The effect of H. pylori eradication on meal-associated changes in plasma ghrelin and leptin - PubMed (original) (raw)
Controlled Clinical Trial
The effect of H. pylori eradication on meal-associated changes in plasma ghrelin and leptin
Fritz Francois et al. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011.
Abstract
Background: Appetite and energy expenditure are regulated in part by ghrelin and leptin produced in the gastric mucosa, which may be modified by H. pylori colonization. We prospectively evaluated the effect of H. pylori eradication on meal-associated changes in serum ghrelin and leptin levels, and body weight.
Methods: Veterans referred for upper GI endoscopy were evaluated at baseline and ≥8 weeks after endoscopy, and H. pylori status and body weight were ascertained. During the first visit in all subjects, and during subsequent visits in the initially H. pylori-positive subjects and controls, blood was collected after an overnight fast and 1 h after a standard high protein meal, and levels of eight hormones determined.
Results: Of 92 enrolled subjects, 38 were H. pylori-negative, 44 H. pylori-positive, and 10 were indeterminate. Among 23 H. pylori-positive subjects who completed evaluation after treatment, 21 were eradicated, and 2 failed eradication. After a median of seven months following eradication, six hormones related to energy homeostasis showed no significant differences, but post-prandial acylated ghrelin levels were nearly six-fold higher than pre-eradication (p=0.005), and median integrated leptin levels also increased (20%) significantly (p<0.001). BMI significantly increased (5 ± 2%; p=0.008) over 18 months in the initially H. pylori-positive individuals, but was not significantly changed in those who were H. pylori-negative or indeterminant at baseline.
Conclusions: Circulating meal-associated leptin and ghrelin levels and BMI changed significantly after H. pylori eradication, providing direct evidence that H. pylori colonization is involved in ghrelin and leptin regulation, with consequent effects on body morphometry.
© 2011 Francois et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.
Figures
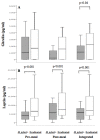
Figure 1
Comparison of _H. pylori_+ persons at baseline, and then after eradication of H. pylori. A standardized meal was administered to 21 subjects, and pre-meal, post-meal, and integrated values (mean of pre-meal and post-meal) were calculated for acyl-ghrelin (Panel A) and leptin (Panel B). H. pylori+(grey), Eradicated (white). Boxes indicate median and interquartile range, and bars indicate minimum and maximum values. P-values represent significant (< 0.05) differences between the H. pylori+ and post-eradication samples.
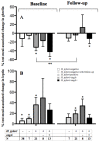
Figure 2
Comparison of test-meal induced changes in plasma acyl-ghrelin and leptin levels according to H. pylori at baseline and after eradication. Data are for seven _H. pylori_-negative, 21 _H. pylori_-positive subjects including eight _H. pylori+_cagA- and 13 H. pylori+cagA+ subjects. (* P < 0.05, comparing either pre-meal to post-meal values, or **comparing the first and second evaluations). Data also are shown for all of the 38 _H. pylori_-negative subjects at baseline, for comparison with the subset who also had follow-up studies. Panel A: Ghrelin levels. Panel B: Leptin Levels.
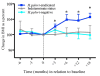
Figure 3
Change in BMI in 69 study subjects over a 2-year period. BMI is calculated relative to the baseline (at time 0), and is shown from 6 months prior to baseline and during 18 months of follow-up in 38 _H. pylori_-negative, 21 _H. pylori_-eradicated, and 10 subjects who were _H. pylori_-indeterminate at baseline (*p < 0.05, comparing time 0 to other follow-up months).
Similar articles
- Changes in plasma ghrelin and leptin levels in patients with peptic ulcer and gastritis following eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection.
Kasai C, Sugimoto K, Moritani I, Tanaka J, Oya Y, Inoue H, Tameda M, Shiraki K, Ito M, Takei Y, Takase K. Kasai C, et al. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016 Oct 4;16(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12876-016-0532-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27716077 Free PMC article. - The influence of the eradication of Helicobacter pylori on gastric ghrelin, appetite, and body mass index in patients with peptic ulcer disease.
Jang EJ, Park SW, Park JS, Park SJ, Hahm KB, Paik SY, Sin MK, Lee ES, Oh SW, Park CY, Baik HW. Jang EJ, et al. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Dec;23 Suppl 2:S278-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05415.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 19120912 Clinical Trial. - Changes in plasma ghrelin levels, gastric ghrelin production, and body weight after Helicobacter pylori cure.
Osawa H, Kita H, Ohnishi H, Nakazato M, Date Y, Bowlus CL, Ishino Y, Watanabe E, Shiiya T, Ueno H, Hoshino H, Satoh K, Sugano K. Osawa H, et al. J Gastroenterol. 2006 Oct;41(10):954-61. doi: 10.1007/s00535-006-1880-4. Epub 2006 Nov 9. J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17096064 - Efficacy of Vonoprazan for Helicobacter pylori Eradication.
Kiyotoki S, Nishikawa J, Sakaida I. Kiyotoki S, et al. Intern Med. 2020 Jan 15;59(2):153-161. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2521-18. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 31243237 Free PMC article. Review. - Ghrelin and Helicobacter pylori infection.
Osawa H. Osawa H. World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Nov 7;14(41):6327-33. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6327. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 19009647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Helicobacter pylori Infection Aggravates Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiome in Children With Gastritis.
Yang L, Zhang J, Xu J, Wei X, Yang J, Liu Y, Li H, Zhao C, Wang Y, Zhang L, Gai Z. Yang L, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Nov 7;9:375. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00375. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31781514 Free PMC article. - Brain-gut axis in the pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection.
Budzyński J, Kłopocka M. Budzyński J, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2014 May 14;20(18):5212-25. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i18.5212. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24833851 Free PMC article. Review. - Microbiome and potential targets for chemoprevention of esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Neto AG, Whitaker A, Pei Z. Neto AG, et al. Semin Oncol. 2016 Feb;43(1):86-96. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2015.09.005. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Semin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26970127 Free PMC article. Review. - The gut microbiome in cardio-metabolic health.
Hansen TH, Gøbel RJ, Hansen T, Pedersen O. Hansen TH, et al. Genome Med. 2015 Mar 31;7(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13073-015-0157-z. eCollection 2015. Genome Med. 2015. PMID: 25825594 Free PMC article. Review. - Differences in glycated hemoglobin levels and cholesterol levels in individuals with diabetes according to Helicobacter pylori infection.
Haj S, Chodick G, Goren S, Na'amnih W, Shalev V, Muhsen K. Haj S, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 19;11(1):8416. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87808-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33875700 Free PMC article.
References
- Shintani M, Ogawa Y, Ebihara K, Aizawa-Abe M, Miyanaga F, Takaya K, Hayashi T, Inoue G, Hosoda K, Kojima M. et al.Ghrelin, an endogenous growth hormone secretagogue, is a novel orexigenic peptide that antagonizes leptin action through the activation of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y/Y1 receptor pathway. Diabetes. 2001;50(2):227–232. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.2.227. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23CA107123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1UL1RR029893/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK090989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM63270/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NCRRM01RR0096/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 DK090989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical