Natural history of tuberculosis: duration and fatality of untreated pulmonary tuberculosis in HIV negative patients: a systematic review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Natural history of tuberculosis: duration and fatality of untreated pulmonary tuberculosis in HIV negative patients: a systematic review
Edine W Tiemersma et al. PLoS One. 2011.
Abstract
Background: The prognosis, specifically the case fatality and duration, of untreated tuberculosis is important as many patients are not correctly diagnosed and therefore receive inadequate or no treatment. Furthermore, duration and case fatality of tuberculosis are key parameters in interpreting epidemiological data.
Methodology and principal findings: To estimate the duration and case fatality of untreated pulmonary tuberculosis in HIV negative patients we reviewed studies from the pre-chemotherapy era. Untreated smear-positive tuberculosis among HIV negative individuals has a 10-year case fatality variously reported between 53% and 86%, with a weighted mean of 70%. Ten-year case fatality of culture-positive smear-negative tuberculosis was nowhere reported directly but can be indirectly estimated to be approximately 20%. The duration of tuberculosis from onset to cure or death is approximately 3 years and appears to be similar for smear-positive and smear-negative tuberculosis.
Conclusions: Current models of untreated tuberculosis that assume a total duration of 2 years until self-cure or death underestimate the duration of disease by about one year, but their case fatality estimates of 70% for smear-positive and 20% for culture-positive smear-negative tuberculosis appear to be satisfactory.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
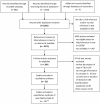
Figure 1. Selection of papers.
Flowchart schematically showing inclusion and exclusion of papers. Those marked with a * were excluded either because they were referred to at places in the text that did not discuss duration of tuberculosis, tuberculosis mortality, case fatality, life tables or natural history, or because the title indicated that the paper was not about one of these topics; ** for two of these, data were included to the extent mentioned by Berg (see legend of Table 3).
Similar articles
- Tuberculosis chemotherapy and sputum conversion among HIV-seropositive and HIV-seronegative patients in south-eastern Uganda.
Bwire R, Borgdorff MW, Sticht-Groh V, Rieder HL, Kawuma HJ, Bretzel G, Rüsch-Gerdes S. Bwire R, et al. East Afr Med J. 1999 Jun;76(6):307-13. East Afr Med J. 1999. PMID: 10750516 - Two-year follow-up of persons with HIV-1- and HIV-2-associated pulmonary tuberculosis treated with short-course chemotherapy in West Africa.
Kassim S, Sassan-Morokro M, Ackah A, Abouya LY, Digbeu H, Yesso G, Coulibaly IM, Coulibaly D, Whitaker PJ, Doorly R, et al. Kassim S, et al. AIDS. 1995 Oct;9(10):1185-91. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199510000-00011. AIDS. 1995. PMID: 8519456 Clinical Trial. - API TB Consensus Guidelines 2006: Management of pulmonary tuberculosis, extra-pulmonary tuberculosis and tuberculosis in special situations.
API Consensus Expert Committee. API Consensus Expert Committee. J Assoc Physicians India. 2006 Mar;54:219-34. J Assoc Physicians India. 2006. PMID: 16800350 - A review of the diagnosis and treatment of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis.
Colebunders R, Bastian I. Colebunders R, et al. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2000 Feb;4(2):97-107. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2000. PMID: 10694086 Review. - Xpert® MTB/RIF assay for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults.
Steingart KR, Schiller I, Horne DJ, Pai M, Boehme CC, Dendukuri N. Steingart KR, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 21;2014(1):CD009593. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24448973 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
Cited by
- Reevaluating progression and pathways following Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection within the spectrum of tuberculosis.
Horton KC, Richards AS, Emery JC, Esmail H, Houben RMGJ. Horton KC, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Nov 21;120(47):e2221186120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2221186120. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37963250 Free PMC article. - Associations between systemic inflammation, mycobacterial loads in sputum and radiological improvement after treatment initiation in pulmonary TB patients from Brazil: a prospective cohort study.
Mesquita ED, Gil-Santana L, Ramalho D, Tonomura E, Silva EC, Oliveira MM, Andrade BB, Kritski A; Rede-TB Study group. Mesquita ED, et al. BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 5;16:368. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1736-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27494953 Free PMC article. - Modeling the implementation of population-level isoniazid preventive therapy for tuberculosis control in a high HIV-prevalence setting.
Rhines AS, Feldman MW, Bendavid E. Rhines AS, et al. AIDS. 2018 Sep 24;32(15):2129-2140. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001959. AIDS. 2018. PMID: 30096067 Free PMC article. - The potential impact and cost-effectiveness of tobacco reduction strategies for tuberculosis prevention in Canadian Inuit communities.
N'Diaye DS, Nsengiyumva NP, Uppal A, Oxlade O, Alvarez GG, Schwartzman K. N'Diaye DS, et al. BMC Med. 2019 Feb 4;17(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12916-019-1261-5. BMC Med. 2019. PMID: 30712513 Free PMC article. - Screening for latent and active tuberculosis infection in the elderly at admission to residential care homes: A cost-effectiveness analysis in an intermediate disease burden area.
Li J, Yip BHK, Leung C, Chung W, Kwok KO, Chan EYY, Yeoh E, Chung P. Li J, et al. PLoS One. 2018 Jan 2;13(1):e0189531. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189531. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29293514 Free PMC article.
References
- Dubos RJ. New Brunswick: Rutgers University Press; 1987. The white plague: Tuberculosis, man, and society.320
- Johnston W. Harvard East Asian Monographs 162. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Asia Center; 1995. The modern epidemic: A history of tuberculosis in Japan.432
- Ryan F. Bromsgrove: Swift Publishers; 1992. Tuberculosis: The greatest story never told.446
- Anonymous . Pnom Penh, Cambodia: National Tuberculosis Program; 2005. National TB prevalence survey, 2002.77
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources