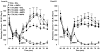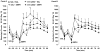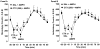Glutamate transporter subtype 1 (GLT-1) activator ceftriaxone attenuates amphetamine-induced hyperactivity and behavioral sensitization in rats - PubMed (original) (raw)
Glutamate transporter subtype 1 (GLT-1) activator ceftriaxone attenuates amphetamine-induced hyperactivity and behavioral sensitization in rats
Bruce Rasmussen et al. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011.
Abstract
Background: The β-lactam antibiotic and glutamate transporter subtype 1 (GLT-1) activator ceftriaxone prevents relapse to cocaine-seeking and inhibits morphine-induced physical dependence and tolerance in rats, but its efficacy against amphetamine-induced behaviors is unknown.
Methods: Here, we tested the hypothesis that ceftriaxone (200mg/kg, i.p.) inhibits hyperactivity produced by acute amphetamine administration (2mg/kg, i.p.) and sensitization of hyperactivity induced by repeated amphetamine exposure (2mg/kg, i.p.). For acute experiments, rats treated with ceftriaxone for 5 days were injected with amphetamine or saline on day 6.
Results: Amphetamine elicited less ambulatory and stereotypical activity in ceftriaxone-treated rats than in ceftriaxone-naïve rats. For chronic experiments, rats injected with ceftriaxone or saline for 8 days were also injected with amphetamine or saline on days 6-8 and then challenged with amphetamine 5 days later. Amphetamine produced greater ambulatory and stereotypical activity in amphetamine-pretreated rats than in rats previously naïve to amphetamine. Amphetamine challenge produced less ambulatory and stereotypical activity in rats pretreated with a combination of ceftriaxone (200mg/kg) and amphetamine than in rats pretreated with only amphetamine.
Conclusion: The present demonstration that ceftriaxone attenuates amphetamine-induced hyperactivity and behavioral sensitization suggests its documented efficacy against adverse cocaine and morphine effects extends to amphetamine.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Fig. 1
Effect of repeated ceftriaxone (CTX) (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) or saline (SAL) injections on the stereotypical (Panel A) or ambulatory (Panel B) response to an acute injection of amphetamine (AMPH) (2 mg/kg) or SAL. Data are expressed as mean stereotypical or ambulatory counts + S.E.M. quantified in 10-min bins. N = 8 rats/group except for the SAL + AMPH group (N=15). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to respective SAL + SAL group and +p < 0.05 compared to respective SAL + AMPH group.
Fig. 2
Effect of repeated ceftriaxone (CTX) (200 mg/kg) or saline (SAL) injections on sensitization of stereotypical (Panel A) or ambulatory (Panel B) activity produced by repeated amphetamine (AMPH) (2 mg/kg) exposure. All rats were injected with AMPH on day 13 following pretreatment with SAL + SAL, CTX + SAL, SAL + AMPH, or CTX + AMPH. Data are expressed as mean stereotypical or ambulatory counts + S.E.M. quantified in 10-min bins. N = 8 rats/group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to respective SAL + SAL pretreated group and +p < 0.05 compared to respective SAL + AMPH pretreated group.
Fig. 3
Effect of an acute injection of ceftriaxone (CTX) (200 mg/kg) on the stereotypical (Panel A) or ambulatory (Panel B) response to an acute injection of amphetamine (AMPH) (2 mg/kg) or saline (SAL). Data are expressed as mean stereotypical or ambulatory counts + S.E.M. quantified in 10-min bins. N = 8 rats/group.
Similar articles
- Ceftriaxone attenuates locomotor activity induced by acute and repeated cocaine exposure in mice.
Tallarida CS, Corley G, Kovalevich J, Yen W, Langford D, Rawls SM. Tallarida CS, et al. Neurosci Lett. 2013 Nov 27;556:155-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.09.072. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 24120434 Free PMC article. - Beta-lactam antibiotic reduces morphine analgesic tolerance in rats through GLT-1 transporter activation.
Rawls SM, Zielinski M, Patel H, Sacavage S, Baron DA, Patel D. Rawls SM, et al. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010 Mar 1;107(2-3):261-3. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2009.10.010. Epub 2009 Dec 9. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010. PMID: 20004063 Free PMC article. - Impact of mGluR5 during amphetamine-induced hyperactivity and conditioned hyperactivity in differentially reared rats.
Gill MJ, Arnold JC, Cain ME. Gill MJ, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 May;221(2):227-37. doi: 10.1007/s00213-011-2565-0. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22139452 - Dose-dependent effects of differential rearing on amphetamine-induced hyperactivity.
Cain ME, Mersmann MG, Gill MJ, Pittenger ST. Cain ME, et al. Behav Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;23(8):744-53. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e32835a38ec. Behav Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23044829 - The beta-lactam antibiotic ceftriaxone inhibits physical dependence and abstinence-induced withdrawal from cocaine, amphetamine, methamphetamine, and clorazepate in planarians.
Rawls SM, Cavallo F, Capasso A, Ding Z, Raffa RB. Rawls SM, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Apr 28;584(2-3):278-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.02.018. Epub 2008 Feb 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18342307
Cited by
- Clavulanic acid enhances glutamate transporter subtype I (GLT-1) expression and decreases reinforcing efficacy of cocaine in mice.
Kim J, John J, Langford D, Walker E, Ward S, Rawls SM. Kim J, et al. Amino Acids. 2016 Mar;48(3):689-696. doi: 10.1007/s00726-015-2117-8. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Amino Acids. 2016. PMID: 26543027 Free PMC article. - Ceftriaxone upregulates the glutamate transporter in medial prefrontal cortex and blocks reinstatement of methamphetamine seeking in a condition place preference paradigm.
Abulseoud OA, Miller JD, Wu J, Choi DS, Holschneider DP. Abulseoud OA, et al. Brain Res. 2012 May 25;1456:14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.03.045. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22521042 Free PMC article. - Effects of ceftriaxone on GLT1 isoforms, xCT and associated signaling pathways in P rats exposed to ethanol.
Rao PS, Saternos H, Goodwani S, Sari Y. Rao PS, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Jul;232(13):2333-42. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-3868-3. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25619881 Free PMC article. - Levamisole and cocaine synergism: a prevalent adulterant enhances cocaine's action in vivo.
Tallarida CS, Egan E, Alejo GD, Raffa R, Tallarida RJ, Rawls SM. Tallarida CS, et al. Neuropharmacology. 2014 Apr;79:590-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.01.002. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24440755 Free PMC article. - Ceftriaxone as a Novel Therapeutic Agent for Hyperglutamatergic States: Bridging the Gap Between Preclinical Results and Clinical Translation.
Abulseoud OA, Alasmari F, Hussein AM, Sari Y. Abulseoud OA, et al. Front Neurosci. 2022 Jul 5;16:841036. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.841036. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35864981 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Baker DA, McFarland K, Lake RW, Shen H, Tang XC, Toda S, Kalivas PW. Neuroadaptations in cystine-glutamate exchange underlie cocaine relapse. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:743–749. - PubMed
- Chu K, Lee ST, Sinn DI, Ko SY, Kim EH, Kim JM, Kim SJ, Park DK, Jung KH, Song EC, Lee SK, Kim M, Roh JK. Pharmacological induction of ischemic tolerance by glutamate transporter-1 (EAAT2) upregulation. Stroke. 2007;38:177–182. - PubMed
- Creese I, Iversen SD. The pharmacological and anatomical substrates of the amphetamine response in the rat. Brain Res. 1975;83:419–436. - PubMed
- Jayaram P, Steketee JD. Effects of repeated cocaine on medial prefrontal cortical GABAB receptor modulation of neurotransmission in the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system. J Neurochem. 2004;90:839–847. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RC1DA028153/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DA013429/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 DA028153-01/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 DA028153/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007237/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources