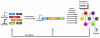Engineering scalable biological systems - PubMed (original) (raw)
Engineering scalable biological systems
Timothy K Lu. Bioeng Bugs. 2010 Nov-Dec.
Abstract
Synthetic biology is focused on engineering biological organisms to study natural systems and to provide new solutions for pressing medical, industrial and environmental problems. At the core of engineered organisms are synthetic biological circuits that execute the tasks of sensing inputs, processing logic and performing output functions. In the last decade, significant progress has been made in developing basic designs for a wide range of biological circuits in bacteria, yeast and mammalian systems. However, significant challenges in the construction, probing, modulation and debugging of synthetic biological systems must be addressed in order to achieve scalable higher-complexity biological circuits. Furthermore, concomitant efforts to evaluate the safety and biocontainment of engineered organisms and address public and regulatory concerns will be necessary to ensure that technological advances are translated into real-world solutions.
Keywords: biological circuits; biological modulators; biological probes; engineered organisms; high-throughput design; modelling; regulatory issues; synthetic biology.
© 2010 Landes Bioscience
Figures
Figure 1
A basic design cycle for synthetic biology includes creating well-characterized parts (e.g., regulatory elements, genes, proteins, RNAs), constructing synthetic devices and modules and designing and assembling higher-order networks. All steps of this cycle are aided by modelling, probes and modulators to analyze circuit performance. Debugging is an iterative process based on parts optimization, fine-tuning regulatory components, modelling and changing circuit architecture.
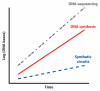
Figure 2
DNA sequencing and synthesis technologies are advancing at exponential rates, outpacing the ability of synthetic biologists to construct useful and scalable biological circuits. These trends are similar to Moore's law for integrated circuits and suggest that there is substantial room for growth in the field of synthetic circuits.
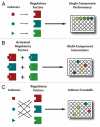
Figure 3
Combinatorial high-throughput methods will be useful in the assembly of well-characterized libraries of synthetic parts and devices. For example, transcriptional regulators and their cognate inducers can be analyzed for (A) single-component performance, (B) interactions between multiple components and (C) inducer crosstalk (e.g., cross-activation and/or cross-inhibition).
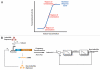
Figure 4
Control theory techniques for modelling synthetic biological circuits. (A) Small-signal linearization of biological components in different regions of operation enables the development of linear models. (B) Linearization can enable frequency-domain analysis, systems modelling using block diagrams and deeper insights into system dynamics. For example, transcription and translation can be understood as low-pass filters and block diagrams can be drawn for simple negative-feedback loops to yield understanding into system interconnections and responses to different input types., In the block diagram shown, s refers to _j_ω where j is √−1 and ω is angular frequency.
Comment on
- Next-generation synthetic gene networks.
Lu TK, Khalil AS, Collins JJ. Lu TK, et al. Nat Biotechnol. 2009 Dec;27(12):1139-50. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1591. Nat Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 20010597 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- Synthetic circuits, devices and modules.
Zhang H, Jiang T. Zhang H, et al. Protein Cell. 2010 Nov;1(11):974-8. doi: 10.1007/s13238-010-0133-8. Epub 2010 Dec 10. Protein Cell. 2010. PMID: 21153514 Free PMC article. Review. - Synthetic gene networks in mammalian cells.
Weber W, Fussenegger M. Weber W, et al. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2010 Oct;21(5):690-6. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2010.07.006. Epub 2010 Aug 4. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20691580 Review. - Designing cell function: assembly of synthetic gene circuits for cell biology applications.
Xie M, Fussenegger M. Xie M, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Aug;19(8):507-525. doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0024-z. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29858606 Review. - Next-generation biocontainment systems for engineered organisms.
Lee JW, Chan CTY, Slomovic S, Collins JJ. Lee JW, et al. Nat Chem Biol. 2018 Jun;14(6):530-537. doi: 10.1038/s41589-018-0056-x. Epub 2018 May 16. Nat Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29769737 - Programming gene expression in multicellular organisms for physiology modulation through engineered bacteria.
Gao B, Sun Q. Gao B, et al. Nat Commun. 2021 May 11;12(1):2689. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22894-7. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33976154 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Diagnostics for stochastic genome-scale modeling via model slicing and debugging.
Tsai KJ, Chang CH. Tsai KJ, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Nov 4;9(11):e110380. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110380. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25368989 Free PMC article. - Validation of an entirely in vitro approach for rapid prototyping of DNA regulatory elements for synthetic biology.
Chappell J, Jensen K, Freemont PS. Chappell J, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Mar 1;41(5):3471-81. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt052. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23371936 Free PMC article. - Rational diversification of a promoter providing fine-tuned expression and orthogonal regulation for synthetic biology.
Blount BA, Weenink T, Vasylechko S, Ellis T. Blount BA, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033279. Epub 2012 Mar 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22442681 Free PMC article.
References
- Watson JD, Crick FH. Molecular structure of nucleic acids; a structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid. Nature. 1953;171:737–778. - PubMed
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
- Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, Li PW, Mural RJ, Sutton GG, et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science. 2001;291:1304–1351. - PubMed
- Fiers W, Contreras R, Duerinck F, Haegeman G, Iserentant D, Merregaert J, et al. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage MS2 RNA: primary and secondary structure of the replicase gene. Nature. 1976;260:500–507. - PubMed
- Fleischmann RD, Adams MD, White O, Clayton RA, Kirkness EF, Kerlavage AR, et al. Whole-genome random sequencing and assembly of Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Science. 1995;269:496–512. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources