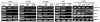The small molecule, LLL12, inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation and induces apoptosis in medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
The small molecule, LLL12, inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation and induces apoptosis in medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cells
Sarah Ball et al. PLoS One. 2011.
Abstract
Tumors of the central nervous system represent a major source of cancer-related deaths, with medulloblastoma and glioblastoma being the most common malignant brain tumors in children and adults respectively. While significant advances in treatment have been made, with the 5-year survival rate for medulloblastoma at 70-80%, treating patients under 3 years of age still poses a problem due to the deleterious effects of radiation on the developing brain, and the median survival for patients with glioblastoma is only 15 months. The transcription factor, STAT3, has been found constitutively activated in a wide variety of cancers and in recent years it has become an attractive therapeutic target. We designed a non-peptide small molecule STAT3 inhibitor, LLL12, using structure-based design. LLL12 was able to inhibit STAT3 phosphorylation, decrease cell viability and induce apoptosis in medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cell lines with elevated levels of p-STAT3 (Y705). IC(50) values for LLL12 were found to be between 1.07 µM and 5.98 µM in the five cell lines expressing phosphorylated STAT3. STAT3 target genes were found to be downregulated and a decrease in STAT3 DNA binding was observed following LLL12 treatment, indicating that LLL12 is an effective STAT3 inhibitor. LLL12 was also able to inhibit colony formation, wound healing and decreased IL-6 and LIF secretion. Our results suggest that LLL12 is a potent STAT3 inhibitor and that it may be a potential therapeutic treatment for medulloblastoma and glioblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
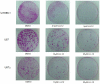
Figure 1. Western blot analysis of cells treated with LLL12.
(A) Medulloblastoma cell lines and (B) glioblastoma cell lines which express constitutively active STAT3 exhibit a decrease in p-STAT3 (Y705) following treatment with LLL12 for 6 and 24 hours respectively. No effect is seen on other kinases such as p-AKTand pERK. Apoptosis is indicated by the cleavage of caspase 3. (C) Normal human lung fibroblasts (WI-38) and human hepatocytes (HH) that do not express p-STAT3, did not show an induction of cleaved caspase-3.
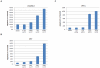
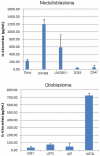
Figure 2. Cell Death ELISA analysis following LLL12 treatment.
(A) UW288-1, (B) U87, and (C) U87Δ exhibit a dose dependent increase in apoptosis following treatment with LLL12 for either 18 hours (UW288-1) or 24 hours (U87 and U87Δ).
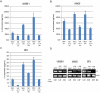
Figure 3. RT-PCR Analysis of STAT3 target genes.
LLL12 treatment was able to downregulate the expression of STAT3 target genes: Cyclin D1, Survivin, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL following 24 hours of treatment.
Figure 4. STAT3 DNA Binding Assay.
Cells showed a dose-dependent decrease in STAT3 activation following treatment with LLL12 for either 18 hours (UW288-1) or 24 hours (u87 and U87Δ), indicating that LLL12 is able to effectively inhibit STAT3's ability to bind DNA.
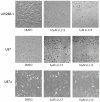
Figure 5. Wound Healing Assay.
Cells showed a dose-dependent decrease in their ability to migrate and heal the created wound following treatment with LLL12.
Figure 6. Colony Formation Assay.
Medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cell lines showed a decreased ability to form colonies following treatment with LLL12 for either 6 hours (UW288-1) or 24 hours (U87 and U87Δ).
Figure 7. IL-6 secretion in medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cell lines.
IL-6 secretion was measured by ELISA after 48 hours. The cell lines UW288-1, UW426 and U87Δ secreted elevated levels of IL-6.
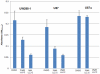
Figure 8. LLL12 inhibition of IL-6 secretion.
(A–C) Cells were treated with LLL12 for 8, 16 and 24 hours and IL-6 levels were measured using an ELISA. IL-6 secretion was reduced at all three time points. (D) LLL12 inhibits the expression of IL-6 mRNA.
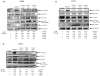
Figure 9. LLL12 inhibits IL-6 and LIF induced STAT3 phosphorylation.
(A) D283 and (B) U373 cells were pretreated with LLL12 for 2 hours and then treated with IL-6 for 30 minutes to induce p-STAT3. LLL12 was able to block STAT3 activation by IL-6 and did not have an effect of p-AKT or p-ERK. (C) D283 cells were pretreated with LLL12 for 2 hours and then treated with LIF for 24 hours to activate STAT3. LLL12 was able to inhibit the phosphorylation of STAT3 induced by LIF and did not inhibit p-AKT or p-ERK expression.
Similar articles
- A novel small molecule, LLL12, inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation and activities and exhibits potent growth-suppressive activity in human cancer cells.
Lin L, Hutzen B, Li PK, Ball S, Zuo M, DeAngelis S, Foust E, Sobo M, Friedman L, Bhasin D, Cen L, Li C, Lin J. Lin L, et al. Neoplasia. 2010 Jan;12(1):39-50. doi: 10.1593/neo.91196. Neoplasia. 2010. PMID: 20072652 Free PMC article. - A small molecule, LLL12 inhibits constitutive STAT3 and IL-6-induced STAT3 signaling and exhibits potent growth suppressive activity in human multiple myeloma cells.
Lin L, Benson DM Jr, DeAngelis S, Bakan CE, Li PK, Li C, Lin J. Lin L, et al. Int J Cancer. 2012 Mar 15;130(6):1459-69. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26152. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Int J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 21520044 Free PMC article. - LLL12, a novel small inhibitor targeting STAT3 for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy.
Zuo M, Li C, Lin J, Javle M. Zuo M, et al. Oncotarget. 2015 May 10;6(13):10940-9. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3458. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25883212 Free PMC article. - STAT3 in medulloblastoma: a key transcriptional regulator and potential therapeutic target.
Zaiter A, Audi ZF, Shawraba F, Saker Z, Bahmad HF, Nabha RH, Harati H, Nabha SM. Zaiter A, et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Nov;49(11):10635-10652. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07694-6. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35716286 Review. - Inhibition of STAT3: A promising approach to enhancing the efficacy of chemotherapy in medulloblastoma.
Kumar S, Arwind DA, Kumar B H, Pandey S, Nayak R, Vithalkar MP, Kumar N, Pai KSR. Kumar S, et al. Transl Oncol. 2024 Aug;46:102023. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102023. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38852276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- LLL12B, a small molecule STAT3 inhibitor, induces growth arrest, apoptosis, and enhances cisplatin-mediated cytotoxicity in medulloblastoma cells.
Chen X, Pan L, Wei J, Zhang R, Yang X, Song J, Bai RY, Fu S, Pierson CR, Finlay JL, Li C, Lin J. Chen X, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 22;11(1):6517. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85888-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33753770 Free PMC article. - A novel small inhibitor, LLL12, targets STAT3 in non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo.
Nie Y, Li Y, Hu S. Nie Y, et al. Oncol Lett. 2018 Oct;16(4):5349-5354. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9262. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30250605 Free PMC article. - STAT3 activation promotes oncolytic HSV1 replication in glioma cells.
Okemoto K, Wagner B, Meisen H, Haseley A, Kaur B, Chiocca EA. Okemoto K, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Aug 2;8(8):e71932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071932. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936533 Free PMC article. - Anti-angiogenic activity of a small molecule STAT3 inhibitor LLL12.
Bid HK, Oswald D, Li C, London CA, Lin J, Houghton PJ. Bid HK, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35513. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035513. Epub 2012 Apr 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22530037 Free PMC article. - α-type-1 polarized dendritic cell-based vaccination in recurrent high-grade glioma: a phase I clinical trial.
Akiyama Y, Oshita C, Kume A, Iizuka A, Miyata H, Komiyama M, Ashizawa T, Yagoto M, Abe Y, Mitsuya K, Watanabe R, Sugino T, Yamaguchi K, Nakasu Y. Akiyama Y, et al. BMC Cancer. 2012 Dec 27;12:623. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-623. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23270484 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- CBTRUS, Central Brain Tumor Registry of the United States. Primary brain tumors of the United States, Statistical Report (2000–2004), Years of Data Collected 2007–2008.
- Huse JT, Holland EC. Targeting brain cancer: advances in the molecular pathology of malignant glioma and medulloblastoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:319–331. - PubMed
- Collins VP. Gliomas. Cancer Surv. 1998;32:37–51. - PubMed
- Dohrmann GJ, Farwell JR, Flannery JT. Glioblastoma multiforme in children. J Neurosurg. 1976;44:442–448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous