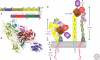Integrin structure, activation, and interactions - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Integrin structure, activation, and interactions
Iain D Campbell et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011.
Abstract
Integrins are large, membrane-spanning, heterodimeric proteins that are essential for a metazoan existence. All members of the integrin family adopt a shape that resembles a large "head" on two "legs," with the head containing the sites for ligand binding and subunit association. Most of the receptor dimer is extracellular, but both subunits traverse the plasma membrane and terminate in short cytoplasmic domains. These domains initiate the assembly of large signaling complexes and thereby bridge the extracellular matrix to the intracellular cytoskeleton. To allow cells to sample and respond to a dynamic pericellular environment, integrins have evolved a highly responsive receptor activation mechanism that is regulated primarily by changes in tertiary and quaternary structure. This review summarizes recent progress in the structural and molecular functional studies of this important class of adhesion receptor.
Figures
Figure 1.
Integrin structure. (A) Domain structure of αxβ2 (Xie et al. 2009); (B) structure of αxβ2 using same color code as A (drawn with PyMOL [DeLano Scientific] using PDB coordinates 3K6S); (C) cartoon representation of bent and upright conformations showing approximate dimensions.
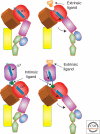
Figure 2.
An illustration of the movement of α7 helix in the I domains and the swing-out of the hybrid domain (the domains are defined in Fig. 1). The top pair corresponds to the closed and open conformations of an integrin without an inserted α-I domain whereas the lower pair represents the situation when there is an α-I domain present. The intrinsic ligand is a glutamate (E310 in αL).
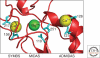
Figure 3.
Three β-I domain metal-binding sites in αXβ2 (Zhu et al. 2008); aspartate ligands to the metal ions are shown in cyan (from PDB:3FCS); figure drawn using PyMOL (DeLano Scientific).
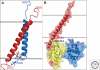
Figure 4.
(A) NMR structure of the complex between the αIIb (blue) and β3 (red) TM domains (PDB: 2K9J). The approximate position of the membrane glycerol backbone is shown by gray lines. (B) The talin F2 (blue)/F3 (yellow) domain pair in complex with a β integrin tail (red). The salt bridge that forms between K324 on F3 and D723 in the tail is shown; some key Lys and Arg residues are indicated in blue near the putative membrane interface with the F2 domain. B was constructed from a composite of coordinates of the talin/β complex (PDB: 3G9W; [Anthis et al. 2009]) and the membrane complex (PDB:2K9J [Lau et al. 2009]). Images made using PyMOL (DeLano Scientific).
Similar articles
- Dual functionality of the anti-beta1 integrin antibody, 12G10, exemplifies agonistic signalling from the ligand binding pocket of integrin adhesion receptors.
Humphries JD, Schofield NR, Mostafavi-Pour Z, Green LJ, Garratt AN, Mould AP, Humphries MJ. Humphries JD, et al. J Biol Chem. 2005 Mar 18;280(11):10234-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411102200. Epub 2005 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15632175 Free PMC article. - Enabling Systemic Identification and Functionality Profiling for Cdc42 Homeostatic Modulators.
Malasala S, Azimian F, Chen YH, Twiss JL, Boykin C, Akhtar SN, Lu Q. Malasala S, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 8:2024.01.05.574351. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.05.574351. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38260445 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint. - Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.
Ryan R, Hill S. Ryan R, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article. - Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.
Salisbury L, Baraitser L. Salisbury L, et al. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Pharmacological treatments in panic disorder in adults: a network meta-analysis.
Guaiana G, Meader N, Barbui C, Davies SJ, Furukawa TA, Imai H, Dias S, Caldwell DM, Koesters M, Tajika A, Bighelli I, Pompoli A, Cipriani A, Dawson S, Robertson L. Guaiana G, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 28;11(11):CD012729. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012729.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38014714 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Myofibroblast-derived extracellular vesicles facilitate cancer stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma via transferring ITGA5 to tumor cells.
Xiao Y, Tao P, Zhang K, Chen L, Lv J, Chen Z, He L, Jia H, Sun J, Cao M, Hong J, Qu C. Xiao Y, et al. Mol Cancer. 2024 Nov 21;23(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02170-0. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39574133 Free PMC article. - Exosomal integrins in tumor progression, treatment and clinical prediction (Review).
Shen YQ, Sun L, Wang SM, Zheng XY, Xu R. Shen YQ, et al. Int J Oncol. 2024 Dec;65(6):118. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5706. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39540373 Free PMC article. Review. - Mechanosensory entities and functionality of endothelial cells.
Mierke CT. Mierke CT. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 23;12:1446452. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1446452. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39507419 Free PMC article. Review. - Unbiased complexome profiling and global proteomics analysis reveals mitochondrial impairment and potential changes at the intercalated disk in presymptomatic R14Δ/+ mice hearts.
Foo B, Amedei H, Kaur S, Jaawan S, Boshnakovska A, Gall T, de Boer RA, Silljé HHW, Urlaub H, Rehling P, Lenz C, Lehnart SE. Foo B, et al. PLoS One. 2024 Oct 24;19(10):e0311203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311203. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39446877 Free PMC article. - Aplospojaveedins A-C, unusual sulfur-containing alkaloids produced by the endophytic fungus Aplosporella javeedii using OSMAC strategy.
Gao Y, Frank M, Teusch N, Woschko D, Janiak C, Mándi A, Kurtán T, Hartmann R, Schiedlauske K, van Geelen L, Kalscheuer R, Kaiser J, Gertzen CGW, Gohlke H, Wang BG, Proksch P, Liu Z. Gao Y, et al. Front Microbiol. 2024 Sep 27;15:1458622. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1458622. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39397793 Free PMC article.
References
- Alon R, Dustin ML 2007. Force as a facilitator of integrin conformational changes during leukocyte arrest on blood vessels and antigen-presenting cells. Immunity 26: 17–27 - PubMed
- Alonso JL, Essafi M, Xiong JP, Stehle T, Arnaout MA 2002. Does the integrin αA domain act as a ligand for its βA domain? Curr Biol 12: R340–R342 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources