Microarray-based evaluation of whole-community genome DNA amplification methods - PubMed (original) (raw)
Microarray-based evaluation of whole-community genome DNA amplification methods
Jian Wang et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Jun.
Abstract
Three whole-community genome amplification methods, Bst, REPLI-g, and Templiphi, were evaluated using a microarray-based approach. The amplification biases of all methods were <3-fold. For pure-culture DNA, REPLI-g and Templiphi showed less bias than Bst. For community DNA, REPLI-g showed the least bias and highest number of genes, while Bst had the highest success rate and was suitable for low-quality DNA.
Figures
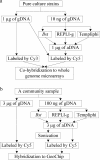
Fig. 1.
Outline of evaluation of three MDA methods using pure cultures (a) and a community sample (b). gDNA, unamplified genomic DNA; aDNA, amplified DNA.
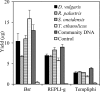
Fig. 2.
Yields of the three amplification methods for pure culture and community DNA. Error bars represent the standard deviations of the results for 3 replicates.
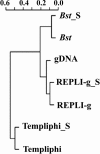
Fig. 3.
Hierarchical cluster analysis of amplified and unamplified community DNA based on GeoChip results. gDNA, unamplified DNA; Bst, amplified with Bst; Bst_S, amplified with Bst and sonicated before labeling; REPLI-g, amplified with REPLI-g; REPLI-g_S, amplified with REPLI-g and sonicated before labeling; Templiphi, amplified with Templiphi; Templiphi_S, amplified with Templiphi and sonicated before labeling.
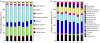
Fig. 4.
Relative abundance of all functional gene categories (a) and microbial classes (b) detected by GeoChip in gDNA and aDNA. Relative abundance was calculated based on the gene number. Bars: 1, gDNA; 2, aDNA amplified with Bst; 3, aDNA amplified with Bst and sonicated before labeling; 4, aDNA amplified with REPLI-g; 5, aDNA amplified with REPLI-g and sonicated before labeling; 6, aDNA amplified with Templiphi; 7, aDNA amplified with Templiphi and sonicated before labeling.
Similar articles
- Assessment of REPLI-g Multiple Displacement Whole Genome Amplification (WGA) Techniques for Metagenomic Applications.
Ahsanuddin S, Afshinnekoo E, Gandara J, Hakyemezoğlu M, Bezdan D, Minot S, Greenfield N, Mason CE. Ahsanuddin S, et al. J Biomol Tech. 2017 Apr;28(1):46-55. doi: 10.7171/jbt.17-2801-008. Epub 2017 Mar 21. J Biomol Tech. 2017. PMID: 28344519 Free PMC article. - PCR amplification-independent methods for detection of microbial communities by the high-density microarray PhyloChip.
DeAngelis KM, Wu CH, Beller HR, Brodie EL, Chakraborty R, DeSantis TZ, Fortney JL, Hazen TC, Osman SR, Singer ME, Tom LM, Andersen GL. DeAngelis KM, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Sep;77(18):6313-22. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05262-11. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21764955 Free PMC article. - Profiling in situ microbial community structure with an amplification microarray.
Chandler DP, Knickerbocker C, Bryant L, Golova J, Wiles C, Williams KH, Peacock AD, Long PE. Chandler DP, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Feb;79(3):799-807. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02664-12. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23160129 Free PMC article. - Something from (almost) nothing: the impact of multiple displacement amplification on microbial ecology.
Binga EK, Lasken RS, Neufeld JD. Binga EK, et al. ISME J. 2008 Mar;2(3):233-41. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2008.10. Epub 2008 Feb 7. ISME J. 2008. PMID: 18256705 Review. - Metagenomics for studying unculturable microorganisms: cutting the Gordian knot.
Schloss PD, Handelsman J. Schloss PD, et al. Genome Biol. 2005;6(8):229. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-8-229. Epub 2005 Aug 1. Genome Biol. 2005. PMID: 16086859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Nitrogen Cycle Evaluation (NiCE) Chip for Simultaneous Analysis of Multiple N Cycle-Associated Genes.
Oshiki M, Segawa T, Ishii S. Oshiki M, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Apr 2;84(8):e02615-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02615-17. Print 2018 Apr 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29427421 Free PMC article. - Testing the reproducibility of multiple displacement amplification on genomes of clonal endosymbiont populations.
Ellegaard KM, Klasson L, Andersson SG. Ellegaard KM, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Nov 27;8(11):e82319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082319. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24312412 Free PMC article. - Metagenomic analysis of the airborne environment in urban spaces.
Be NA, Thissen JB, Fofanov VY, Allen JE, Rojas M, Golovko G, Fofanov Y, Koshinsky H, Jaing CJ. Be NA, et al. Microb Ecol. 2015 Feb;69(2):346-55. doi: 10.1007/s00248-014-0517-z. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Microb Ecol. 2015. PMID: 25351142 Free PMC article. - Caught in the middle with multiple displacement amplification: the myth of pooling for avoiding multiple displacement amplification bias in a metagenome.
Marine R, McCarren C, Vorrasane V, Nasko D, Crowgey E, Polson SW, Wommack KE. Marine R, et al. Microbiome. 2014 Jan 30;2(1):3. doi: 10.1186/2049-2618-2-3. Microbiome. 2014. PMID: 24475755 Free PMC article. - Selection in coastal Synechococcus (cyanobacteria) populations evaluated from environmental metagenomes.
Tai V, Poon AF, Paulsen IT, Palenik B. Tai V, et al. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024249. Epub 2011 Sep 9. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21931665 Free PMC article.
References
- Blanco L., et al. 1989. Highly efficient DNA synthesis by the phage phi 29 DNA polymerase. Symmetrical mode of DNA replication. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 8935–8940 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources