Predictions of hot spot residues at protein-protein interfaces using support vector machines - PubMed (original) (raw)
Predictions of hot spot residues at protein-protein interfaces using support vector machines
Stefano Lise et al. PLoS One. 2011.
Abstract
Protein-protein interactions are critically dependent on just a few 'hot spot' residues at the interface. Hot spots make a dominant contribution to the free energy of binding and they can disrupt the interaction if mutated to alanine. Here, we present HSPred, a support vector machine(SVM)-based method to predict hot spot residues, given the structure of a complex. HSPred represents an improvement over a previously described approach (Lise et al, BMC Bioinformatics 2009, 10:365). It achieves higher accuracy by treating separately predictions involving either an arginine or a glutamic acid residue. These are the amino acid types on which the original model did not perform well. We have therefore developed two additional SVM classifiers, specifically optimised for these cases. HSPred reaches an overall precision and recall respectively of 61% and 69%, which roughly corresponds to a 10% improvement. An implementation of the described method is available as a web server at http://bioinf.cs.ucl.ac.uk/hspred. It is free to non-commercial users.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
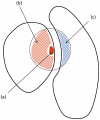
Figure 1. Schematic overview of protein structural regions which define the different energy contributions.
The red filled area, (a), corresponds to side-chain atoms of the mutated residue; the red and blue striped regions, (b) and (c) respectively, correspond to atoms within  of the
of the  of the mutated residue. We distinguish
of the mutated residue. We distinguish  types of interactions: side-chain inter-molecular between (a) and (c), environment inter-molecular between (b) and (c), side-chain intra-molecular between (a) and (b).
types of interactions: side-chain inter-molecular between (a) and (c), environment inter-molecular between (b) and (c), side-chain intra-molecular between (a) and (b).
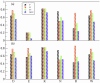
Figure 2. Predictions results for different amino acids.
Only the most frequent amino acid in the database are reported. In (a) are the results for SVM , in (b) for HSPred, which includes SVM
, in (b) for HSPred, which includes SVM and SVM
and SVM .
.
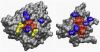
Figure 3. Ras/RalGDS complex.
Mapping of HSPred predictions onto the the complex (PDB code: 1LFD). The monomers have been rotated to display the interface. Red residues are correctly predicted hot spots (true positives); blue residues are correctly predicted non hot spots (true negatives); yellow residues are non hot spots erroneously predicts as hot spots (false positives).
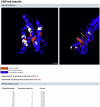
Figure 4. Sample output for the HSPred server.
Screenshot of the results page for the IL-4/IL-4R complex (PDB code: 1IAR). On top, predictions are visualised using a Jmol applet. On the left is IL-4 (chain A), on the right IL-4R
complex (PDB code: 1IAR). On top, predictions are visualised using a Jmol applet. On the left is IL-4 (chain A), on the right IL-4R (chain B). Predicted hot spots are in red, non hot spots in white. Residues not part of the interface are in blue. Below, predictions scores for each interface residues (excluding Pro and Gly amino acids) are reported (note that only the first few residues are displayed here). Scores greater than zero corresponds to predicted hot spots.
(chain B). Predicted hot spots are in red, non hot spots in white. Residues not part of the interface are in blue. Below, predictions scores for each interface residues (excluding Pro and Gly amino acids) are reported (note that only the first few residues are displayed here). Scores greater than zero corresponds to predicted hot spots.
Similar articles
- Prediction of hot spot residues at protein-protein interfaces by combining machine learning and energy-based methods.
Lise S, Archambeau C, Pontil M, Jones DT. Lise S, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Oct 30;10:365. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-365. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19878545 Free PMC article. - APIS: accurate prediction of hot spots in protein interfaces by combining protrusion index with solvent accessibility.
Xia JF, Zhao XM, Song J, Huang DS. Xia JF, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Apr 8;11:174. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-174. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20377884 Free PMC article. - Identification of computational hot spots in protein interfaces: combining solvent accessibility and inter-residue potentials improves the accuracy.
Tuncbag N, Gursoy A, Keskin O. Tuncbag N, et al. Bioinformatics. 2009 Jun 15;25(12):1513-20. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp240. Epub 2009 Apr 8. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19357097 - Machine Learning Approaches for Protein⁻Protein Interaction Hot Spot Prediction: Progress and Comparative Assessment.
Liu S, Liu C, Deng L. Liu S, et al. Molecules. 2018 Oct 4;23(10):2535. doi: 10.3390/molecules23102535. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30287797 Free PMC article. Review. - Protein-protein interface analysis and hot spots identification for chemical ligand design.
Chen J, Ma X, Yuan Y, Pei J, Lai L. Chen J, et al. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(8):1192-200. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990065. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 23713772 Review.
Cited by
- A simple recipe for the non-expert bioinformaticist for building experimentally-testable hypotheses for proteins with no known homologs.
Zawaira A, Shibayama Y. Zawaira A, et al. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2012 Dec;13(4):185-200. doi: 10.1007/s10969-012-9141-7. Epub 2012 Sep 7. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22956349 Review. - From laptop to benchtop to bedside: structure-based drug design on protein targets.
Chen L, Morrow JK, Tran HT, Phatak SS, Du-Cuny L, Zhang S. Chen L, et al. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(9):1217-39. doi: 10.2174/138161212799436386. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22316152 Free PMC article. Review. - Computational prediction of protein hot spot residues.
Morrow JK, Zhang S. Morrow JK, et al. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(9):1255-65. doi: 10.2174/138161212799436412. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22316154 Free PMC article. Review. - Hot spots in a network of functional sites.
Ozbek P, Soner S, Haliloglu T. Ozbek P, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Sep 2;8(9):e74320. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074320. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24023934 Free PMC article.
References
- Cunningham BC, Wells JA. High-resolution epitope mapping of hGH-receptor interactions by alanine-scanning mutagenesis. Science. 1989;244:1081–1085. - PubMed
- Moreira IS, Fernandes PA, Ramos MJ. Hot spots–a review of the protein-protein interface determinant amino-acid residues. Proteins. 2007;68:803–812. - PubMed
- Guerois R, Nielsen JE, Serrano L. Predicting changes in the stability of proteins and protein complexes: a study of more than 1000 mutations. J Mol Biol. 2002;320:369–387. - PubMed
- Gao Y, Wang R, Lai L. Structure-based method for analyzing protein-protein interfaces. J Mol Model. 2004;10:44–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources