Luminal and basal-like breast cancer cells show increased migration induced by hypoxia, mediated by an autocrine mechanism - PubMed (original) (raw)
Luminal and basal-like breast cancer cells show increased migration induced by hypoxia, mediated by an autocrine mechanism
Melanie J Voss et al. BMC Cancer. 2011.
Abstract
Background: Some breast cancer patients receiving anti-angiogenic treatment show increased metastases, possibly as a result of induced hypoxia. The effect of hypoxia on tumor cell migration was assessed in selected luminal, post-EMT and basal-like breast carcinoma cell lines.
Methods: Migration was assessed in luminal (MCF-7), post-EMT (MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-435S), and basal-like (MDA-MB-468) human breast carcinoma cell lines under normal and oxygen-deprived conditions, using a collagen-based assay. Cell proliferation was determined, secreted cytokine and chemokine levels were measured using flow-cytometry and a bead-based immunoassay, and the hypoxic genes HIF-1α and CA IX were assessed using PCR. The functional effect of tumor-cell conditioned medium on the migration of neutrophil granulocytes (NG) was tested.
Results: Hypoxia caused increased migratory activity but not proliferation in all tumor cell lines, involving the release and autocrine action of soluble mediators. Conditioned medium (CM) from hypoxic cells induced migration in normoxic cells. Hypoxia changed the profile of released inflammatory mediators according to cell type. Interleukin-8 was produced only by post-EMT and basal-like cell lines, regardless of hypoxia. MCP-1 was produced by MDA-MB-435 and -468 cells, whereas IL-6 was present only in MDA-MB-231. IL-2, TNF-α, and NGF production was stimulated by hypoxia in MCF-7 cells. CM from normoxic and hypoxic MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435S cells and hypoxic MCF-7 cells, but not MDA-MB-468, induced NG migration.
Conclusions: Hypoxia increases migration by the autocrine action of released signal substances in selected luminal and basal-like breast carcinoma cell lines which might explain why anti-angiogenic treatment can worsen clinical outcome in some patients.
Figures
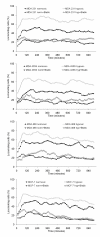
Figure 1
Migratory activity of tumor cells lines in response to hypoxia. The graphs show mean values of three independent experiments (90 cells were analyzed per sample). Blebbistatin (Blebb) was used at a concentration of 100 μM.
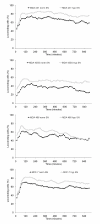
Figure 2
Influence of cell culture supernatants on the migratory activity of the tumor cell lines. The graphs show mean values of three independent experiments (90 cells were analyzed per sample). SN = supernatant.
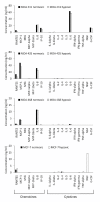
Figure 3
Release of cytokines and chemokines under normoxic and hypoxic cell culture conditions. Concentrations are given in ng per ml culture medium, which accounts for 500,000 cells that were initially seeded. Please note, that the scale of the ordinate differs between the cell lines
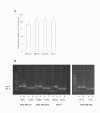
Figure 4
Growth and HIF-1α/CA IX expression of the tumor cell lines in response to hypoxia. (A) The growth of tumor cells under hypoxic conditions was compared to the growth under normal (normoxic) cell culture conditions. The graph shows mean values and standard deviations of three independent experiments. (B) The expression of HIF-1α and its target gene CA IX in the tumor cells under normoxic (n) and hypoxic (h) conditions was analysed by PCR. Numbers show the percent increase of staining intensities in hypoxic cells in comparison to normoxic cells. The shown blot holds true for three independently performed analyses with similar results.
Figure 5
Response of neutrophil granulocytes to cell culture media conditioned by tumor cells under normoxic (norm) or hypoxic (hyp) conditions. The graphs show mean values of four independent experiments (120 cells were analyzed per sample). SN = supernatant.
Similar articles
- Expression and activity of carbonic anhydrase IX is associated with metabolic dysfunction in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.
Li Y, Wang H, Oosterwijk E, Tu C, Shiverick KT, Silverman DN, Frost SC. Li Y, et al. Cancer Invest. 2009 Jul;27(6):613-23. doi: 10.1080/07357900802653464. Cancer Invest. 2009. PMID: 19367501 Free PMC article. - Hypoxia and metabolic phenotypes during breast carcinogenesis: expression of HIF-1alpha, GLUT1, and CAIX.
Chen CL, Chu JS, Su WC, Huang SC, Lee WY. Chen CL, et al. Virchows Arch. 2010 Jul;457(1):53-61. doi: 10.1007/s00428-010-0938-0. Epub 2010 Jun 5. Virchows Arch. 2010. PMID: 20526721 - Evaluation of CAIX and CAXII Expression in Breast Cancer at Varied O2 Levels: CAIX is the Superior Surrogate Imaging Biomarker of Tumor Hypoxia.
Tafreshi NK, Lloyd MC, Proemsey JB, Bui MM, Kim J, Gillies RJ, Morse DL. Tafreshi NK, et al. Mol Imaging Biol. 2016 Apr;18(2):219-31. doi: 10.1007/s11307-015-0885-x. Mol Imaging Biol. 2016. PMID: 26276155 Free PMC article. - CA IX is upregulated in CoCl2-induced hypoxia and associated with cell invasive potential and a poor prognosis of breast cancer.
Chu CY, Jin YT, Zhang W, Yu J, Yang HP, Wang HY, Zhang ZJ, Liu XP, Zou Q. Chu CY, et al. Int J Oncol. 2016 Jan;48(1):271-80. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3253. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26648580 - Para-toluenesulfonamide, a novel potent carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, improves hypoxia-induced metastatic breast cancer cell viability and prevents resistance to αPD-1 therapy in triple-negative breast cancer.
Chen HY, Lin CE, Wu SC, Yang ZY, Chiang YF, Huang KC, Wang KL, Ali M, Shieh TM, Chang HY, Huang TC, Hsia SM. Chen HY, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Nov;167:115533. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115533. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37748406
Cited by
- Hypoxia Alters the Expression of CC Chemokines and CC Chemokine Receptors in a Tumor-A Literature Review.
Korbecki J, Kojder K, Barczak K, Simińska D, Gutowska I, Chlubek D, Baranowska-Bosiacka I. Korbecki J, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 6;21(16):5647. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165647. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32781743 Free PMC article. Review. - A 3D microvascular network model to study the impact of hypoxia on the extravasation potential of breast cell lines.
Song J, Miermont A, Lim CT, Kamm RD. Song J, et al. Sci Rep. 2018 Dec 18;8(1):17949. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36381-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30560881 Free PMC article. - Hypoxia and estrogen are functionally equivalent in breast cancer-endothelial cell interdependence.
George AL, Rajoria S, Suriano R, Mittleman A, Tiwari RK. George AL, et al. Mol Cancer. 2012 Oct 22;11:80. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-80. Mol Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23088607 Free PMC article. - Prognostic Value of Lymphangiogenesis Determinants in Luminal and Non-luminal Breast Carcinomas.
Widodo I, Dwianingsih EK, Utoro T, Anwar SL, Aryandono T, Soeripto S. Widodo I, et al. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018 Sep 26;19(9):2461-2467. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.9.2461. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018. PMID: 30255700 Free PMC article. - Endothelial cell HIF-1α and HIF-2α differentially regulate metastatic success.
Branco-Price C, Zhang N, Schnelle M, Evans C, Katschinski DM, Liao D, Ellies L, Johnson RS. Branco-Price C, et al. Cancer Cell. 2012 Jan 17;21(1):52-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.11.017. Cancer Cell. 2012. PMID: 22264788 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous