Oral epithelial dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: clinical presentation and treatment outcomes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Multicenter Study
Oral epithelial dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: clinical presentation and treatment outcomes
H Mawardi et al. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011 Jun.
Abstract
Late complications of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) include a risk of secondary malignancies. Optimization for early diagnosis and treatment of oral premalignant or malignant lesions requires an assessment of potential predisposing risk factors. The medical records of patients who developed oral epithelial dysplasia (OED) and oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) following allogeneic-HSCT were reviewed. Data on HSCT course, chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD), and clinical outcome were recorded; landmark survival was calculated. Twenty-six patients with OED (n=8) and OSCC (n=18) were identified with a median follow-up of 26.5 and 21.5 months, respectively. Premalignant and malignant oral lesions were diagnosed at a median time of 2.5 and 8 years after HSCT, respectively. Chronic GVHD was present in 96% of patients and of these, 96% had oral involvement. Multifocal oral cancer was found in 28% of cases, and localized recurrence was observed in 44% of cases. These results suggest that oral cGVHD may be considered a potential risk factor for the development of OSCC following allogeneic-HSCT. The observation that oral cancers were frequently multifocal and recurred locally suggests that these cancers may be more aggressive. Vigilant follow-up and coordination of care are critical.
Figures
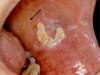
Figure 1
Exophytic plaque on the left buccal mucosa that demonstrated verrucous hyperplasia histopathologically. Note the lighter white reticulations attributed to long-standing oral cGVHD (arrow).
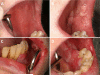
Figure 2
Exophytic plaque on the lower lip that demonstrated dysplasia histopathologically (Day +390 post allo-HSCT) showing A) white reticular changes involving the uppper and lower lip; B) round dysplastic plaque on the lower lip; and C) complete healing of the lower lip dysplastic lesion after excision and topical treatment with 5-FU (Day +592).
Figure 3
Invasive squamous cell carcinoma that initially presented as persistent erythema of the left buccal mucosa (Panel A; Day +5080) that then developed into multiple pink exophytic verrucous masses (Panel B; Day +5290) as well as more flat, erythematous and speckled involvement of the right mandibular facial gingiva (Panel C) and left lingual alveolar ridge (Panel D).
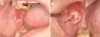
Figure 4
Invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the right buccal mucosa. A) Lesion prior to biopsy that presented as a distinct area of erythema and atrophy in the context of bilateral oral cGVHD changes; B) painful, exophytic indurated white and red mass with focal ulceration (arrow).
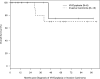
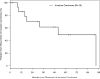
Figure 5A. Overall Survival
Kaplan-Meier curve of overall survival (OS) for patients who developed VH/dysplasia (N = 8) or invasive carcinoma (N = 18) post-HSCT. Curves are calculated from the time of diagnosis of VH/dysplasia or invasive carcinoma.
Figure 5B. Freedom from Recurrence (FFR)
Kaplan-Meier curve of freedom from recurrence (FFR) for patients who developed invasive carcinoma (N = 18) post-HSCT. Curves are calculated from the time of diagnosis of invasive carcinoma.
Similar articles
- Multiple squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity in a young patient with graft-versus-host disease following allogenic bone marrow transplantation.
Montebugnoli L, Gissi DB, Marchetti C, Foschini MP. Montebugnoli L, et al. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011 May;40(5):556-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2010.11.008. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011. PMID: 21163622 - Continuing increased risk of oral/esophageal cancer after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adults in association with chronic graft-versus-host disease.
Atsuta Y, Suzuki R, Yamashita T, Fukuda T, Miyamura K, Taniguchi S, Iida H, Uchida T, Ikegame K, Takahashi S, Kato K, Kawa K, Nagamura-Inoue T, Morishima Y, Sakamaki H, Kodera Y; Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Atsuta Y, et al. Ann Oncol. 2014 Feb;25(2):435-41. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt558. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Ann Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24399081 - High incidence of oral squamous cell carcinoma independent of HPV infection after allogeneic hematopoietic SCT in Taiwan.
Chen MH, Chang PM, Li WY, Hsiao LT, Hong YC, Liu CY, Gau JP, Liu JH, Chen PM, Chiou TJ, Tzeng CH. Chen MH, et al. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011 Apr;46(4):567-72. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2010.163. Epub 2010 Jul 12. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011. PMID: 20622906 - Clinicopathologic characteristics of secondary squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck in survivors of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for hematologic malignancies.
Chaulagain CP, Sprague KA, Pilichowska M, Cowan J, Klein AK, Kaul E, Miller KB. Chaulagain CP, et al. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019 Apr;54(4):560-566. doi: 10.1038/s41409-018-0299-x. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30127467 Free PMC article. Review. - Oral malignancies following HSCT: graft versus host disease and other risk factors.
Demarosi F, Lodi G, Carrassi A, Soligo D, Sardella A. Demarosi F, et al. Oral Oncol. 2005 Oct;41(9):865-77. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2005.02.001. Epub 2005 Apr 14. Oral Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16084755 Review.
Cited by
- Oncological Outcomes of Patients With Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders.
Villa A, Lodolo M, Ha P. Villa A, et al. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Nov 21:e243719. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2024.3719. Online ahead of print. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024. PMID: 39570632 - Multiple Oral Manifestations in a Patient With Chronic Graft Versus Host Disease: A Case Report.
Li D, Shan Y, Sun W, Wang X. Li D, et al. Cureus. 2024 Sep 26;16(9):e70233. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70233. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39463526 Free PMC article. - MASCC/ISOO Clinical Practice Statement: The risk of secondary oral cancer following hematopoietic cell transplantation.
Raber-Durlacher JE, Treister NS, Zadik Y, Dean DR, Miranda-Silva W, Fregnani ER, Epstein JB, Elad S. Raber-Durlacher JE, et al. Support Care Cancer. 2024 Jul 25;32(8):545. doi: 10.1007/s00520-024-08685-y. Support Care Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39048762 Free PMC article. Review. - Late Presentation of Oral Chronic Graft Versus Host Disease Manifesting As Hyperkeratotic Plaque: A Case Report.
Felemban MF, AlRasheed RS, Alshagroud RS, Aldosari AM. Felemban MF, et al. Cureus. 2024 May 12;16(5):e60147. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60147. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38864049 Free PMC article. - Oral squamous cell carcinoma arising from areas of Graft-versus-host disease: A systematic review.
Monteiro MF, Lemos JG, Pontes FS, Silva AC, Silva MH, Silva NF, Souza LL, Uchôa DC, Pontes HA. Monteiro MF, et al. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2024 Jan 1;29(1):e135-e144. doi: 10.4317/medoral.26133. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2024. PMID: 37992141 Free PMC article.
References
- Curtis RE, Rowlings PA, Deeg HJ, Shriner DA, Socie G, Travis LB, et al. Solid cancers after bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1997;336(13):897–904. - PubMed
- Bhatia S, Louie AD, Bhatia R, O'Donnell MR, Fung H, Kashyap A, et al. Solid cancers after bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(2):464–71. - PubMed
- Baker KS, DeFor TE, Burns LJ, Ramsay NK, Neglia JP, Robison LL. New malignancies after blood or marrow stem-cell transplantation in children and adults: incidence and risk factors. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(7):1352–8. - PubMed
- Otsubo H, Yokoe H, Miya T, Atsuta F, Miura N, Tanzawa H, et al. Gingival squamous cell carcinoma in a patient with chronic graft-versus-host disease. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1997;84(2):171–4. - PubMed
- Gluckman E, Socie G, Devergie A, Bourdeau-Esperou H, Traineau R, Cosset JM. Bone marrow transplantation in 107 patients with severe aplastic anemia using cyclophosphamide and thoraco-abdominal irradiation for conditioning: long-term follow-up. Blood. 1991;78(9):2451–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical