peak 1 in the Cdkn1c upstream area were confirmed using ChIP real-time PCR (see Fig. S5 in the supplemental material). Slc22a18 exhibited some allele-specific chromatin marks in the absence of high-level transcription in MEFs (see Fig. S4 in the supplemental material). Other details are as described in Fig. 2.
Fig. 4.
Chromatin analysis of Inpp5f_ v2. Inpp5f_ v2 is paternally expressed in the brain but is not expressed in MEFs. Allele-specific marks can be discerned at Inpp5f_ v2 but not at the nonimprinted Inpp5f in MEFs, including maternal DNA methylation in the Inpp5f_ v2 DMR. Other details are as described in Fig. 2.
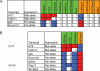
Fig. 5.
Derivation and testing an imprinted gene predictor algorithm. (A) Allele-specific peaks of epigenetic marks were tabulated at four annotated transcripts according to the allele-specific expression profile of the transcript. Allele-specific peaks were identified for activation and repressive epigenetic marks in the promoter region (−5 kb to +2 kb from the TSS) of four known imprinted genes, located on distal Chr7, in MatDup.dist7 and PatDup.dist7 MEFs (see Table S3 in the supplemental material). From these, the activation mark peaks in the expressed allele (green) and the repression mark peaks in the silent allele (orange) were considered for maternally expressed and paternally expressed transcripts. From this table, a consensus imprinted gene signature was derived: H3K9ac and H3K4me3 or CTCF in the expressed allele and H3K9me3 in the silent allele. These are colored: maternal allele (red) and paternal allele (blue). (B) The consensus was then tested as a bimodal predictor using chromatin data of annotated transcripts along distal Chr7, central Chr7, and distal Chr15 (see Table S4 and Fig. S9 in the supplemental material). The predictor was further tested by a sliding-window approach, which did not depend on transcript annotations (see Table S5 in the supplemental material).
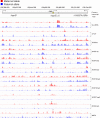
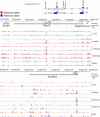
Fig. 6.
Chromatin analysis of imprinted genes on distal Chr15. A map depicting the imprinting status of the Peg13 and the Slc38a4 imprinted regions along distal Chr15 is shown at the top. ChIP-on-chip results are shown for the maternal allele in PatDup.dist7 (red bars) and for the paternal allele in MatDup.dist7 (blue bars) MEFs, with the antibodies indicated to the right. The last two rows depict MIRA analysis.
Similar articles
- CTCF is the master organizer of domain-wide allele-specific chromatin at the H19/Igf2 imprinted region.
Han L, Lee DH, Szabó PE. Han L, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Feb;28(3):1124-35. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01361-07. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18039862 Free PMC article. - CTCF-dependent chromatin bias constitutes transient epigenetic memory of the mother at the H19-Igf2 imprinting control region in prospermatogonia.
Lee DH, Singh P, Tsai SY, Oates N, Spalla A, Spalla C, Brown L, Rivas G, Larson G, Rauch TA, Pfeifer GP, Szabó PE. Lee DH, et al. PLoS Genet. 2010 Nov 24;6(11):e1001224. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001224. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 21124827 Free PMC article. - Coordinated allele-specific histone acetylation at the differentially methylated regions of imprinted genes.
Singh P, Cho J, Tsai SY, Rivas GE, Larson GP, Szabó PE. Singh P, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Dec;38(22):7974-90. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq680. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20693536 Free PMC article. - Mechanisms of Igf2/H19 imprinting: DNA methylation, chromatin and long-distance gene regulation.
Sasaki H, Ishihara K, Kato R. Sasaki H, et al. J Biochem. 2000 May;127(5):711-5. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022661. J Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10788777 Review. - How genome-wide approaches can be used to unravel the remaining secrets of the imprintome.
Cooper WN, Constância M. Cooper WN, et al. Brief Funct Genomics. 2010 Jul;9(4):315-28. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elq018. Brief Funct Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20675687 Review.
Cited by
- H19 lncRNA controls gene expression of the Imprinted Gene Network by recruiting MBD1.
Monnier P, Martinet C, Pontis J, Stancheva I, Ait-Si-Ali S, Dandolo L. Monnier P, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Dec 17;110(51):20693-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1310201110. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24297921 Free PMC article. - Characterization of the imprinting signature of mouse embryo fibroblasts by RNA deep sequencing.
Tran DA, Bai AY, Singh P, Wu X, Szabó PE. Tran DA, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Feb;42(3):1772-83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1042. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24217910 Free PMC article. - A genome-wide screen in human embryonic stem cells reveals novel sites of allele-specific histone modification associated with known disease loci.
Prendergast JG, Tong P, Hay DC, Farrington SM, Semple CA. Prendergast JG, et al. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2012 May 19;5(1):6. doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-5-6. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2012. PMID: 22607690 Free PMC article. - Chromatin immunoprecipitation to characterize the epigenetic profiles of imprinted domains.
Singh P, Szabó PE. Singh P, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;925:159-72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-011-3_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22907496 Free PMC article. - Drug-induced loss of imprinting revealed using bioluminescent reporters of Cdkn1c.
Dimond A, Van de Pette M, Taylor-Bateman V, Brown K, Sardini A, Whilding C, Feytout A, Prinjha RK, Merkenschlager M, Fisher AG. Dimond A, et al. Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 6;13(1):5626. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32747-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37024615 Free PMC article.
References
- Babak T., et al. 2008. Global survey of genomic imprinting by transcriptome sequencing. Curr. Biol. 18:1735–1741 - PubMed
- Barski A., et al. 2007. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 129:823–837 - PubMed
- Bartolomei M. S., Tilghman S. M. 1992. Parental imprinting of mouse chromosome 7. Semin. Dev. Biol. 3:107–117
- Bartolomei M. S., Zemel S., Tilghman S. M. 1991. Parental imprinting of the mouse H19 gene. Nature 351:153–155 - PubMed
- Bell A. C., Felsenfeld G. 2000. Methylation of a CTCF-dependent boundary controls imprinted expression of the Igf2 gene. Nature 405:482–485 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous