A hydrogen peroxide-responsive hyperpolarized 13C MRI contrast agent - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2011 Mar 23;133(11):3776-9.
doi: 10.1021/ja111589a. Epub 2011 Mar 2.
Affiliations
- PMID: 21366297
- PMCID: PMC3060273
- DOI: 10.1021/ja111589a
A hydrogen peroxide-responsive hyperpolarized 13C MRI contrast agent
Alexander R Lippert et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2011.
Abstract
We report a new reaction-based approach for the detection of hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) using hyperpolarized (13)C magnetic resonance imaging ((13)C MRI) and the H(2)O(2)-mediated oxidation of α-ketoacids to carboxylic acids. (13)C-Benzoylformic acid reacts selectively with H(2)O(2) over other reactive oxygen species to generate (13)C-benzoic acid and can be hyperpolarized using dynamic nuclear polarization, providing a method for dual-frequency detection of H(2)O(2). Phantom images collected using frequency-specific imaging sequences demonstrate the efficacy of this responsive contrast agent to monitor H(2)O(2) at pre-clinical field strengths. The combination of reaction-based detection chemistry and hyperpolarized (13)C MRI provides a potentially powerful new methodology for non-invasive multi-analyte imaging in living systems.
Figures
Figure 1
(a) 13C NMR spectra of hyperpolarized 13C-BFA after 21 s of reaction with 10, 100, 250, 500, 750, and 1000 µM H2O2 at 11.7T. Spectra were acquired with a single scan every 3 s with a 5° pulse, except for 10 and 100 µM which were acquired after 21 s with a 90° pulse. (b) Linear correlation of the ratio of integrated peak intensities of the C1 (carboxylate carbon) of 13C-BA to the C1 (carboxylate carbon) of 13C-BFA versus the concentration of H2O2; R2 = 0.988.
Figure 2
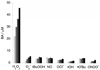
Response of 50 µM BFA to various ROS. All ROS were added at 5 mM, except for O2− which was generated enzymatically at a rate of 24 µmol/min for 120 min (2.9 mM total). Concentrations of benzoic acid were measured by HPLC after 0, 5, 10, 15, and 20 min of reaction except for O2− which was measured after 0, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min of reaction.
Figure 3
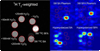
Phantom images of 5 M thermally polarized 13C-BFA in H2O, 5 M thermally polarized 13C-BA in DMA, and 20 mM hyperpolarized 13C-BFA in 100 mM phosphate, 0.3 mM EDTA buffered at pH 7.8 with 0, 25, 50, 100, and 200 mM H2O2. (a) 1H spin echo image. (b) Frequency specific image with selective excitation of the resonance of 5 M 13C-BA in DMA. (c) Frequency specific image with selective excitation of the resonance of 5 M 13C-BFA in H2O. (d) Frequency specific image with selective excitation of the resonance of 13C-BA buffered at pH 7.8 (e) Frequency specific image with selective excitation of the resonance of 13C-BFA buffered at pH 7.8. Images in (b)–(e) were acquired after ~37 s of reaction with H2O2 with a TR = 150 ms, FOV 40 × 40 × 40 mm, 16 × 12 × 12 matrix and zerofilled to a final resolution of 1.25 mm isotropic.
Scheme 1
Design of a hyperpolarized 13C MRI contrast agent for detection of H2O2 through H2O2-mediated α-ketoacid oxidative decarboxylation and the synthesis of 13C-BFA and its H2O2-mediated conversion to 13C-BA.
Similar articles
- High-resolution low-field molecular magnetic resonance imaging of hyperpolarized liquids.
Coffey AM, Kovtunov KV, Barskiy DA, Koptyug IV, Shchepin RV, Waddell KW, He P, Groome KA, Best QA, Shi F, Goodson BM, Chekmenev EY. Coffey AM, et al. Anal Chem. 2014 Sep 16;86(18):9042-9. doi: 10.1021/ac501638p. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Anal Chem. 2014. PMID: 25162371 Free PMC article. - Hyperpolarized [13C]-2-hydroxyethylpropionate.
Zhang H. Zhang H. 2008 Jan 31 [updated 2008 Mar 5]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2008 Jan 31 [updated 2008 Mar 5]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641315 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Hyperpolarized α-keto[1-13C]isocaproate as a 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopic agent for profiling branched chain amino acid metabolism in tumors.
Shan L. Shan L. 2010 Jan 15 [updated 2010 May 19]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2010 Jan 15 [updated 2010 May 19]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641995 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Hyperpolarized agents for advanced MRI investigations.
Viale A, Reineri F, Santelia D, Cerutti E, Ellena S, Gobetto R, Aime S. Viale A, et al. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009 Dec;53(6):604-17. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009. PMID: 20016452 Review. - Investigating tumor perfusion by hyperpolarized 13 C MRI with comparison to conventional gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI and pathology in orthotopic human GBM xenografts.
Park I, von Morze C, Lupo JM, Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH, Kadambi A, Vigneron DB, Nelson SJ. Park I, et al. Magn Reson Med. 2017 Feb;77(2):841-847. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26155. Epub 2016 Feb 19. Magn Reson Med. 2017. PMID: 26892398 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Rotaxane Probes for the Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide by 129 Xe HyperCEST NMR Spectroscopy.
Klass SH, Truxal AE, Fiala TA, Kelly J, Nguyen D, Finbloom JA, Wemmer DE, Pines A, Francis MB. Klass SH, et al. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Jul 15;58(29):9948-9953. doi: 10.1002/anie.201903045. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31004389 Free PMC article. - A H2O2-Responsive Theranostic Probe for Endothelial Injury Imaging and Protection.
Wang CK, Cheng J, Liang XG, Tan C, Jiang Q, Hu YZ, Lu YM, Fukunaga K, Han F, Li X. Wang CK, et al. Theranostics. 2017 Aug 23;7(15):3803-3813. doi: 10.7150/thno.21068. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 29109778 Free PMC article. - Chemiluminescent Measurement of Hydrogen Peroxide in the Exhaled Breath Condensate of Healthy and Asthmatic Adults.
Quimbar ME, Davis SQ, Al-Farra ST, Hayes A, Jovic V, Masuda M, Lippert AR. Quimbar ME, et al. Anal Chem. 2020 Nov 3;92(21):14594-14600. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02929. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Anal Chem. 2020. PMID: 33064450 Free PMC article. - [(11)C]Ascorbic and [(11)C]dehydroascorbic acid, an endogenous redox pair for sensing reactive oxygen species using positron emission tomography.
Carroll VN, Truillet C, Shen B, Flavell RR, Shao X, Evans MJ, VanBrocklin HF, Scott PJ, Chin FT, Wilson DM. Carroll VN, et al. Chem Commun (Camb). 2016 Apr 7;52(27):4888-90. doi: 10.1039/c6cc00895j. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Chem Commun (Camb). 2016. PMID: 26963495 Free PMC article. - Photogenerated Radical in Phenylglyoxylic Acid for in Vivo Hyperpolarized 13C MR with Photosensitive Metabolic Substrates.
Marco-Rius I, Cheng T, Gaunt AP, Patel S, Kreis F, Capozzi A, Wright AJ, Brindle KM, Ouari O, Comment A. Marco-Rius I, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2018 Oct 31;140(43):14455-14463. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b09326. Epub 2018 Oct 22. J Am Chem Soc. 2018. PMID: 30346733 Free PMC article.
References
- Rhee SG. Science. 2006;312:1882–1883. - PubMed
- Stone JR, Yang S. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006;8:243–270. - PubMed
- Miller EW, Chang CJ. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2007;11:620–625. - PMC - PubMed
- Winterbourn CC. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008;4:278–286. - PubMed
- Poole LB, Nelson KJ. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2008;12:18–24. - PMC - PubMed
- Paulsen CE, Carroll KS. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010;5:47–62. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM 79465/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 GM079465-05/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM079465/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM079465-04/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources