OTUbase: an R infrastructure package for operational taxonomic unit data - PubMed (original) (raw)
OTUbase: an R infrastructure package for operational taxonomic unit data
Daniel Beck et al. Bioinformatics. 2011.
Abstract
Summary: OTUbase is an R package designed to facilitate the analysis of operational taxonomic unit (OTU) data and sequence classification (taxonomic) data. Currently there are programs that will cluster sequence data into OTUs and/or classify sequence data into known taxonomies. However, there is a need for software that can take the summarized output of these programs and organize it into easily accessed and manipulated formats. OTUbase provides this structure and organization within R, to allow researchers to easily manipulate the data with the rich library of R packages currently available for additional analysis.
Availability: OTUbase is an R package available through Bioconductor. It can be found at http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/OTUbase.html.
Figures
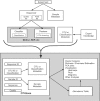
Fig. 1.
Organization of data within OTUbase. Data analysis starts by either clustering or classifying the reads obtained from the sequencer with an extermal application. The clustering or classification results are collected by OTUbase along with read and quality data and sample metadata. OTUbase then organizes the data into an R object. The library of R tools can then be used to analyze and visualize the data.
Similar articles
- msa: an R package for multiple sequence alignment.
Bodenhofer U, Bonatesta E, Horejš-Kainrath C, Hochreiter S. Bodenhofer U, et al. Bioinformatics. 2015 Dec 15;31(24):3997-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv494. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26315911 - ClassifyR: an R package for performance assessment of classification with applications to transcriptomics.
Strbenac D, Mann GJ, Ormerod JT, Yang JY. Strbenac D, et al. Bioinformatics. 2015 Jun 1;31(11):1851-3. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv066. Epub 2015 Feb 1. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25644269 - Girafe--an R/Bioconductor package for functional exploration of aligned next-generation sequencing reads.
Toedling J, Ciaudo C, Voinnet O, Heard E, Barillot E. Toedling J, et al. Bioinformatics. 2010 Nov 15;26(22):2902-3. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq531. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20861030 Free PMC article. - DNA barcoding in plants: evolution and applications of in silico approaches and resources.
Bhargava M, Sharma A. Bhargava M, et al. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2013 Jun;67(3):631-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2013. PMID: 23500333 Review. - spicyR: spatial analysis of in situ cytometry data in R.
Canete NP, Iyengar SS, Ormerod JT, Baharlou H, Harman AN, Patrick E. Canete NP, et al. Bioinformatics. 2022 May 26;38(11):3099-3105. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btac268. Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35438129 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Characterization of the diversity and temporal stability of bacterial communities in human milk.
Hunt KM, Foster JA, Forney LJ, Schütte UM, Beck DL, Abdo Z, Fox LK, Williams JE, McGuire MK, McGuire MA. Hunt KM, et al. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021313. Epub 2011 Jun 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21695057 Free PMC article. - Lesion Material From _Treponema_-Associated Hoof Disease of Wild Elk Induces Disease Pathology in the Sheep Digital Dermatitis Model.
Wilson-Welder JH, Mansfield K, Han S, Bayles DO, Alt DP, Olsen SC. Wilson-Welder JH, et al. Front Vet Sci. 2022 Jan 12;8:782149. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.782149. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35097043 Free PMC article. - Metagenomics: tools and insights for analyzing next-generation sequencing data derived from biodiversity studies.
Oulas A, Pavloudi C, Polymenakou P, Pavlopoulos GA, Papanikolaou N, Kotoulas G, Arvanitidis C, Iliopoulos I. Oulas A, et al. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2015 May 5;9:75-88. doi: 10.4137/BBI.S12462. eCollection 2015. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2015. PMID: 25983555 Free PMC article. Review. - mcaGUI: microbial community analysis R-Graphical User Interface (GUI).
Copeland WK, Krishnan V, Beck D, Settles M, Foster JA, Cho KC, Day M, Hickey R, Schütte UM, Zhou X, Williams CJ, Forney LJ, Abdo Z. Copeland WK, et al. Bioinformatics. 2012 Aug 15;28(16):2198-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts338. Epub 2012 Jun 12. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22692220 Free PMC article. - Correlation of lesion severity with bacterial changes in Treponeme-Associated Hoof Disease from free-roaming wild elk (Cervus canadensis).
Wilson-Welder JH, Han S, Bayles DO, Alt DP, Kanipe C, Garrison K, Mansfield KG, Olsen SC. Wilson-Welder JH, et al. Anim Microbiome. 2024 Apr 22;6(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s42523-024-00304-9. Anim Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 38650043 Free PMC article.
References
- Kunin V, et al. Wrinkles in the rare biosphere: pyrosequencing errors can lead to artificial inflation of diversity estimates. Environ. Microbiol. 2010;12:118–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases