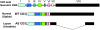Abnormalities of T cell signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Abnormalities of T cell signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus
Vaishali R Moulton et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011.
Abstract
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease resulting from a loss of tolerance to multiple self antigens, and characterized by autoantibody production and inflammatory cell infiltration in target organs, such as the kidneys and brain. T cells are critical players in SLE pathophysiology as they regulate B cell responses and also infiltrate target tissues, leading to tissue damage. Abnormal signaling events link to defective gene transcription and altered cytokine production, contributing to the aberrant phenotype of T cells in SLE. Study of signaling and gene transcription abnormalities in SLE T cells has led to the identification of novel targets for therapy.
Figures
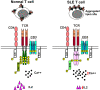
Figure 1
Schematic showing the T cell receptor signaling architecture in normal and systemic lupus erythematosus T cells. SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; TCR, T cell receptor.
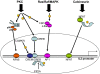
Figure 2
Schematic showing transcription factors involved in IL2 production in T cells. AP1, activated protein 1; CAMKIV, calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase IV; CREB, cAMP response element-binding; CREM, cAMP response element modulator; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; PKC, protein kinase C; PP, protein phosphatase.
Figure 3
Schematic showing the _CD3_ζ gene. Genomic DNA with eight exons (top), the mRNA with a full-length 906-bp 3' UTR (WT; middle) and the 344-bp alternatively spliced (AS) 3' UTR variant (bottom). SLE T cells express increased amounts of the unstable AS splice variant relative to the stable WT isoform.
Similar articles
- T cell signaling abnormalities contribute to aberrant immune cell function and autoimmunity.
Moulton VR, Tsokos GC. Moulton VR, et al. J Clin Invest. 2015 Jun;125(6):2220-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI78087. Epub 2015 May 11. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25961450 Free PMC article. Review. - T-cell signaling abnormalities in human systemic lupus erythematosus.
Nambiar MP, Krishnan S, Tsokos GC. Nambiar MP, et al. Methods Mol Med. 2004;102:31-47. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-805-6:031. Methods Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 15286379 - Methods and protocols to study T cell signaling abnormalities in human systemic lupus erythematosus.
Moulton VR, Lo MS, Tsokos GC. Moulton VR, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;900:25-60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-720-4_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22933064 - T cells as a therapeutic target in SLE.
Comte D, Karampetsou MP, Tsokos GC. Comte D, et al. Lupus. 2015 Apr;24(4-5):351-63. doi: 10.1177/0961203314556139. Lupus. 2015. PMID: 25801878 Free PMC article. Review. - Identification of microRNA-31 as a novel regulator contributing to impaired interleukin-2 production in T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Fan W, Liang D, Tang Y, Qu B, Cui H, Luo X, Huang X, Chen S, Higgs BW, Jallal B, Yao Y, Harley JB, Shen N. Fan W, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Nov;64(11):3715-25. doi: 10.1002/art.34596. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22736314
Cited by
- BTLA Expression and Function Are Impaired on SLE B Cells.
Wiedemann A, Lettau M, Weißenberg SY, Stefanski AL, Schrezenmeier EV, Rincon-Arevalo H, Reiter K, Alexander T, Hiepe F, Lino AC, Dörner T. Wiedemann A, et al. Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 22;12:667991. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.667991. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33968071 Free PMC article. - Decreased microRNA(miR)-145 and increased miR-224 expression in T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus involved in lupus immunopathogenesis.
Lu MC, Lai NS, Chen HC, Yu HC, Huang KY, Tung CH, Huang HB, Yu CL. Lu MC, et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013 Jan;171(1):91-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2012.04676.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23199328 Free PMC article. - Identifying key genes in CD4+ T cells of systemic lupus erythematosus by integrated bioinformatics analysis.
Li Z, Wang Z, Sun T, Liu S, Ding S, Sun L. Li Z, et al. Front Genet. 2022 Aug 15;13:941221. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.941221. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36046235 Free PMC article. - Disease Stage-Specific Pathogenicity of CD138 (Syndecan 1)-Expressing T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
Liu L, Takeda K, Akkoyunlu M. Liu L, et al. Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 28;11:1569. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01569. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849532 Free PMC article. - Imbalance of helper T cell type 1, helper T cell type 2 and associated cytokines in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A meta-analysis.
Xiang S, Zhang J, Zhang M, Qian S, Wang R, Wang Y, Xiang Y, Ding X. Xiang S, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 29;13:988512. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.988512. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36249802 Free PMC article.
References
- Krishnan S, Nambiar MP, Warke VG, Fisher CU, Mitchell J, Delaney N, Tsokos GC. Alterations in lipid raft composition and dynamics contribute to abnormal T cell responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2004;172:7821–7831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical